Lesson type: lesson on introducing new knowledge
Goals:
- learn to read and write information presented in the form of various mathematical models;
- consolidate the ability to solve problems for movement based on formulas;
- improve oral counting skills, develop auditory and visual attention, memory, logical thinking, mathematical speech;
consolidate knowledge of the relationship between the studied units of measurement; - get acquainted with the new concept of "rapprochement speed";
- continue to learn to check correct and evaluate the results of their work.
Equipment: presentation, cards.
Do not tow a forklift if the engine is not working properly, or the steering system is not working properly, or the brake system is not working properly. Uniforms, safety helmets, safety shoes, etc. Trolley signs describe hazards and how to handle the trolley. Repair and replenishment of missing signs and icons.
Control after 8 hours of operation or after change
Check oil, fuel or water for leaks. Repair before starting the engine. Check the tightness of the engine, hydraulic pipes, coolers and transmission system. Do not use an open flame to check the fluid level. Check the coolant level in the radiator.
DURING THE CLASSES
1. Psychological attitude students
2. Actualization of students' knowledge
3. Working with cards
All students have cards.
- Let's start with a warm-up:
SPEED |
DISTANCE |
|
- A cyclist was moving at a speed of 100 m/min, how far did he cover in 3 minutes?
- In 20 minutes on a skateboard, the boy overcame 800 meters. How fast was he moving?
- Tourists on a hike move at a speed of 5 km / h, how long will it take them to overcome 25 km?
- Write a problem for a classmate.
Self-compilation of the conditions of the problem, a classmate reports the answer. Examination
If there is not enough fluid to replenish. Otherwise, the engine may be damaged. Gently unscrew the plug to relieve pressure, then remove the plug. Do not use gloves when unscrewing the cap as the hot liquid may melt on your hands. Coolant is hazardous to health. Wash hands thoroughly after contact with skin.
If winter refrigerant is used, use the same fluid when charging. The fuel gauge is located on the dashboard. Make sure you have enough fuel for a day's work. The fuel filler is located in the left rear pillar of the protective chamber.
- Guys, what do you think is the topic of our today's lesson? (Problem solving)
What quantities will we work with in today's lesson? (speed, time, distance)
What is our goal at this stage of the lesson? (To consolidate problem solving skills, remember the relationship of quantities)
- Let's look at our ladder of success, and everyone will determine for themselves what step you are on in mastering this topic. ( Attachment 1 ) Draw your little man on the corresponding step.
Check engine oil level. Pull out the oil scoop, clean it and put it back. Pull it out again and check the oil level. The level must be between the symbols on the gauge. Checking the brake fluid level. Check fluid level in fluid reservoir. The level must be between the two symbols on the tank. Make sure no air gets into the brake hoses.
Avoid skin contact. Check battery electrolyte level. The battery has markers that allow the operator to check the electrolyte level. The level must be between the two markers. When there is not enough water to fill the top marker. Transmission oil level Open the cap and remove the filler cap. Check the oil level so that the oil level is at the upper mark.
4. Group work
Each group receives an A3 sheet and a task (musical intro)(Attachment 1 )
a) - Tell us about these values according to the plan
1. Definition
2. Formula
3. Units of measurement
(One representative comes to the board)
b) Make up a problem according to the picture
–
Listen to the condition of the problem: two ships set off at the same time to meet each other. The speed of one is 70 km/h, the speed of the other is 80 km/h. After 10 hours they met. What is the distance between ports?
What does "at the same time" mean?
Let's simulate the problem. (At the board is a visual display)
- How many km per hour did the first ship approach the meeting point? Second?
Hydraulic oil level Check the oil level in the hydraulic oil tank. The oil level must be between the two slots. Checking the brake pedal and clutch pedal. Press the pedal all the way down while the engine is running. The distance from the pedal to the floor must be greater than 60 mm.
Make sure the handbrake is in good condition. Press your finger on the belt between the water pump roller and the generator shaft with a force of 10 kg. Check belt deflection from standard position. Horn Click sound signal to give a warning sound.
Children solve the problem, the student at the blackboard. We check the solution.
70*10 = 700 km distance traveled by 1 vessel;
80 * 10 = 800 km distance traveled by 1 vessel;
700 + 800 = 1500 km distance between two ports.
- If someone has decided the second way, we invite you to the board, please explain.
What did you learn in the first act?
If no one decides:
Installing the Operator's Seat Position the seat in a position convenient for the operator and allow easy access to all controls. Gear lever. Check out the levers for smooth play and smooth movement. Lift Lever, Tilt Lever and Additional Lever Adjustment Check the levers for Lucy and move smoothly. Increase the engine speed and make sure the levers are in good condition.
Indicators Check that the turn signals work properly when the turn signal lever is moved. Indicators and Gauges Check that the meter, water temperature, oil temperature, box oil gauge and fuel gauge, etc. are working correctly. Screw screw 1 to prevent spontaneous change of screws.
Let's get back to our modeling. By how many kilometers per hour did the distance between the ships decrease? (The ships left at the same time, which means that every hour the distance between them decreases by the sum of two speeds.)
This sum of speeds is called approach speed
70 + 80 =150 (km/h)
– Knowing the speed and time, what can we find? (Distance)
Mast Lubricate the mast from the sliding bearing. The lubrication period depends on the conditions in which the truck operates. If the operating conditions are heavily used a large number of lubricants on the mast. Lubricate the parts where the rolls are located and where they move and come into contact.
