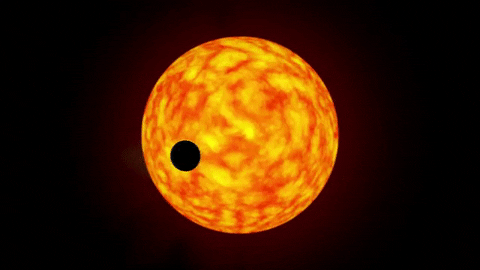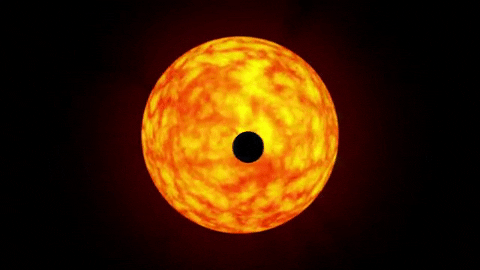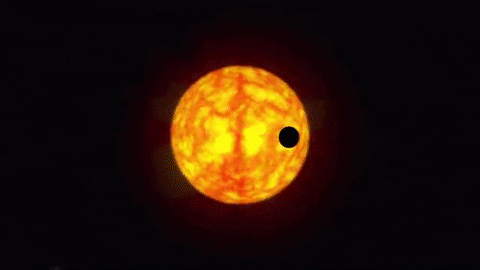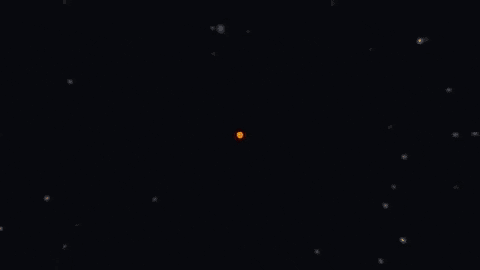
Hell beyond Earth: very hot, very dark giant HD 149026b. Artist's eye

Detailed temperature map on the gas giant HD 189733b: the hottest place is offset from the place where the rays of the local sun fall vertically

HD 189733b through the eyes of an artist. The temperature peak corresponds to the red spot in the atmosphere

Research combines two more facts. First, both of them were carried out using the Spitzer infrared orbiting telescope. Secondly, both studied objects belong to the class of "Hot Jupiters" - gas giants, whose orbits lie in close proximity to hot stars.
Hot giant HD 149026b was discovered by the group of Professor Joseph Harrington (Joseph Harrington) in the constellation Hercules, at a distance of 279 light-years from us. The temperature on the planet's surface reaches a record 2040C - it is only slightly hotter than some small stars. HD 149026b belongs to the number of transit planets - moving in orbit, it periodically passes between the parent star and the earth observer. Of the more than 200 extrasolar planets discovered to date, there are only 17 in transit. The difference between the amount of infrared radiation coming from the star in phases when HD 149026b is in front of it and behind it, allowed scientists to calculate the planet's own radiation and with a high degree of accuracy determine its temperature.
The climate here is really hellish: HD 149026b is not only colossally hot, but also dark. The planet practically does not reflect the light emitted by the parent star. However, due to the high temperature, it should glow a little in the visible range - like slightly smoldering charcoal. The reasons why the planet became so hot remain unclear. The gas giant is 25 times closer to its sun than the Earth, and yet the temperature on its surface is anomalously high. Probably, the answer lies in the unusual composition of this celestial body.
HD 149026b contains a very large amount of heavy elements - heavier than hydrogen and helium. Judging by the data obtained, there are more such substances in it than in all the bodies of the solar system combined (if we do not take into account the Sun itself). A significant part of heavy substances is concentrated in the solid core of the planet, the mass of which is estimated at 70-90 Earth. In general, HD 149026b is not only an anomalously hot, but also an anomalously dense gas giant. Scientists suggest that in its atmosphere there is some unknown component that actively absorbs the radiation of the mother star and additionally warms the planet. A dense layer of clouds of gaseous titanium oxide could act as such an additive, but at the recorded temperatures, all titanium should condense and fall out of the atmosphere in the form of liquid precipitation.
From childhood, we memorize elementary truths about the structure of the Universe: all the planets are round, there is nothing in space, the sun burns. Meanwhile, this is not true. No wonder the new Minister of Education and Science Olga Vasilyeva recently announced that it is necessary to return astronomy lessons to school. Editorial medialeaks fully supports this initiative and invites readers to update their understanding of the planets and stars.
1. The earth is a flat ball
The real shape of the Earth is somewhat different from the globe from the store. Many people know that our planet is slightly flattened from the poles. But besides this, different points of the earth's surface are removed from the center of the core at different distances. It's not just the terrain, it's just that the whole Earth is uneven. For clarity, use such a slightly exaggerated illustration.
Closer to the equator, the planet generally has a kind of ledge. Therefore, for example, the most distant point on the earth's surface from the center of the planet is not Everest (8848 m), but the Chimborazo volcano (6268 m) - its peak is 2.5 km further. This is not visible on the pictures from space, since the deviation from the ideal ball is no more than 0.5% of the radius, in addition, the atmosphere smooths out the flaws in the appearance of our beloved planet. The correct name for the shape of the Earth is the geoid.
2. The sun is burning
We are used to thinking that the Sun is a huge fireball, so it seems to us that it is burning, there is a flame on its surface. In fact, combustion is a chemical reaction that requires an oxidizing agent and fuel, and an atmosphere. (By the way, this is why explosions in outer space are almost impossible).

