Instruction
At the first stage, you need to parse the sentence by members and underline them: the subject - with one line, the predicate - with two - with a wavy line, the addition - with a dotted line, and the circumstance - with an alternation of dashes and dots. Sometimes it is also required to indicate the links between the members of the sentence and ask questions to each of them.
If the sentence is simple, indicate the type of predicate: simple (PGS), compound verb (CGS), or compound nominal (CIS). If there are several, indicate the type of each. If, however, number each of its parts and draw up a diagram of this sentence, indicating the means of communication (and allied words). In addition, indicate the types of clauses (definitive, explanatory or adverbial: clauses of time, place, cause, effect, condition, purpose, concession, comparison, mode of action, measure and degree or adjunctive) and the types of relations between them (sequential, parallel or homogeneous ).
Next, describe the sentence, indicating its type by the purpose of the statement (declarative, interrogative or incentive), by intonation (exclamatory or non-exclamatory) and by quantity (simple or complex: , complex, non-union). If the sentence is simple, continue the analysis, indicating the type by the number of main members (two-part or one-part: nominative, definite-personal, indefinitely-personal, generalized-personal or impersonal), by the presence of members (common or non-common), by the presence of missing main members ( full or ), and also indicate how it is complicated (homogeneous members, isolated members, introductory or plug-in constructions, or not complicated by anything). If the sentence is complex, continue the analysis in the same way, but for each of its parts separately.
Related videos
Related article
The scheme of the proposal is not just a whim of the teachers. It allows you to better understand the structure of the sentence, determine its specifics, and finally, parse it faster. Any scheme is first of all visibility; agree that when you are dealing, for example, with Lev Nikolaevich, visibility is very necessary for understanding the proposal.

Instruction
You need to start by determining which members of the sentence are words. First determine the subject and predicate - the grammatical basis. So you will already have a well-defined "stove" from which you can "dance". Then we distribute the remaining words among the members of the sentence, given that they are all divided into a subject and a predicate group. In the first group, in the second - addition and circumstance. Keep in mind that some words are not members of a sentence (for example, conjunctions, interjections, introductory and interstitial constructions), but also that several words at once all together make up one member of the sentence (participle and participle turns).
Chart suggestions Explain punctuation marks.
Related videos
Morphemic analysis the words - analysis by composition, definition and selection of significant derivational parts of the word. Morphemic analysis precedes derivational - determining how the word appeared.

Instruction
With syntactic analysis e simple sentence stands out (subject and predicate). Then the type of sentence is determined according to the purpose of the statement (narrative, interrogative or incentive), its emotional coloring (exclamatory or). After that, it is necessary to establish the type of sentence according to its grammatical basis (one-part or two-part), by members (common or non-common), by the presence or absence of any member (complete or incomplete). Also, simple can be complicated (homogeneous or isolated members are present) or uncomplicated.
With syntactic analysis For a complex sentence, in addition to determining the grammatical basis and type of sentence for the purpose of the statement, it is necessary to prove that it is complex and establish the type of connection between simple sentences (allied or non-union). If the connection is allied, then the type of sentence is determined by the nature of the union: compound. If the sentence is compound, then it is necessary to find out what kind of conjunction the parts of the sentence are connected with: connecting, dividing or adversative. In the complex, the main and subordinate clauses are defined, the means of communication between the subordinate clause and the main clause, the question that the subordinate clause answers, type. If the complex sentence is non-union, then the semantic relations between simple sentences are determined and the punctuation mark is explained. It is also necessary to draw a proposal scheme.
Related videos
Tip 6: How to define a vaguely personal sentence
A sentence expresses a message, a prompt, or a question. Two-part sentences have a grammatical basis consisting of a subject and a predicate. The grammatical basis of a one-part sentence is represented by either the subject or the predicate.

Instruction
All verbal one-part sentences have a predicate but no subject. Moreover, in a definite personal sentence, the form of the verb and the meaning of the message suggest that the action refers to a specific person: “I love books”, “Find the right solution”, “Take care, and honor from a young age”.
The verb can be in the form of the first or second person singular or indicative or imperative. The first person means that the verbal question is asked from the pronouns "I", "we"; second person - from the pronouns "you", "you". The imperative mood encourages action, the indicative simply conveys information.
