Almost everyone who is interested in the history of the development of science, engineering and technology has at least once in his life thought about how the development of mankind could go without knowledge of mathematics or, for example, if we didn’t have such a necessary item as a wheel, which became almost basis for human development. However, only key discoveries are often considered and paid attention to, while less known and widespread discoveries are sometimes simply not mentioned, which, however, does not make them insignificant, because each new knowledge gives humanity the opportunity to climb a step higher in its development.
The 20th century and its scientific discoveries turned into a real Rubicon, crossing which, progress has accelerated its pace several times, identifying itself with a sports car that is impossible to keep up with. In order to stay on the crest of the scientific and technological wave now, not hefty skills are needed. Of course, you can read scientific journals, various kinds of articles and works of scientists who are struggling to solve a particular problem, but even in this case, it will not be possible to keep up with progress, and therefore it remains to catch up and observe.
As you know, in order to look into the future, you need to know the past. Therefore, today we will talk about the 20th century, the century of discoveries, which changed the way of life and the world around us. It should be noted right away that this will not be a list of the best discoveries of the century or any other top, this will be a brief overview of some of those discoveries that have changed, and possibly are changing the world.

In order to talk about discoveries, it is necessary to characterize the concept itself. We take the following definition as a basis:
Discovery - a new achievement made in the process of scientific knowledge of nature and society; the establishment of previously unknown, objectively existing patterns, properties and phenomena of the material world.