The sun is a huge piece of plasma in a state of thermonuclear reaction, it does not burn, but glows, emitting a stream of photons and charged particles. That is, the Sun is not fire, it is a large and very, very warm light.
3. The Earth rotates on its axis in exactly 24 hours.
It often seems that some days go by faster than others. Oddly enough, this is true. A sunny day, that is, the time during which the Sun returns to the same position in the sky, varies within plus or minus about 8 minutes at different times of the year in different parts of the planet. This is due to the fact that the linear velocity of movement and the angular velocity of the Earth's rotation around the Sun are constantly changing as it moves along an elliptical orbit. Days either increase slightly, or decrease slightly.

In addition to solar, there is also a sidereal day - the time during which the Earth makes one revolution around its axis in relation to distant stars. They are more constant, their duration is 23 hours 56 minutes 04 seconds.
4. Complete weightlessness in orbit
It is customary to think that the astronaut on the space station is in a state of complete weightlessness and his weight is zero. Yes, the influence of the Earth's gravity at an altitude of 100-200 km from its surface is less noticeable, but it remains just as powerful: that is why the ISS and the people in it remain in orbit, and do not fly away in a straight line into outer space.

In simple terms, both the station and the astronauts in it are in endless free fall (only they do not fall down, but forward), and the very rotation of the station around the planet maintains the soaring. It would be more correct to call it microgravity. A state close to total weightlessness can only be experienced outside the Earth's gravitational field.
5. Instant death in space without a spacesuit
Oddly enough, for a man who fell out of the hatch of a spaceship without a spacesuit, death is not so inevitable. It will not turn into an icicle: yes, the temperature in outer space is -270 ° C, but heat transfer in a vacuum is impossible, so the body, on the contrary, will begin to heat up. Internal pressure is also not enough to blow up a person from the inside.

The main danger is explosive decompression: gas bubbles in the blood will begin to expand, but theoretically this can be survived. In addition, in space conditions there is not enough pressure to maintain the liquid state of matter, therefore, water will begin to evaporate very quickly from the mucous membranes of the body (tongue, eyes, lungs). In Earth orbit under direct sunlight, instantaneous burns of unprotected skin areas are inevitable (by the way, here the temperature will be like in a sauna - about 100 ° C). All this is very unpleasant, but not fatal. It is very important to be in space on an exhalation (holding air will lead to barotrauma).

As a result, according to NASA scientists, under certain conditions, there is a chance that 30-60 seconds of being in outer space will not cause damage to the human body that is incompatible with life. Death will eventually come from suffocation.
6 The Asteroid Belt Is A Dangerous Place For Starships
Science fiction films have taught us that asteroid clusters are a pile of space debris that fly in close proximity to each other. On maps of the solar system, the asteroid belt also usually looks like a serious obstacle. Yes, there is a very high density of celestial bodies in this place, but only by cosmic standards: half-kilometer blocks fly at a distance of hundreds of thousands of kilometers from each other.