- Describe the sentence according to the purpose of the statement: narrative, interrogative or incentive.
- By emotional coloring: exclamatory or non-exclamatory.
- By the presence of grammatical foundations: simple or complex.
- Then, depending on whether the sentence is simple or complex:
| If simple: 5. Describe the sentence by the presence of the main members of the sentence: two-part or one-part, indicate which main member of the sentence, if it is one-part (subject or predicate). 6. Characterize by the presence of secondary members of the proposal: common or non-common. 7. Indicate whether the sentence is complicated by anything (homogeneous members, appeal, introductory words) or not complicated. 8. Underline all members of the sentence, indicate parts of speech. 9. Draw up a sentence outline, indicating the grammatical basis and complication, if any. | If complex: 5. Indicate which connection is in the proposal: allied or non-union. 6. Indicate what is the means of communication in the sentence: intonation, coordinating unions or subordinating unions. 7. Conclude what kind of sentence this is: unionless (BSP), compound (CSP), complex (CSP). 8. Parse each part of a complex sentence as a simple one, starting from point No. 5 of the adjacent column. 9. Underline all members of the sentence, indicate parts of speech. 10. Draw up a sentence outline, indicating the grammatical basis and complication, if any. |
An example of parsing a simple sentence
Oral analysis:
The sentence is narrative, non-exclamatory, simple, two-part, grammatical basis: pupils and pupils study, common, complicated by homogeneous subjects.
Writing:
Narrative, non-exclamatory, simple, two-part, grammatical stem pupils and pupils study, common, complicated by homogeneous subjects.
An example of parsing a complex sentence
Oral analysis:
The sentence is narrative, non-exclamatory, complex, allied connection, means of communication subordinating union because, a complex sentence. The first simple sentence: one-part, with the main member - the predicate did not ask common, not complicated. Second simple sentence: two-part, grammatical basis we went with the class, common, uncomplicated.
Writing:
Narrative, non-exclamatory, complex, allied connection, subordinating union means of communication because, SPP.
1st PP: one-part, with the main member - the predicate did not ask common, not complicated.
2nd PP: two-part, grammatical basis - we went with the class, spread, not complicated.
Schematic example (sentence followed by schema)
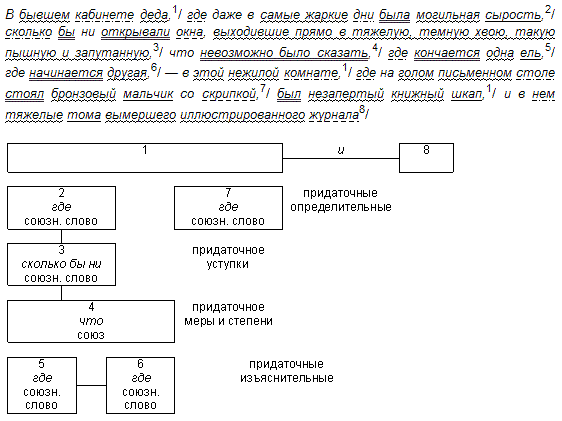
Another option for parsing
Syntax parsing. Order in parsing.
In phrases:
- Select the correct phrase from the sentence.
- We consider the structure - we highlight the main word and the dependent. We indicate what part of speech is the main and dependent word. Next, we indicate in what syntactic way this phrase is connected.
- And finally, we denote what its grammatical meaning is.
In a simple sentence:
- We determine what the sentence is for the purpose of the statement - narrative, incentive or interrogative.
- We find the basis of the sentence, we establish that the sentence is simple.
- Next, you need to talk about how this proposal is built.
- It is two-part or one-part. If it is one-part, then determine the type: personal, impersonal, nominative or indefinitely personal.
- Common or non-common
- incomplete or complete. If the sentence is incomplete, then it is necessary to indicate which member of the sentence is missing in it.
- If this proposal is complicated in any way, whether it be homogeneous members or isolated members of the proposal, this must be noted.
- Next, you need to analyze the sentence by members, while indicating what parts of speech they are. It is important to follow the order of parsing. First, the predicate and the subject are determined, then the secondary ones, which are part of the first - the subject, then - the predicate.
- We explain why one way or another punctuation marks are placed in the sentence.
Predicate
- We note what the predicate is - a simple verb or compound (nominal or verbal).