Top 25 Great Scientific Discoveries of the 20th Century
- Planck's quantum theory. He derived a formula that determines the shape of the spectral radiation curve and the universal constant. He discovered the smallest particles - quanta and photons, with the help of which Einstein explained the nature of light. In the 1920s, quantum theory developed into quantum mechanics.
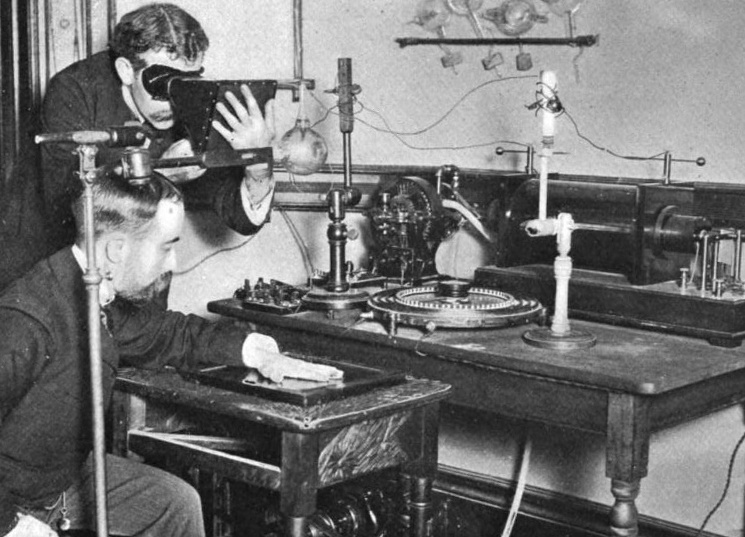
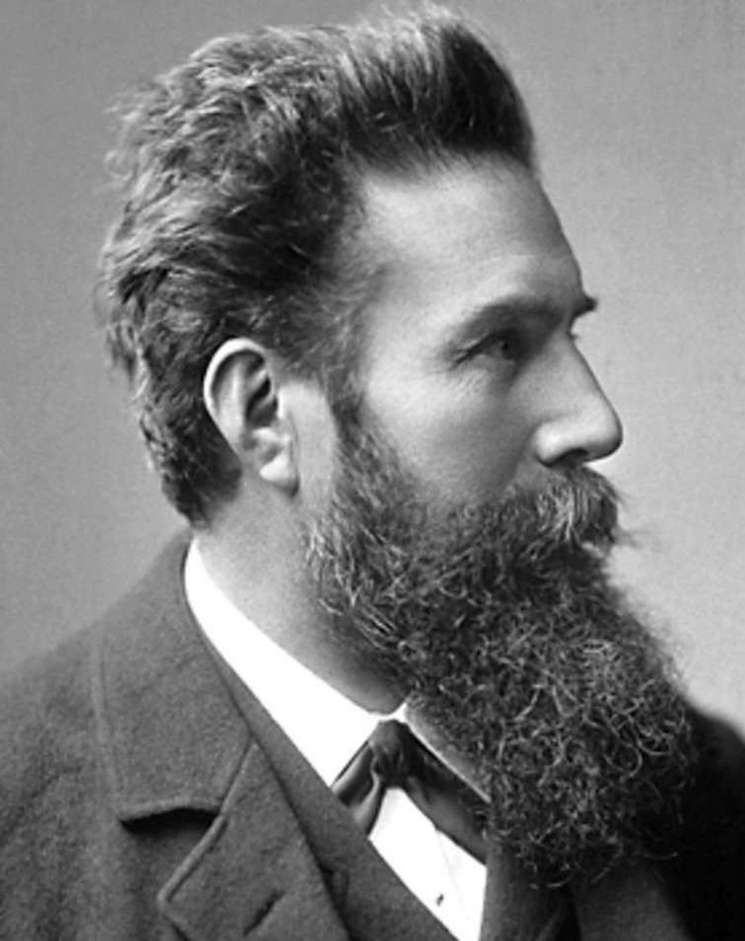
- Discovery of X-rays - electromagnetic radiation with a wide range of wavelengths. The discovery of X-rays by Wilhelm Roentgen greatly influenced human life, and today it is impossible to imagine modern medicine without them.
- Einstein's theory of relativity. In 1915, Einstein introduced the concept of relativity and derived an important formula relating energy and mass. The theory of relativity explained the essence of gravity - it arises due to the curvature of four-dimensional space, and not as a result of the interaction of bodies in space.
- Discovery of penicillin. The fungus Penicillium notatum, getting into the culture of bacteria, causes their complete death - this was proved by Alexander Flemming. In the 40s, a production was developed, which later began to be produced on an industrial scale.
- De Broglie waves. In 1924, it was found that wave-particle duality is inherent in all particles, not just photons. Broglie presented their wave properties in a mathematical form. The theory made it possible to develop the concept of quantum mechanics, explained the diffraction of electrons and neutrons.
- Discovery of the structure of the new DNA helix. In 1953, a new model of the structure of the molecule was obtained by combining the X-ray diffraction information of Rosalyn Franklin and Maurice Wilkins and the theoretical developments of Chargaff. She was brought out by Francis Crick and James Watson.
- Rutherford's planetary model of the atom. He deduced a hypothesis about the structure of the atom and extracted energy from atomic nuclei. The model explains the fundamentals of the laws of charged particles.
- Ziegler-Nath catalysts. In 1953 they carried out the polarization of ethylene and propylene.
- Discovery of transistors. A device consisting of 2 p-n junctions, which are directed towards each other. Thanks to his invention by Julius Lilienfeld, the technique began to shrink in size. The first working bipolar transistor was introduced in 1947 by John Bardeen, William Shockley and Walter Brattain.
- Creation of a radiotelegraph. Alexander Popov's invention, using Morse code and radio signals, first saved a ship at the turn of the 19th and 20th centuries. But the first to patent a similar invention was Gulielmo Marcone.
- Discovery of neutrons. These uncharged particles with a mass slightly larger than that of protons made it possible to penetrate the nucleus without obstacles and destabilize it. Later it was proved that under the influence of these particles, the nuclei are divided, but even more neutrons are produced. So the artificial one was discovered.
- Method of in vitro fertilization (IVF). Edwards and Steptoe figured out how to extract an intact egg from a woman, created optimal conditions for her life and growth in a test tube, figured out how to fertilize her and at what time to return her back to her mother's body.
- The first manned flight into space. In 1961, it was Yuri Gagarin who was the first to realize this, which became the real embodiment of the dream of the stars. Mankind has learned that the space between the planets is surmountable, and bacteria, animals and even humans can easily live in space.
- Discovery of fullerene. In 1985, scientists discovered a new kind of carbon - fullerene. Now, due to its unique properties, it is used in many devices. Based on this technique, carbon nanotubes were created - twisted and cross-linked layers of graphite. They show a wide variety of properties: from metallic to semiconductor.
- Cloning. In 1996, scientists succeeded in obtaining the first clone of a sheep, named Dolly. The egg was gutted, the nucleus of an adult sheep was inserted into it and planted in the uterus. Dolly was the first animal that managed to survive, the rest of the embryos of different animals died.
- Discovery of black holes. In 1915, Karl Schwarzschild put forward a hypothesis about the existence of a black hole whose gravity is so great that even objects moving at the speed of light - black holes - cannot leave it.
- Theory. This is a generally accepted cosmological model, which previously described the development of the Universe, which was in a singular state, characterized by infinite temperature and matter density. The model was started by Einstein in 1916.
- Discovery of relic radiation. This is the cosmic microwave background radiation, which has been preserved since the beginning of the formation of the Universe and fills it evenly. In 1965, its existence was experimentally confirmed, and it serves as one of the main confirmations of the Big Bang theory.
- Approaching the creation of artificial intelligence. It is a technology for building intelligent machines, first defined in 1956 by John McCarthy. According to him, researchers to solve specific problems can use methods of understanding a person that may not be biologically observed in humans.
- The invention of holography. This special photographic method was proposed in 1947 by Dennis Gabor, in which, with the help of a laser, three-dimensional images of objects close to real are recorded and restored.
- Discovery of insulin. In 1922, the pancreatic hormone was obtained by Frederick Banting, and diabetes mellitus ceased to be a fatal disease.
- Blood groups. This discovery in 1900-1901 divided the blood into 4 groups: O, A, B and AB. It became possible to properly transfuse blood to a person, which would not end tragically.
- Mathematical information theory. Claude Shannon's theory made it possible to determine the capacity of a communication channel.
- Invention of Nylon. Chemist Wallace Carothers in 1935 discovered a method for obtaining this polymeric material. He discovered some of its varieties with high viscosity even at high temperatures.
- Discovery of stem cells. They are the progenitors of all existing cells in the human body and have the ability to self-renew. Their possibilities are great and are just beginning to be explored by science.
There is no doubt that all these discoveries are only a small part of what the 20th century showed to society, and it cannot be said that only these discoveries were significant, and all the rest became just a background, this is not at all the case.