Mankind has launched about a dozen probes that went beyond the orbit of Mars and flew to the orbit of Jupiter without the slightest problem. Impenetrable clumps of space rocks and rocks, like those shown in Star Wars, can result from the collision of two massive celestial bodies. And then - not for long.
7. We see millions of stars
The expression "myriad stars" until recently was nothing more than a rhetorical exaggeration. With the naked eye from the Earth in the clearest weather, you can see no more than 2-3 thousand celestial bodies at the same time. In total, in both hemispheres - about 6 thousand. But in the photographs of modern telescopes, you can really find hundreds of millions, if not billions of stars (no one has counted yet).

A recent Hubble Ultra Deep Field image captured about 10,000 galaxies, the most distant of which are about 13.5 billion light-years away. According to scientists, these ultra-distant star clusters appeared "only" 400-800 million years after the Big Bang.
8. The stars are fixed
It is not the stars that move across the sky, but the Earth rotates - until the 18th century, scientists were sure that, with the exception of planets and comets, most of the celestial bodies remained motionless. However, over time, it was proved that all stars and galaxies without exception are in motion. If we went back several tens of thousands of years ago, we would not recognize the starry sky above our heads (as well as the moral law, by the way).
Of course, this happens slowly, but individual stars change their position in outer space in such a way that it becomes noticeable after a few years of observations. Bernard's star "flies" the fastest - its speed is 110 km / s. Galaxies are also moving.

For example, the Andromeda Nebula, visible to the naked eye from Earth, is approaching the Milky Way at a speed of about 140 km/s. In about 5 billion years, we will collide.
9. The moon has a dark side
The Moon always faces the Earth on one side, because its rotation around its own axis and around our planet is synchronized. However, this does not mean that the rays of the Sun never fall on the half invisible to us.

On a new moon, when the side facing the Earth is completely in shadow, the reverse is completely illuminated. However, on the natural satellite of the Earth, the day changes at night somewhat more slowly. A full lunar day lasts approximately two weeks.
10 Mercury Is The Hottest Planet In The Solar System
It is quite logical to assume that the planet closest to the Sun is also the hottest in our system. Also not true. The maximum temperature on the surface of Mercury is 427 °C. This is less than on Venus, where an indicator of 477 ° C is recorded. The second planet is almost 50 million km farther from the Sun than the first, but Venus has a dense atmosphere of carbon dioxide, which, due to the greenhouse effect, retains and accumulates temperature, while Mercury has practically no atmosphere.

There is one more moment. Mercury completes a full revolution around its axis in 58 Earth days. A two-month night cools the surface to -173 °C, which means that the average temperature at the equator of Mercury is about 300 °C. And at the poles of the planet, which always remain in the shadows, there is even ice.
11. The solar system is made up of nine planets.
Since childhood, we have been accustomed to thinking that the solar system has nine planets. Pluto was discovered in 1930, and for more than 70 years he remained a full member of the planetary pantheon. However, after much discussion, in 2006 Pluto was downgraded to the rank of the largest dwarf planet in our system. The fact is that this celestial body does not correspond to one of the three definitions of a planet, according to which such an object must clear the neighborhood of its orbit with its mass. Pluto's mass is only 7% of the combined mass of all Kuiper belt objects. For example, another planetoid from this region, Eris, is only 40 km smaller than Pluto in diameter, but noticeably heavier. For comparison, the mass of the Earth is 1.7 million times greater than that of all other bodies in the vicinity of its orbit. That is, there are still eight full-fledged planets in the solar system.