- Specify how the predicate is expressed:
- simple - what form of the verb;
- compound verb - what it consists of;
- compound nominal - what connection is used, how the nominal part is expressed.
In a sentence that has homogeneous members.
If we have a simple sentence, then when parsing it, it should be noted what kind of homogeneous members of the sentence are and how they are related to each other. Either through intonation, or intonation with conjunctions.
In sentences with separate members:
If we have a simple sentence, then when parsing it, it should be noted what the turnover will be. Next, we analyze the words that are included in this turnover by the members of the sentence.
In sentences with isolated members of speech:
First, we note that in this sentence, there is a direct speech. We indicate the direct speech and the text of the author. We analyze, explain why punctuation marks are placed in the sentence in this way and not otherwise. We draw the scheme of the offer.
In a compound sentence:
First, we indicate which sentence for the purpose of the statement is interrogative, declarative or incentive. We find simple sentences in the sentence, we single out the grammatical basis in them.
We find unions with the help of which simple sentences are connected in a complex one. We note what kind of unions they are - adversative, connecting or dividing. We determine the meaning of this entire compound sentence - opposition, alternation or enumeration. We explain why punctuation marks are placed in the sentence in this way. Then each simple sentence that makes up the complex one must be parsed in the same way as a simple sentence is parsed.
In a complex sentence with a subordinate clause (one)
First, we indicate what the sentence is in terms of the purpose of the statement. We single out the grammatical basis of all simple sentences that make up a complex one. Let's read them.
We name which sentence is the main one, and which is subordinate. We explain what kind of complex sentence it is, pay attention to how it is built, how the subordinate clause to the main clause is connected and what it refers to.
We explain why the punctuation marks in this sentence are arranged in this way. Then, the subordinate and main clauses must be parsed, in the same way as simple sentences are parsed.
In a complex sentence with subordinate clauses (several)
We call what the sentence is according to the purpose of the statement. We single out the grammatical basis of all the simple sentences that make up the complex one, and read them out. We indicate which sentence is the main one, and which is subordinate. It is necessary to indicate what the subordination in the sentence is - either it is a parallel subordination, or sequential, or homogeneous. If there is a combination of several types of subordination, this should be noted. We explain why, in this way, punctuation marks are placed in the sentence. And, at the end, we analyze the subordinate and main clauses as simple sentences.
In a complex non-union sentence:
We call what the sentence is according to the purpose of the statement. We find the grammatical basis of all simple sentences that make up this complex sentence. We read them out, call the number of simple sentences that make up the complex one. We determine what the meaning is the relationship between simple sentences. It can be - sequence, cause with effect, opposition, simultaneity, explanation or addition.
We note what are the features of the structure of this sentence, what kind of complex sentence it is. How are simple words connected in this sentence and what do they refer to.
We explain why punctuation marks are placed in the sentence in this way.
In a complex sentence in which there are different types of communication.
We call what, according to the purpose of the statement, this sentence is. We find and highlight the grammatical basis of all simple sentences that make up a complex one, read them out. We establish that this proposal will be a proposal in which there are different types of communication. Why? We determine what connections are present in this sentence - allied coordinating, subordinating, or any other.
According to the meaning, we establish how simple ones are formed in a complex sentence. We explain why punctuation marks are placed in the sentence in this way. We analyze all simple sentences that make up a complex one in the same way as a simple sentence is parsed.
All for study » Russian language » Parsing of a sentence
To bookmark a page, press Ctrl+D.
Link: https://site/russkij-yazyk/sintaksicheskij-razbor
The syntactic analysis of a simple sentence has firmly entered the practice of elementary and secondary schools. This is the most difficult and voluminous type of grammatical analysis. It includes a description and scheme of the sentence, analysis by members, indicating the parts of speech.
The structure and meaning of a simple sentence is studied starting from grade 5. The full set of features of a simple sentence is indicated in the 8th grade, and in the 9th grade the focus is on complex sentences.
In this type of analysis, the levels of morphology and syntax are correlated: the student must be able to identify parts of speech, recognize their forms, find conjunctions, understand the ways of connecting words in a phrase, and know the signs of the main and secondary members of a sentence.