It was the last century that showed us the new boundaries of the Universe, saw the light, quasars (superpowerful sources of radiation in our Galaxy) were discovered, the first carbon nanotubes with unique superconductivity and strength were discovered and created.

All these discoveries, one way or another, are just the tip of the iceberg, which includes more than a hundred significant discoveries over the past century. Naturally, all of them have become a catalyst for changes in the world in which we now live, and the fact remains undeniable that the changes do not end there.
The 20th century can be safely called, if not the “golden”, then certainly the “silver” age of discoveries, but looking back and comparing new achievements with the past, it seems that in the future we will have quite a few interesting great discoveries, in fact, the successor of the last century, the current XXI only confirms these views.
Bitkin Ilya, Makarov Mikhail, Klementiev Igor
The presentation is dedicated to the great inventions of Russian scientists of the 20th century. Computer, TV, backpack parachute, laser - all this was invented by Russian scientists.
Download:
Preview:
To use the preview of presentations, create a Google account (account) and sign in: https://accounts.google.com
Slides captions:
Inventions of Russian scientists of the 20th century
Today we will tell you about five amazing inventions.
A computer
Inventor of the computer Back in 1968, 8 years before the first Apple, Soviet electrical engineer Arseniy Anatolyevich Gorokhov invented a machine called “Device for setting the program for reproducing the contour of a part.
In the 1960s, he took the computer to the United States, where they released the first commercial computer equipped with a keyboard and monitor. Then it becomes faster, more powerful, more compact.
The name is not accidental, because the developed apparatus was intended, first of all, to create complex engineering drawings.
A computer game invented in the USSR by Alexei Pajitnov and presented to the public on June 6, 1984. The idea of "Tetris" was suggested to him by the pentomino game he bought.
Inventor of Tetris The most legendary Russian game programmer is, of course, Alexey Pajitnov, the author of Tetris. The legend says that an ordinary Russian programmer created an ingenious game that went around the world, multiplying millions of copies, but did not bring a penny to its creator. You can't say it's not true. Indeed: Tetris won unheard of popularity, and Pajitnov did not receive the income due to him in full. However, the history of the spread of Tetris is full of nuances that few people know about...
rules Random figures fall from above into a rectangular glass. In flight, the player can turn the figure and move it horizontally. It is also possible to “drop” a figure, that is, to accelerate its fall, when it has already been decided where the figure should fall. The figurine flies until it hits another figurine or the bottom of the glass. If at the same time a horizontal row of 10 cells is filled, it disappears and everything above it falls by one cell. In a special field, the player sees a figure that will follow the current one - this hint allows you to plan your actions. The pace of the game gradually increases. The name of the game comes from the number of cells that each piece consists of. The game ends when the new figure cannot fit into the glass.
TV set
TV today is so familiar and accessible that even the most modest interiors cannot do without its presence: Putin is also shown on it. And if someone does not watch TV shows, it is only because of being very busy or wanting to be original. However, such people usually still watch TV movies using the TV as a home theater.
On July 25, 1907, Professor of the Technological Institute in St. Petersburg, Boris Lvovich Rosing, filed his application for an invention called "Method of electrical transmission of images over distances." It was he who then proved that it is possible to use a cathode ray tube to convert electrical signals into points of a visual image. inventor
In 1878, the idea was put forward for a new device capable of transmitting an image over wires. It belongs to the Portuguese professor Adriano De Paiva. However, at this stage, it was not possible to ensure the glow of the screen at the receiving station.
backpack parachute
In the 20th century, aviation began to develop rapidly. Parachutes were needed to save the pilots. Parachutes of the previous design were bulky and could not be used in aviation. A special parachute for pilots was created by the Russian inventor Gleb Evgenievich Kotelnikov. In 1911, he registered his invention - a free action backpack parachute. The parachute had a round shape, fit into a metal satchel.
The inventor of the parachute Kotelnikov was not a designer - he was an actor. But he set to work with enthusiasm. Rescue domes were already used by aeronauts, it was necessary to make them an emergency response tool that would always be at hand.
Today, the importance of parachutes is difficult to overestimate. They are also used to ensure the safety of pilots, passengers, and for organizing entertainment events, and for independent jumps. Parachutes have become much more reliable and durable. Interruptions in their functioning are almost impossible.
Laser technology is still very young - it is not even half a century old. However, in this very short time, the laser has turned from a curious laboratory device into a means of scientific research, into a tool used in industry. It is difficult to find such an area of modern technology where lasers would not work.
Inventors In the Laboratory of Oscillations of the Physical Institute of the USSR Academy of Sciences, senior researcher Alexander Prokhorov and his post-graduate student Nikolai Basov dealt with the same topic. In May 1952, at the All-Union Conference on Radio Spectroscopy, they made a report on the possibility of creating a quantum amplifier for microwave radiation operating on a beam of molecules of the same ammonia. Townes, Basov and Prokhorov were awarded the Nobel Prize in 1964 for their research.
Light is a stream of special particles emitted by atoms - photons, or quanta of electromagnetic radiation. They should be thought of as segments of a wave, and not as particles of matter. Each photon carries a strictly defined portion of the energy emitted by the atom. But for an atom to be able to radiate energy, it must have some supply of it.
The twentieth century has transformed people's lives. Of course, the development of mankind has never stopped, and in every century there have been important scientific inventions, but truly revolutionary changes, and even on a serious scale, occurred not so long ago. What were the most significant discoveries of the twentieth century?
Aviation
Brothers Orville and Wilbur Wright entered the history of mankind as the first pilots. Not least the great discoveries of the 20th century - this and new Orville Wright managed to make a controlled flight in 1903. The plane, developed by him together with his brother, lasted only 12 seconds in the air, but it was a real breakthrough for the aviation of those times. The date of the flight is considered the birthday of this type of transport. The Wright brothers were the first to design a system that would twist the wing panels with cables, allowing you to control the machine. In 1901, a wind tunnel was also created. They also invented the propeller. Already by 1904, a new model of the aircraft saw the light, more advanced and capable of not only flying, but also performing maneuvers. In 1905, a third version appeared, which could remain in the air for about thirty minutes. Two years later, the brothers signed a contract with the US Army, and later the French also bought the plane. Many began to think about carrying passengers, and the Wrights made the necessary adjustments to their model, installing an additional seat and making the engine more powerful. So the beginning of the 20th century opened up completely new opportunities for humanity.
x-ray
Like many great discoveries of the 20th century, it was partly made in the 19th century, but then people did not succeed immediately. For example, X-rays were first used in 1885. Then he discovered that photographic plates are darkened under the action of a special spectrum, and when parts of the body are irradiated, an image of the skeleton can be obtained. Nevertheless, he had to work for 15 years in order to make research on organs and tissues possible. That is why the beginning of the 20th century is associated with the name "X-ray": it was not previously known to the general public. By 1919, many hospitals were already using this technique. The appearance of X-rays changed the development of medicine: new branches of diagnostics and analysis appeared in it. To date, the device has saved millions of lives. So in cases where outstanding scientists are mentioned, Wilhelm Roentgen should also be mentioned.