12 Exoplanets Are Like Earth
Almost every month, astronomers delight us with reports that they have discovered another exoplanet on which life could theoretically exist. Imagination immediately draws a green-blue ball somewhere near Proxima Centauri, where it will be possible to dump when our Earth finally breaks. In fact, scientists have no idea what exoplanets look like and what conditions they have. The fact is that they are so far away that we cannot yet calculate their actual size, composition of the atmosphere and temperature on the surface with modern methods.
As a rule, only the estimated distance between such a planet and its star is known. Of the hundreds of exoplanets found that are inside the habitable zone, potentially suitable for supporting Earth-like life, only a few could potentially be similar to our home planet.
13. Jupiter and Saturn - balls of gas
We all know that the largest planets in the solar system are gas giants, but this does not mean at all that once in the gravitational zone of these planets, the body will fall through them until it reaches the solid core.

Jupiter and Saturn are mostly made up of hydrogen and helium. Under the clouds, at a depth of several thousand kilometers, a layer begins in which hydrogen, under the influence of monstrous pressure, gradually passes from gaseous to the state of liquid boiling metal. The temperature of this substance reaches 6 thousand ° C. Interestingly, Saturn radiates into space 2.5 times more energy that the planet receives from the Sun, while it is not entirely clear why.
14. In the solar system, life can only exist on Earth
If something similar to terrestrial life existed somewhere else in the solar system, we would notice it ... Right? For example, the first organics appeared on Earth more than 4 billion years ago, but for hundreds of millions of years not a single external observer would have seen any clear signs of life, and the first multicellular organisms appeared only after 3 billion years. In fact, in addition to Mars, there are at least two other places in our system where life could well exist: these are the satellites of Saturn - Titan and Enceladus.

Titan has a dense atmosphere, as well as seas, lakes and rivers - though not from water, but from liquid methane. But in 2010, NASA scientists said they found signs of the possible existence of the simplest life forms on this satellite of Saturn, using methane and hydrogen instead of water and oxygen.

Enceladus is covered with a thick layer of ice, it would seem, what kind of life is there? However, under the surface at a depth of 30-40 km, as planetologists are sure, there is an ocean of liquid water about 10 km thick. The core of Enceladus is hot, and in this ocean there may be hydrothermal vents like the terrestrial "black smokers". According to one hypothesis, life on Earth appeared precisely due to this phenomenon, so why not the same thing happen on Enceladus. By the way, water breaks through the ice in some places and erupts outward in fountains up to 250 km high. Recent data confirm that this water contains organic compounds.
15. Space - empty
There is nothing in interplanetary and interstellar space, many have been sure since childhood. In fact, the vacuum of space is not absolute: there are atoms and molecules in microscopic quantities, the cosmic microwave background radiation that remains from the Big Bang, and cosmic rays, which contain ionized atomic nuclei and various subatomic particles.
Moreover, scientists have recently suggested that the cosmic void is actually composed of matter that we cannot yet detect. Physicists have called this hypothetical phenomenon dark energy and dark matter. Presumably, our Universe is 76% dark energy, 22% dark matter, 3.6% interstellar gas. Our usual baryonic matter: stars, planets, and so on - is only 0.4% of the total mass of the universe.