Let's start with the simplest: we will help the guys prepare for parsing in 5th grade. In elementary school, the student memorizes the sequence of analysis and performs it at an elementary level, indicating the grammatical basis, syntactic relationships between words, the type of sentence in terms of the composition and purpose of the statement, learns to draw up diagrams and find homogeneous members.
The elementary school uses different programs in the Russian language, so the level of requirements and preparation of students are different. In the fifth grade, I accepted children who studied in elementary school according to the programs of the educational system "School 2100", "School of Russia" and "Elementary School of the XXI Century". There are big differences. Primary school teachers do a tremendous job to compensate for the shortcomings of their textbooks, and themselves "lay" successive links between elementary and secondary schools.
In grade 5, the material for parsing a sentence is generalized, expanded and built into a more complete form, in grades 6-7 it is improved taking into account the newly studied morphological units (verbal forms: participle and gerund; adverb and category of state; service words: prepositions, conjunctions and particles ).

Let's use examples to show the differences between the level of requirements in the format of parsing.
|
In 4th grade |
In 5th grade |
|
In a simple sentence, the grammatical basis is highlighted, familiar parts of speech are indicated above the words, homogeneous members are emphasized, phrases are written out or syntactic links between words are drawn. Scheme: [O -, O]. Narrative, non-exclamatory, simple, common, with homogeneous predicates. Exist. (main word) + adj., Ch. (main word) + noun. Ch. (main word) + places. Adverb + ch. (main word) |
Syntactic links are not drawn, phrases are not written out, the scheme and basic designations are the same, but the characteristics are different: narrative, non-exclamatory, simple, two-part, common, complicated by homogeneous predicates. Parsing is constantly practiced in the classroom and participates in the grammar tasks of control dictations. |
|
In a complex sentence, grammatical foundations are emphasized, parts are numbered, familiar parts of speech are signed above the words, the type is indicated according to the purpose of the statement and emotional coloring, according to the composition and presence of secondary members. Parsing scheme: [O and O] 1 , 2 , and 3 . Narrative, non-exclamatory, complex, common. |
The scheme remains the same, but the characteristics are different: narrative, non-exclamatory, complex, consists of 3 parts that are connected by an allied and allied connection, in 1 part there are homogeneous members, all parts are two-part and common. Parsing a complex sentence in grade 5 is educational in nature and is not a means of control. |
|
Sentence schemes with direct speech: A: "P!" or "P," - a. The concept of quotation is introduced, which coincides in design with direct speech. |
The schemes are supplemented by a break in direct speech with the words of the author: "P, - a. - P." and "P, - a, - p". The concept of dialogue and ways of its design are introduced. Schemes are made up, but the characteristics of sentences with direct speech are not made. |
Plan for parsing a simple sentence
1. Determine the type of sentence according to the purpose of the statement (narrative, interrogative, incentive).
2. Find out the type of sentence by emotional coloring (non-exclamatory or exclamatory).
3. Find the grammatical basis of the sentence, underline it and indicate the ways of expression, indicate that the sentence is simple.
4. Determine the composition of the main members of the proposal (two-part or one-part).
5. Determine the presence of minor members (common or non-common).
6. Underline the secondary members of the sentence, indicate the ways of their expression (parts of speech): from the composition of the subject and the composition of the predicate.
7. Determine the presence of missing members of the proposal (complete or incomplete).
8. Determine the presence of complications (complicated or not complicated).
9. Write down the characteristics of the proposal.
10. Draw up a proposal scheme.
For analysis, we used sentences from the beautiful fairy tales of Sergei Kozlov about the Hedgehog and the Bear cub.
1) It was an extraordinary autumn day!
2) Everyone's duty is to work.
3) Thirty mosquitoes ran out into the clearing and played their squeaky violins.
4) He has no father, no mother, no Hedgehog, no Bear cub.
5) And Squirrel took nuts and a cup and hurried after.
6) And they put things in a basket: mushrooms, honey, a kettle, cups - and went to the river.
7) And pine needles, and fir cones, and even cobwebs - they all straightened up, smiled and sang with all their might the last autumn song of the grass.
8) The Hedgehog lay, covered up to the very nose with a blanket, and looked at the Bear Cub with quiet eyes.
9) The hedgehog sat on a hill under a pine tree and looked at the moonlit valley flooded with fog.
10) Across the river, blazing with aspens, the forest darkened.