TV set
Scientific and technological inventions have transformed the life of the twentieth century. One of the key events was the emergence of a new way of disseminating information - television. In 1907, it was patented by the Russian physicist Boris Rosing. He used a photocell to convert signals. By 1912, he finalized his invention, and already in 1931, for the first time, a method of broadcasting in color was proposed. Since 1939, the first television channel began to function. In 1944, the modern television standard was created. Perhaps other discoveries of scientists of the 20th century were more significant scientifically, but the impact of this novelty on people's lives cannot be denied. Broadcasting has changed the way we communicate and has transformed the way people perceive the world.

Mobile phone
Now it seems almost impossible to imagine life without a smartphone. they appeared recently. Scientific inventions allowed people to communicate by telephone, but wireless communication was not invented until 1973. Martin Cooper, the inventor of the cell phone, was able to call the office from the streets of Manhattan. Ten years later, mobile phones became available to a wide range of buyers. The first Motorola cost almost four thousand dollars, but the Americans were so impressed with the idea that people signed up to buy it. Moreover, the device did not look much like a modern smartphone: the handset was just huge, weighed almost a kilogram, and on a tiny display you could only see the dialed number. The charge was enough for half an hour of conversation. Nevertheless, the mass production of various models soon began, and with each generation of phones, people were waiting for more and more interesting discoveries. Today, a completely small device is a real miniature computer with many functions that the creators of the cellular Motorola did not even think about in 1973.

Internet
Not all the discoveries of the last century are used by people every day. But the invention of the Internet has changed life even in small things, today it is used in almost every country in the world. This is a means for communication, information search, data exchange. It is a universal source of communication. Therefore, when listing the great discoveries of the 20th century, one should not forget about the Internet. It is believed that the first steps in this direction were made by Dr. Licklider, a scientist who led the American military information exchange project. Thus, the Arpanet network was created, with the help of which, in 1969, data was transferred from the University of Los Angeles to the Utah laboratory. A start was made, and in 1972 the Internet was introduced to the public. The concept of e-mail appeared. The invention of the Internet became known all over the world, and within a few years it was used by thousands of people. By the end of the twentieth century there were already twenty million of them.