There is an assumption that it is the increase in the amount of dark energy that causes the Universe to expand. Sooner or later, this alternative entity, in theory, will tear the atoms of our reality into pieces of individual bosons and quarks. However, by that time, neither Olga Vasilyeva, nor the lessons of astronomy, nor mankind, nor the Earth, nor the Sun will exist for several billion years.
Unfortunately, intrigue, at least at the beginning of the article, will not work. The fact that the hottest planet is Mercury was known even to repeaters of secondary schools in the Soviet Union, to say nothing of people living in the era of the developed Internet. In everyday life, the Sun, like its planets, is only interested in the upcoming weather the next day - whether to wear a warm jacket when going out, or in summer, as usual, the day will be clear and little snow. Therefore, refreshing your memory with facts from the school astronomy course, as well as learning something new, is always interesting and useful.
Without going into the abstruse theory of the origin, expansion of the Universe, the Big Bang, galaxies scattering from each other, which only astronomers can imagine and realize, it is better to focus on the more studied celestial bodies closest to the Earth - the planets and holding them in their gravitational field star - the native luminary of the Sun.
What scientists have managed to learn about the star and planets so far, based on astronomical observations that do not stand still, new research methods, data collected by man-made space bodies regularly launched into near-Earth space and to the limits of the system:
Since the flight of Yu.A. Gagarin and the following dozens of cosmonauts, not only astronomers, but also designers, geologists, even politicians with financiers began to look with genuine interest at the nearest planets of the so-called terrestrial group - Mercury, Venus and Mars, in terms of how to populate them or at least start developing them deposits of highly mineral resources that were not harmful to the global economy. There are reasons for this, because these planets, like the Earth, are mostly composed of silicates and metals, including rare and expensive ones.
Unfortunately, not much is known about Mercury to terrestrial science today. One of the main reasons is precisely the fact that it is very close to the Sun, and it is impossible to fly to it, as in a joke, at night, when the sun is “sleeping”. But, of course, we managed to find out something:
But it is worth hoping that everything is still ahead, and research stations will be established on this planet closest to the Sun, which will allow us to learn much more about Mercury.
According to observations and calculations, the Sun is at the middle stage of the evolution of a star, while it is gradually becoming brighter, so Mercury is not in danger of losing its title for a long time - the hottest in the solar system, because the reserves for a thermonuclear reaction should be enough for an unimaginable, from a human point of view, period .
quoted1 > > Why is Venus so hot?
Venus is the hottest planet in the solar system: causes, surface and atmosphere temperature, distance to the Sun, orbit description, greenhouse effect.
You may have already heard that among all the planets in our system, the maximum heating is present on Venus. But why Venus is the hottest planet in the solar system?
Why is Venus so hot?
Answer: greenhouse effect. In many ways, Venus literally mirrors our planet Earth. But it differs sharply in the presence of a dense atmosphere. If you were on the surface, you could not withstand the pressure, which exceeds the earth's pressure by 93 times.
In addition, the atmosphere itself is represented by a composition of carbon dioxide, leading to the greenhouse effect. This is a mechanism where heat does not return to space, but accumulates on the surface.
The average temperature of Venus is 461°C. Moreover, it does not change between day, night and seasons. The tectonic activity of the second planet from the Sun stopped billions of years ago. Without this, carbon could not linger in the rock and is released into the atmosphere. All the oceans boiled and the water evaporated (literally blown out by the solar wind). Now you know what the temperature is on Venus and why the planet has become the hottest in the system.
The science
We all know from childhood that at the center of our solar system is the Sun, around which the four nearest planets of the terrestrial group, including Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars. They are followed by four gas giant planets: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune.
After Pluto ceased to be considered a planet in the solar system in 2006, and moved into the category of dwarf planets, the number of major planets has been reduced to 8.
Although many people know the general structure, there are many myths and misconceptions regarding the solar system.
Here are 10 facts you may not have known about the solar system.
1. The hottest planet is not closest to the Sun
Many people know that Mercury is the closest planet to the Sun, whose distance is almost two times less than the distance from the Earth to the Sun. It's no surprise that many people believe that Mercury is the hottest planet.

Actually Venus is the hottest planet in the solar system- the second planet close to the Sun, where the average temperature reaches 475 degrees Celsius. This is enough to melt tin and lead. At the same time, the maximum temperature on Mercury is about 426 degrees Celsius.
But due to the absence of an atmosphere, Mercury's surface temperature can vary by hundreds of degrees, while the carbon dioxide on Venus's surface maintains a virtually constant temperature at any time of the day or night.
2. The boundary of the solar system is a thousand times farther from Pluto
We tend to think that the solar system extends to the orbit of Pluto. Today, Pluto is not even considered a major planet, but this idea has remained in the minds of many people.

Scientists have discovered many objects orbiting the Sun, which are much further than Pluto. These are the so-called trans-Neptunian or Kuiper belt objects. The Kuiper belt extends for 50-60 astronomical units (the astronomical unit or the average distance from the Earth to the Sun is 149,597,870,700 m).
3. Almost everything on planet Earth is a rare element
The earth is mainly made up of iron, oxygen, silicon, magnesium, sulfur, nickel, calcium, sodium and aluminum.