11) So until the evening they ran, jumped, jumped off a cliff and yelled at the top of their lungs, emphasizing the stillness and silence of the autumn forest.
12) And he jumped like a real kangaroo.
13) Water, where are you running?
14) Maybe he's crazy?
15) It seems to me that he imagined himself ... as the wind.
Examples of Parsing Simple Sentences




To correctly punctuate, you need to clearly understand the structure of the sentence. Syntactic analysis, that is, analysis of the sentence by members, is intended to help to understand it. Our article is devoted to the syntactic analysis of the sentence.
Syntax units
Syntax studies the relationship of words within phrases or sentences. Thus, the units of syntax are phrases and sentences - simple or complex. In this article, we will talk about how to parse a sentence, not a phrase, although it is often asked at school to do it too.
Why is parsing a sentence necessary?
The syntactic analysis of a sentence involves a detailed examination of its structure. This is absolutely necessary in order to correctly punctuate. In addition, it helps to understand the relationship of words within a phrase. In the course of syntactic analysis, as a rule, a sentence is characterized, all members of the sentence are determined and it is displaced by what parts of speech they are expressed. This is the so-called full parsing. But sometimes this term is used in relation to a short, partial, syntactic analysis, during which the student only underlines the members of the sentence.
Members of the proposal
Among the members of the proposal, the main ones are always distinguished first: subject and predicate. They usually form the grammatical basis. If a sentence has one grammatical basis, it simple, more than one complex.
The grammatical basis can consist of two main members, or include only one of them: either only the subject, or only the predicate. In the second case, we say that the sentence one-component. If both main terms are present - two-part.
If, apart from the grammatical basis, there are no words in the sentence, it is called uncommon. AT widespread the sentence also has secondary members: addition, definition, circumstance; application is a special case of definition.
if the sentence contains words that are not members of the sentence (for example, an appeal), it is still considered non-common.
When parsing, it is necessary to name the part of speech that expresses one or another member of the sentence. The guys work out this skill by studying Russian in the 5th grade.
Offer characteristics
To characterize a proposal, you must specify it, you must describe it.
- according to the purpose of the statement;
- by intonation;
- by the number of grammatical bases and so on.
Below we offer a proposal characterization plan.
For the purpose of the statement: narrative, interrogative, motivating.
By intonation: exclamatory or non-exclamatory.
Exclamatory sentences can be any for the purpose of the statement of the proposal, and not just incentives.
By the number of grammatical bases: simple or complex.
By the number of main members in the grammatical basis: one-part or two-part.
If the proposal is one-part, it is necessary determine its type: nominative, definitely-personal, indefinitely-personal, impersonal.
By the presence of secondary members: widespread or non-common.
If the proposal is complicated by something, then this must also be indicated. This is the parsing plan for the sentence; better to stick with it.
Complicated sentence
The sentence can be complicated by appeal, introductory and plug-in constructions, homogeneous members, isolated members, direct speech. If any of these types of complications is present, then it is necessary to indicate that the sentence is complicated, and write with what.
for example, sentence “Guys, let's live together!” complicated by the appeal "guys".
If the sentence is complex
If it is necessary to analyze a complex sentence, you must first indicate that it is complex and determine its type: allied or non-union, and if allied, then also compound or complex. Then characterize each of the parts in terms of the composition of the grammatical basis (two-part or one-part, type of one-part) and the presence / absence of secondary members.
The table shows the minor members and their questions.
Minor members can be expressed by different parts of speech, for example definition:
woolen skirt- adjective;
wool skirt- noun;
skirt ironed- participle;
winning habit- infinitive...
An example of parsing a sentence
Let's analyze the offer “I didn’t know that you, Masha, moved from the village to the city”.
We emphasize grammar basics. There are two of them: I knew and you moved . Let's define parts of speech: knew- the predicate is expressed by the verb in a personal form, etc.
Now we emphasize minor members:
Moved from where? from the village - a circumstance expressed by a noun; where? to the city is also a circumstance, also expressed by a noun. Masha- this is an appeal, it is not a member of the proposal.
Now let's give characteristic. The sentence is narrative, non-exclamatory, complex, allied, complex.
The first part of "did not know" is incomplete, not widespread.
The second part is two-part, common. Complicated by handling.