A computer
The great discoveries of the 20th century are most often associated with technological progress. The computer is no exception. If we understand this word as an arithmetic machine, then such mechanisms have existed since the seventeenth century. But the device in the modern sense appeared only in the twentieth. In 1927, it was created and developed in America. By the middle of the century, an electronic device appeared. The Mark I machine was created - the first real computer. After that, progress went at a record pace. The way data was stored changed from punched cards to floppy disks, and then to compact disks and drives. Programming languages have also changed. The first computer was suitable only for performing algebraic operations, and modern devices are a multifunctional apparatus suitable for a variety of tasks.

Instant noodles
When listing the great discoveries of the 20th century, one should not forget about what seems at first glance a trifle. Instant noodles are a familiar household product, but their introduction has changed the nutrition landscape in the absence of a kitchen or in the workplace and was also a major achievement. This type of pasta was invented by the Japanese Ando Momofuki. Post-war Japan was in need of food, and affordable food without too much difficulty in preparation would clearly remedy the situation. So Ando decided to start looking for special noodles. He tried many cooking methods until he came across a yeast-free batter that was great for drying. In 1958, he began producing his noodles, and today more than forty billion servings of this product are consumed annually. Another discovery of Ando Momofuki was the use of special plastic cups that would allow you to prepare a quick meal without dishes.
Penicillin
Many prominent scientists of the 20th century are associated with the exact sciences, but there has been a major breakthrough in medicine as well. It was in this century that penicillin appeared, a drug that saved the lives of millions. It was invented by an Englishman in 1928 who discovered the effect of mold on bacteria. Interestingly, the great discoveries of the 20th century might not have been supplemented by the advent of antibiotics. All Fleming's colleagues believed that the main thing was not the fight against microbes, but the strengthening of immunity. Antibiotics seemed pointless and remained unclaimed for a couple of years after they were created. Only by 1943 did the medicine become widely used in medical institutions. Fleming did not abandon the study of microbes and not only improved penicillin, but also created several paintings with the help of his discovery, drawing bacteria on a special substance.

Ball pen
Studying scientific and technical inventions, you can forget about small household improvements that are of great importance. For example, the ballpoint pen familiar to everyone appeared only in 1943. It was invented by someone who watched the process of printing newspapers and wondered why not fill the pen reservoir with the same quick-drying ink? They should be thick. So that they do not clog the hole in the handle, a ball must be placed there. After considering all this, Biro created a prototype. Having emigrated to Argentina, he found a sponsor and began the production of ink fountain pens. The first buyers were pilots who could use them at altitude: a regular pen leaked in the absence of pressure. In 1953, the Frenchman Marcel Bic transformed the shape of the ink pen and was able to create cheap options that became available to anyone and conquered the whole world.
Washing machine
Another invention that has markedly improved life is helping most people cope with dirty clothes. The washing machine appeared only in 1947, replacing the laundresses at the post. For the first time such an invention was offered on the American market by two firms - General Electric and Bendix Corporation. The cars were noisy and uncomfortable, only functionality mattered. The Whirlpool developers decided to change the situation, who created a new version of the washing machine in the middle of the twentieth century. She was covered with plastic lining to reduce noise, models could be made in different colors, and the overall design solution became much more elegant. Since then, the washing machine has become a completely aesthetic object. the first such device appeared in 1975 and was called the Volga-10, but only the Vyatka-automatic-12, which began to be produced in 1981, became the most successful. Modern machines can be built-in and with a drying function, have different loading methods, displays, delayed start timers, and even the ability to connect to the Internet.
Aristotle (384-322 BC)
Aristotle is an ancient Greek encyclopedist, philosopher and logician, the founder of classical (formal) logic. Considered one of the greatest geniuses in history and the most influential philosopher of antiquity. He made a huge contribution to the development of logic and natural sciences, especially astronomy, physics and biology. Although many of his scientific theories have been refuted, they have contributed significantly to the search for new hypotheses to explain them.
Archimedes (287-212 BC)

Archimedes is an ancient Greek mathematician, inventor, astronomer, physicist and engineer. Generally considered the greatest mathematician of all time and one of the leading scientists of the classical period of antiquity. Among his contributions to the field of physics are the fundamental principles of hydrostatics, statics and an explanation of the principle of action on a lever. He is credited with inventing pioneering mechanisms, including siege engines and the screw pump named after him. Archimedes also invented the spiral that bears his name, formulas for calculating the volumes of surfaces of revolution, and an original system for expressing very large numbers.
Galileo (1564–1642)

In eighth place in the ranking of the greatest scientists in the history of the world is Galileo - an Italian physicist, astronomer, mathematician and philosopher. He has been called "the father of observational astronomy" and "the father of modern physics". Galileo was the first to use a telescope to observe celestial bodies. Thanks to this, he made a number of outstanding astronomical discoveries, such as the discovery of the four largest satellites of Jupiter, sunspots, the rotation of the Sun, and also established that Venus changes phases. He also invented the first thermometer (without a scale) and a proportional compass.
Michael Faraday (1791–1867)