Although all of these elements have been found in various places throughout the universe, they are only trace elements that overshadow the abundance of hydrogen and helium. Thus, the Earth for the most part consists of rare elements. This does not speak of any special place on planet Earth, since the cloud from which the Earth formed contained a large amount of hydrogen and helium. But since they are light gases, they were blown into space by the heat of the sun as the Earth formed.
4. The solar system has lost at least two planets
Pluto was originally considered a planet, but due to its very small size (much smaller than our moon), it was renamed a dwarf planet. Astronomers also once believed that there is a planet Vulcan, which is closer to the Sun than Mercury. Its possible existence was discussed 150 years ago to explain some of the features of Mercury's orbit. However, later observations ruled out the possibility of Vulcan's existence.

In addition, recent studies have shown that it is possible once there was a fifth giant planet, similar to Jupiter, which revolved around the Sun, but was ejected from the solar system due to gravitational interaction with other planets.
5. Jupiter has the largest ocean of all the planets
Jupiter, which orbits in cold space five times further from the Sun than planet Earth, was able to hold much higher levels of hydrogen and helium during formation than our planet.

One might even say that Jupiter is mostly made up of hydrogen and helium. Given the mass of the planet and the chemical composition, as well as the laws of physics, under cold clouds, an increase in pressure should lead to the transition of hydrogen to a liquid state. That is, on Jupiter there should be deepest ocean of liquid hydrogen.
According to computer models on this planet, not only is the largest ocean in the solar system, its depth is approximately 40,000 km, that is, it is equal to the circumference of the Earth.
6. Even the smallest bodies in the solar system have satellites
It was once believed that only such large objects as planets could have natural satellites or moons. The fact that satellites exist is sometimes even used to determine what a planet really is. It seems counterintuitive that small cosmic bodies could have enough gravity to hold a satellite. After all, Mercury and Venus don't have them, and Mars only has two tiny moons.

But in 1993, the Galileo interplanetary station discovered the Dactyl satellite, just 1.6 km wide, near the asteroid Ida. Has since been found moons orbiting about 200 other minor planets, which greatly complicated the definition of "planet".
7. We live inside the sun
We usually think of the Sun as a huge hot ball of light located at a distance of 149.6 million km from the Earth. Actually the outer atmosphere of the sun extends much further than the visible surface.

Our planet orbits within its rarefied atmosphere, and we can see this when gusts of the solar wind cause the aurora to appear. In this sense, we live inside the Sun. But the solar atmosphere doesn't end on Earth. Auroras can be observed on Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and even distant Neptune. The farthest region of the solar atmosphere is the heliosphere extends at least 100 astronomical units. This is about 16 billion kilometers. But since the atmosphere is shaped like a drop due to the movement of the Sun in space, its tail can reach from tens to hundreds of billions of kilometers.
8. Saturn isn't the only planet with rings.
While Saturn's rings are by far the most beautiful and easy to observe, Jupiter, Uranus and Neptune also have rings. While Saturn's bright rings are made of ice particles, Jupiter's very dark rings are mostly dust particles. They may contain minor fragments of decayed meteorites and asteroids, and possibly particles of the volcanic moon Io.

The ring system of Uranus is slightly more visible than that of Jupiter, and may have formed after the collision of small moons. Neptune's rings are faint and dark, like those of Jupiter. The dim rings of Jupiter, Uranus and Neptune impossible to see through small telescopes from Earth, because Saturn became best known for its rings.
Contrary to popular belief, there is a body in the solar system with an atmosphere essentially similar to that of Earth. This is Saturn's moon Titan.. It is larger than our Moon and is close in size to the planet Mercury. Unlike the atmospheres of Venus and Mars, which are much thicker and thinner, respectively, than those of Earth and are composed of carbon dioxide, Titan's atmosphere is mostly nitrogen.
The Earth's atmosphere is approximately 78 percent nitrogen. The similarity with the Earth's atmosphere, and especially the presence of methane and other organic molecules, led scientists to the idea that Titan can be considered an analogue of the early Earth, or there is some kind of biological activity. For this reason, Titan is considered the best place in the solar system to look for signs of life.