At the end of the analysis, it is necessary to draw up a scheme of a complex sentence.
What have we learned?
Parsing is intended to help understand the structure of a sentence, so everything that can be associated with it must be indicated. It is better to carry out the analysis according to the plan, then there are more chances that you will not forget anything. It is necessary not only to emphasize the members of the sentence, but also to determine the parts of speech, and to characterize the sentence.
Topic quiz
Article rating
Average rating: 4.4. Total ratings received: 84.
Not all students are easily given a complete syntactic analysis of a sentence. We will show you the correct sequence of actions that will make it easier to cope with such a task.
Step 1: Read the sentence carefully and determine the purpose of the statement.
According to the purpose of the statement, the proposals are divided into:
- narrative - "Beauty will save the world"(F. Dostoevsky);
- interrogative - "Rus, where are you going?"(N. Gogol);
- incentive - “My friend, let us dedicate our souls to the homeland with wonderful impulses!”(A. Pushkin); “A testament to writers: no need to invent intrigues and plots. Use the stories that life itself provides "(F. Dostoevsky).
Declarative sentences contain a message about something and are characterized by a calm narrative intonation. The content and structure of such proposals can be very diverse.
The purpose of interrogative sentences is to get an answer from the interlocutor to the question posed in the sentence. In some cases, when the question is rhetorical (i.e., does not require an answer), the purpose of such a sentence is different - the pathetic expression of some thought, idea, expression of the speaker's attitude to something, etc.
The purpose of uttering an incentive sentence is to motivate the addressee of the message to take some action. An incentive can express a direct order, advice, request, warning, call to action, etc. The differences between some of these options are often expressed not by the structure of the sentence itself, but by the intonation of the speaker.
Step 2: Determine the intonation and emotional tone of the sentence.
At this stage of parsing a sentence, look for the punctuation mark at the end of the sentence. According to this parameter, the proposals are divided into:
- exclamatory - “Well, what a neck! What eyes!”(I. Krylov);
- non-exclamatory - "Thought flies, but words go step by step"(A. Green).
Step 3: Find the grammatical bases in the sentence.
The number of grammatical stems in a sentence determines what that sentence is:
- simple sentence - "Wine turns a person into a beast and a beast, brings him to a frenzy"(F. Dostoevsky);
- difficult sentence - “It seems to me that people do not understand how much squalor and misfortune in their lives arises from laziness”(Ch. Aitmatov).
In the future, the syntactic analysis of a complex sentence and the syntactic analysis of a simple sentence follow different paths.
First, let's look at the parsing of a simple sentence with examples.
Stage 4 for a simple sentence: Find the main members and characterize the proposal.
A simple sentence, depending on the presence of a complete set of main members of the proposal or the absence of any of them, can be:
- one-piece - "It is not difficult to despise the court of people, it is impossible to despise one's own court"(A. Pushkin), there is no subject; "Autumn. Fairy-tale palace, open to everyone for review. Clearings of forest roads, looking into the lakes»(B. Pasternak), there is no predicate;
- two-part - “A very bad sign is the loss of the ability to understand humor, allegories, jokes”(F. Dostoevsky).
Indicate which main member is present in a one-part sentence. Depending on this, one-component sentences are nominal (there is a subject: nominal) and verbal (there is a predicate: definitely personal, indefinitely personal, generalized personal, impersonal).
Stage 5 for a simple sentence: See if there are secondary members in the sentence.
By the presence / absence of additions, definitions and circumstances, a simple sentence can be:
- common - “My goal was to visit Old Street”(I. Bunin);
- uncommon - "The attack is over. Sadness in disgrace"(S. Yesenin).
Stage 6 for a simple sentence: Decide if the sentence is complete or incomplete.
Whether a sentence is complete or incomplete depends on whether its structure includes all the members of the sentence that are needed for a complete, meaningful statement. In incomplete, any of the main or minor members is missing. And the meaning of the statement is determined by the context or previous sentences.
- complete offer - "Prishvin's words bloom, sparkle"(K. Paustovsky);
- incomplete sentence - "What is your name? - Me Anochka "(K. Fedin).
When parsing a sentence for an incomplete one, indicate which members of the sentence are missing.
Stage 7 for a simple sentence: Determine if the sentence is complicated or not complicated.