Michael Faraday was an English physicist and chemist, primarily known for the discovery of electromagnetic induction. Faraday also discovered the chemical effect of current, diamagnetism, the effect of a magnetic field on light, and the laws of electrolysis. He also invented the first, albeit primitive, electric motor, and the first transformer. He introduced the terms cathode, anode, ion, electrolyte, diamagnetism, dielectric, paramagnetism, etc. In 1824 he discovered the chemical elements benzene and isobutylene. Some historians consider Michael Faraday the best experimenter in the history of science.
Thomas Alva Edison (1847–1931)

Thomas Alva Edison is an American inventor and businessman, founder of the prestigious scientific journal Science. Considered one of the most prolific inventors of his time, with a record 1,093 patents in his name and 1,239 elsewhere. Among his inventions are the creation in 1879 of an electric incandescent lamp, a system for distributing electricity to consumers, a phonograph, an improvement in the telegraph, telephone, film equipment, etc.
Marie Curie (1867–1934)

Maria Sklodowska-Curie - French physicist and chemist, teacher, public figure, pioneer in the field of radiology. The only woman to win the Nobel Prize in two different fields of science - physics and chemistry. First female professor teaching at the Sorbonne University. Her accomplishments include the development of the theory of radioactivity, methods for separating radioactive isotopes, and the discovery of two new chemical elements, radium and polonium. Marie Curie is one of the inventors who died from their inventions.
Louis Pasteur (1822–1895)

Louis Pasteur - French chemist and biologist, one of the founders of microbiology and immunology. He discovered the microbiological essence of fermentation and many human diseases. Initiated a new department of chemistry - stereochemistry. Pasteur's most important achievement is considered to be his work in bacteriology and virology, which resulted in the creation of the first vaccines against rabies and anthrax. His name is widely known thanks to the pasteurization technology he created and named after him later. All Pasteur's works have become a vivid example of a combination of fundamental and applied research in the field of chemistry, anatomy and physics.
Sir Isaac Newton (1643–1727)

Isaac Newton was an English physicist, mathematician, astronomer, philosopher, historian, bible scholar, and alchemist. He is the discoverer of the laws of motion. Sir Isaac Newton discovered the law of universal gravitation, laid the foundations of classical mechanics, formulated the principle of conservation of momentum, laid the foundations of modern physical optics, built the first reflecting telescope and developed the theory of color, formulated the empirical law of heat transfer, built the theory of the speed of sound, proclaimed the theory of the origin of stars and many other mathematical and physical theories. Newton was also the first to mathematically describe the phenomenon of tides.
Albert Einstein (1879–1955)

Second place in the list of the greatest scientists in the history of the world is occupied by Albert Einstein - a German physicist of Jewish origin, one of the greatest theoretical physicists of the twentieth century, the creator of general and special relativity, discovered the law of the relationship between mass and energy, as well as many other significant physical theories. Winner of the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1921 for his discovery of the law of the photoelectric effect. Author of more than 300 scientific papers in physics and 150 books and articles in the field of history, philosophy, journalism, etc.
Nikola Tesla (1856–1943)

Leaving the caves of the Stone Age, human society has passed a great path of mental and spiritual development. This allowed people to sit behind computer screens and communicate with each other at any distance, penetrate the secrets of nature and send spaceships to other planets. This became possible thanks to science, which was created and developed by many generations.
Historical path of development
Science in Russia in pre-Petrine times lagged far behind that of Europe. This is due to the social and cultural characteristics of the state and the insignificant influence of Byzantium.
The first mathematical work in Ancient Russia was created in 1136 by the monk Kirik. Somewhat later, translations of books on logic, cosmography and arithmetic appeared.
Science as a social institution arose in our state under Peter I. It was during the era of his reign that the first expeditions and expeditions went to America and Siberia.
1724 was marked by the opening of the St. Petersburg Academy of Sciences. Many well-known European scientists were invited to work in this institution. The works and activities of Academician Mikhail Lomonosov were invaluable for the development of Russian science.
1755 is considered the founding date of Moscow University. The history of science in Russia after that received a new round of its development. Somewhat later, universities were founded in Dorpat (1802), Vilna (1803), Kharkov and Kazan (1804), St. Petersburg (1819). Already at the end of the 19th century. their composition was replenished with Kiev, Warsaw, Tomsk and Odessa institutions of this kind.
The scientific elite in Russia was represented by:
Mathematicians (N. I. Lobachevsky, M. V. Ostrogradsky and others);
- physicists (A. S. Popov, A. G. Stoletov);
- chemists (D. I. Mendeleev, A. M. Butlerov, N. N. Zinin, etc.);
- doctors (S. P. Botkin, N. I. Pirogov);
- historians (N. M. Karamzin, V. O. Klyuchevsky).
Early twentieth century
This period was characterized by the transformation of agrarian Russia into a powerful industrial state. Those reforms carried out by the government attracted capital to the country. In Russia, various industries began to develop intensively, as well as the railway industry.
Already from the end of the nineteenth century, the rise of culture, architecture, literature, etc. began. Science at the beginning of the 20th century also reached its significant flowering. During this period, a real revolution in natural science took place, which was of great importance in the development of society. Major scientific discoveries of the 20th century made during this period caused a revision of existing ideas about the world around man.
Creation of scientific and technical societies
Scientific discoveries of the 20th century in pre-revolutionary Russia were made thanks to the work of various circles. The latter were small communities, which included not only practicing researchers, but also amateur enthusiasts. Such circles existed at the expense of contributions from their members and private donations. Some societies received large subsidies from the government.

In addition to medical and agricultural, metallurgical and botanical, geographical and physico-chemical circles, there were also secret scientific circles. An example of this is the Space Society. Its members were the future great scientists of the 20th century - Tsiolkovsky, Korolev and others.
All these circles were centers for conducting research and promoting scientific knowledge among the population. However, the main contribution to the education of the country still belonged to lyceums and universities, from which the societies listed above came out.
Development of medicine, genetics and biology
What are the achievements of Russian science at the beginning of the 20th century in this area? These include the classic work of Academician I.P. Pavlov. Russian scientists conducted research into the physiology of the digestive organs and the cardiovascular system. For his work in 1904, Pavlov was awarded the Nobel Prize. The same award in 1908 was awarded to I. I. Mechnikov. Her scientist received for his work on infectious diseases and immunology. Mechnikov also studied the influence of higher nervous activity on the course of physiological processes. Based on the knowledge gained, the scientist put forward the theory of conditioned reflexes.
The discoveries of the 20th century in the field of biology became a powerful impetus for the development of medicine. The beginning of the century was marked by the development of vaccinations against rabies, chicken cholera and anthrax. All this was the result of research by the bacteriologist of the Paris Institute L. Pasteur. On the basis of these works, scientists from many countries of the world, including Russia, developed measures aimed at the prevention and prevention of various epidemics.

A great contribution to the development of genetics was made by the scientist I.V. Michurin. This founder of the science of breeding fruit plants worked in the Tambov province, in his hometown of Kozlov. The goal of the scientist was to enrich the gardens of Russia with new crops. Despite the obstacles facing him, the scientist completed his task.

He developed a practical methodology and drew theoretical conclusions for obtaining a variety of hybrids with unusual and beneficial properties for humans.
Improvement of military equipment
The development of this area was facilitated by the aggressiveness of the leading states of the world and the ever-increasing technical capabilities. Already in 1911-1915, Russian engineers V.L. Mendeleev and A.A. Vasiliev created the first draft of an armored vehicle, which was later called a tank.
Inventions and discoveries of the 20th century also apply to the field of aviation. Thus, the first military aircraft took part in the maneuvers conducted in 1911 by the Warsaw, St. Petersburg and Kiev districts. In combat operations, this technique was used during the Balkan wars of 1912-1913. In 1914, the first bomber was adopted by the Russian troops, which was called the Ilya Muromets.
Not lagging behind aviation and the navy. Here the championship belonged to armored steam ships. One of the first among them was "Peter the Great".
The invention of the automaton
Science and technology of the 20th century in Russia often set as their task the strengthening of the country's military potential. Significant progress has been made in this area. So, in 1916, the designer-gunsmith Fedorov invented the world's first machine gun. To do this, it was necessary to shorten the barrel of the rifle of the 1913 model and provide it with a box magazine, as well as a handle for comfortable shooting. The result was a firearm, which today is the basis of infantry armament of any army in the world.
Development of chemistry and physics
Many scientific discoveries of the 20th century in this area were made in Western Europe. Thanks to them, mankind began to switch from steam engines to internal combustion engines. However, it was Russian scientists who proposed new methods for extracting the main raw material for such mechanisms (oil).
The emergence of engines of greater power prompted researchers to create the first breakthrough attempts in the field of aeronautics were carried out in the 19th century. It was then that airships and balloons saw the light.
What are the achievements of Russian science at the beginning of the 20th century in this area? In our country, two- and four-engine aircraft were created, which amazed contemporaries with their impressive size. Engineers such as I. I. Sikorsky and V. G. Lutskoy worked on their creation.

The discoveries of the 20th century in the field of aviation do not end there. The outstanding Russian scientist B.N. Yuryev in 1911 invented the main assembly used in the assembly of modern helicopters. This device made it possible to create equipment with high stability characteristics. Such helicopters can be safely controlled by ordinary pilots. The development of science in the 20th century in the field of helicopter construction was laid down precisely by Yuryev.
In the same period, the origins of modern astronautics were born. The main discoveries of the 20th century in this area were made by the teacher of the Kaluga gymnasium, a nugget K.E. Tsiolkovsky. In 1903, he published brilliant works in which the possibilities of space flights were substantiated.
What are the achievements of Russian science at the beginning of the 20th century in the field of physics? This is the discovery of general patterns inherent in wave processes (electromagnetic, sound, etc.). They were established by the outstanding physicist P. N. Lebedev.