A simple sentence can be complicated or not complicated by introductory words and addresses, homogeneous or isolated members of the sentence, direct speech. Examples of simple compound sentences:
- "Ostap Bender, as a strategist, was great"(I. Ilf, E. Petrov);
- “He, the commissar, had to become on a par with Sarychev, if not by personal charm, not by past military merits, not by military talent, then by everything else: integrity, firmness, knowledge of the matter, and finally, courage in battle”(K. Simonov).
Stage 8 for a simple sentence
First, the subject and predicate are designated, then the secondary ones in the subject and the secondary ones in the predicate.
Stage 9 for a simple sentence
At the same time, indicate the grammatical basis, if the sentence is complicated, indicate the complication.
Look at a sample sentence parsing:
- Oral analysis: narrative sentence, non-exclamatory, simple, two-part, grammatical basis: the porter trampled, moved, did not, stopped, widespread, complete, complicated by homogeneous predicates, a separate definition (participle turnover), a separate circumstance (participle turnover).
- Written review: narration, unexcited, simple, double-sided, g / o the doorman trampled, moved was, did not, stopped, distributed, complicated. homogeneous skaz., sep. def. (participle turnover), esp. obs-vom (participle turnover). Now let's look at the syntactic analysis of a complex sentence with examples.
Stage 4 for a complex sentence: Determine how the connection exists between the parts of a complex sentence.
Depending on the presence or absence of unions, the connection can be:
- allied - "He who strives for self-improvement will never believe that this self-improvement has a limit"(L. Tolstoy);
- unionless - “At the moment when the moon, so huge and pure, rose above the crest of that dark mountain, the stars that were in the sky opened their eyes at once”(Ch. Aitmatov).
Stage 5 for a complex sentence: Find out what links the parts of a complex sentence together:
- intonation;
- coordinating conjunctions;
- subordinating unions.
Stage 6 for a complex sentence: Based on the relationship between the parts of the sentence and the means by which this relationship is expressed, classify the sentence.
Classification of complex sentences:
- compound sentence (CSP) - “ My father had a strange influence on me, and our relationship was strange"(I. Turgenev);
- complex sentence (CSP) - “She did not take her eyes off the road that leads through the grove” (I. Goncharov);
- complex non-union sentence (BSP) - “I know: in your heart there is both pride and direct honor” (A. Pushkin);
- a sentence with different types of connection - “People are divided into two categories: those who first think, and then speak and, accordingly, do, and those who first act, and then think” (L. Tolstoy).
The connection between the parts of an asyndetic complex sentence can be expressed by different punctuation marks: comma, colon, dash, semicolon.
Stage 7 for a complex sentence: Describe the links between the parts of the sentence.
Define:
- what does the adjective refer to;
- whereby the subordinate part is attached to the main part;
- what question is it answering.
Stage 8 for a complex sentence: If there are several subordinate parts, describe the relationship between them:
- consistent - "I heard Gaidar cleaning the kettle with sand and scolding him for the handle falling off" (K. Paustovsky);
- parallel - "It is necessary to accurately take into account the environment in which a poetic work develops so that a word alien to this environment does not accidentally fall" (V. Mayakovsky);
- homogeneous - “It was difficult to understand whether there was a fire somewhere, or the moon was about to rise” (A. Chekhov)
Stage 9 for a complex sentence: Underline all the members of the sentence and indicate what parts of speech they are expressed.
Stage 10 for a complex sentence: Now parse each part of a complex sentence as a simple one, see the diagram above.
Stage 11 for a complex sentence: Make a proposal outline.
In this case, indicate the means of communication, the type of accessory part. Look at the example of parsing a complex sentence:
Conclusion
The scheme of syntactic parsing of the sentence, proposed by us, will help to correctly characterize the sentence in all significant parameters. Use this step-by-step guide regularly at school and at home to better remember the sequence of reasoning when analyzing sentences.
Examples of syntactic analysis of sentences of simple and complex structure will help to correctly characterize sentences in oral and written form. With our instructions, a difficult task will become clearer and easier, help you learn the material and consolidate it in practice.
Write a comment if this scheme was useful to you. And if it turned out to be useful, do not forget to tell your friends and classmates about it.
blog.site, with full or partial copying of the material, a link to the source is required.