The greatest discoveries in science of the 20th century were made by V. I. Vernadsky. This scientist became known all over the world after the publication of his encyclopedic works, which became the basis for the development of the latest trends in radiology, geochemistry and biochemistry. Vernadsky's works on the noosphere and biosphere are the origins of modern ecology.
Invention of the backpack parachute
In 1910, G. E. Kotelnikov visited the All-Russian holiday dedicated to aeronautics. On it, he became one of the witnesses to the tragic death of the pilot L. Matsievich. Kotelnikov was not a designer, but an actor. However, the death of the pilot shocked him so much that a year later he invented the RK-1 parachute, which was fundamentally different from previous designs.
Domes as a means of salvation were previously used by aeronauts. However, the RK-1 was more compact. In addition, the parachute has become an emergency response device, constantly at hand. The slings and the dome of the RK-1 were initially placed in a wooden satchel, which was later replaced with an aluminum one. At the bottom of the box, Kotelnikov placed springs. At the right moment, the parachutist pulled the ring. At this moment, the springs opened the lid of the box and threw the dome out. Currently, this invention is used by skydivers around the world.
The advent of the TV
Russian science in the 20th century presented the world with an invention that became the discovery of the era. In 1907, a professor at the Institute of Technology, located in St. Petersburg, B. L. Rosing, filed a patent application for "a method for the electrical transmission of various images and their reception using a cathode ray tube."
In the autumn of 1910, the scientist made a public report at a meeting of the Russian Technical Society, in which he spoke about the solution of issues that stood in the way of the development of television. Rosing assured that when using such devices it is necessary to use an electron beam. The most surprising thing is that this conclusion was made at a time when electronics as an industry was still in its infancy. For the television system he created, Rosing first received a Russian patent, and then a German, English and American one.
Discoveries in the field of geography
What are the achievements of Russian science at the beginning of the 20th century in the field of studying the structure of the world? During this period, travel was made to the countries of Oceania and to the north of Africa, to East and Central Asia. Each of them was marked by global discoveries. It is worth mentioning that the science of geography at the beginning of the 20th century relied precisely on the achievements obtained by Russian researchers.
Formation of the USSR
Science in Russia under Soviet rule gave the whole world many great discoveries and achievements in various fields of human activity. Even their cursory enumeration indicates the breakthrough that was made by scientists.
The achievements of Soviet science have played a huge role in the development of the country's national economy. At the same time, on their basis, such the latest for that time as tractor and aviation, automotive and metallurgical were created. The results of ongoing scientific research have made it possible to develop the production of synthetic rubber, motor fuel, etc.
Achievements obtained by biologists made it possible to solve the problems of food and light industry, as well as agriculture. In addition, the results of numerous studies have led to the progress of healthcare and the medical field.
Grandiose research programs were launched in the Soviet Union. New research institutes were also opened. Thus, in 1934 Vavilov founded the Physical Institute of the Academy of Sciences, and in the same period the Institute of Organic Chemistry began its work. 1937 - the year of foundation of the Institute of Geophysics. The physiologist Pavlov and the breeder Michurin continued their work. As a result of research conducted by scientists, numerous discoveries have been made in various disciplines. However, during the years of repression, the intellectual potential of the state suffered heavy damage.
post-war period
The revival of Soviet science took place in 1950. Research activities during these years were led by the Academy of Sciences. The Academies of Sciences were also restored in all the republics of the country. This made it possible to take patents for inventions and exercise control over the spending of government-allocated funds for this area.
Already in the mid-fifties, interest in astronautics was growing. There is a growing number of scientists in this field. There are special textbooks and faculties in universities. All this is done purposefully for the education of young scientists.
1957 brought a real sensation. It was the year of the launch of the first artificial satellite of the Earth. The country, relatively recently affected by a terrible war, not only restored its scientific potential, but also became a leader in scientific progress. This event opened a new era of humanity and at the same time became the beginning of the "space race" with America, which did not want to lose its world authority.
In 1959, a Soviet satellite reached the Moon. This again raised Russia's authority in the world community. Already in the early sixties, the Soviet Union became the second superpower in the world after the United States. America overtook our country only in terms of economic potential.
On April 12, 1961, another incredible event occurred, which science fiction writers had previously described in their works. On this day, for the first time in history, a man flew into space and returned to earth.
In the 80s, the development and production of modern electronic computers - computers - began in our country. This technique was compact and did not occupy entire buildings and rooms. These were the years when the Soviet Union spent huge resources on the scientific sphere, which accounted for a tenth of the state budget. No other country in the world could afford this.

Among the huge amount of scientific research carried out in Russia, there are many that have had and continue to have a significant impact on the scientific and technological progress of the entire world community. We are talking about numerous discoveries in the field of chemical, biological and physical and technical sciences. These include the discovery of the phenomenon of paramagnetic resonance by E. K. Zavoisky. Russian scientists also played an important role in solving the problems of obtaining atomic energy.