Make sure that the force of the turn to the right is the same as the turn to the left. Color or bluish Normal: Complete combustion Black Incorrect: Incomplete combustion White Incorrect: Burning water Blue Incorrect: Burning oil. Flue gas is poisonous and life-threatening.
What are our goals for the next stage of the lesson? (To get acquainted with a new concept, using a new concept, derive a formula. Understand that with the joint, simultaneous movement of two objects towards each other, for each unit of time, the distance is reduced by the sum of the speeds of moving objects)
- Let's try to deduce the convergence rate formulas. Let's remember what letters indicate the speed, how the approach occurs.
Check the clutch function manual box. Press the clutch pedal all the way down. The clutch must disengage the drive completely and must not jerk. Automatic Press the pedal slowly to drive slowly and make sure the truck accelerates.
Brake test Drive slowly with the wheelchair and depress the brake pedal, check the effect. Pressing the brake pedal stops the mast. tail light signal and reverse The reversing light turns on and the reverse signal sounds when the shift lever is pushed back.
in) Multi-level task
- Make up problems according to the schemes, choose and solve.
Children solve problems.
- Who chose 1 task? Why How did you solve 1 problem, did you use new knowledge?
- Who chose the 2nd task?Checking the solution (combining groups)
6. Summing up
- Take a card, complete the tasks.
Children work on cards.
Bleeding diesel fuel system. Fuse box The fuse box is located to the left of the cab. Before replacing a blown fuse, you must first find the cause of the burnout. The fuse to be replaced must be the same as the fuse.
Structure and stability of the loader
Tire pressure Use a tire pressure gauge to measure tire pressure. If you need to replenish the air. Make sure air is not venting the valve. Check if the tires are damaged. An inflated tire is potentially dangerous. The loader's center of gravity is at the height of the front wheels.
- Put all the cards on which you worked today in a notebook, hand in notebooks at a break.
– Back to our ladder of success, have you advanced on the steps of knowledge?
- How did you draw the second man? Why?
- What did you learn in the lesson?
– Who needs to practice solving problems of a new type?7. Homework: page 91 №5 read the tasks, choose for homework, the one that is more interesting to you.
It is important that the center of gravity of the product is in the center of the pallet. Do not lower the cart when turning because its speed is much higher than yours. Lift plate Indicates the relationship between the load capacity and the center of gravity of the load. When the heating is finished, its light will turn off. - then turn the key to pos. 3 and start the engine.
Stop the engine by turning the ignition key to position 1 or - do not stop the engine if it overheats. The call is then about 30 seconds. operate in slow gear with no load. The new engine can be loaded when it reaches 60 degrees. When it reaches this temperature, it will be necessary to load the engine as soon as possible. Excessive operation of a new engine under low load can cause oil to enter the exhaust system.
Lesson grades.
First, let's recall the formulas that are used to solve such problems: S = υ t, υ = S: t, t = S: u
where S is the distance, υ is the speed of movement, t is the time of movement.
Raise forks to transport position and tilt mast if possible. When you need to increase the engine speed at rest, depress both accelerator pedals. - release the parking brake. Make sure the truck is moving the right direction when you press the corresponding accelerator pedal. - this pedal controls the speed of the truck - when you want to release or stop the truck, - to stop the truck quickly, depress the brake pedal.
When two objects move uniformly at different speeds, the distance between them either increases or decreases for each unit of time.
Approach speed is the distance that objects approach each other per unit of time.
Removal speed is the distance that objects are removed per unit of time.
Leaning on slopes First depress the left brake pedal and then release the parking brake. At the same time, they press the appropriate accelerator pedal and release the service brake to get the truck moving. Driving on slopes When driving on slopes with a load, the load must always be pointed up the hill, only raised to the desired height and the mast tilted back up. Turning, crossing slopes is prohibited.
Garage trolley system. Loads The mass of the load must not exceed the rated load capacity, and if additional lifting equipment is used with the hoist. Loads must be stable and securely fastened. Be careful with prolonged or high loads.
Approach movement oncoming traffic and pursuit. move to remove can be divided into two types: movement in opposite directions and lagging behind.
The difficulty for some students is to correctly put "+" or "-" between the speeds when finding the speed of approach of objects or the speed of receding.
Load and load the fork with a forklift, slowly with the fork in the transport position. Hold the truck next to the load and set the mast approximately vertical. If necessary, adjust the width of the forks according to the width of the load. Move them slowly under load, sliding as far as you can. Be careful not to damage the ends of the forks with some items in the load. Make sure the forks are at transport height, tilt the mast back and move the cart. - Stop near the unloading point and straighten the mast. - Raise the forks to the required height, then slowly reach the cargo area.
Consider a table.
It can be seen from it that when objects move in opposite sides them speeds add up. When moving in one direction - subtracted.
Examples of problem solving.
Task number 1. Two cars are moving towards each other with speeds of 60 km/h and 80 km/h. Determine the speed at which the cars are approaching.
υ 1 = 60 km/h
υ 2 = 80 km/h
Find υ sat
Solution.
υ sat \u003d υ 1 + υ 2- closing speed in different directions
)
υ sat \u003d 60 + 80 \u003d 140 (km / h)
Answer: the approach speed is 140 km/h.
Slowly lowering the forks while unloading - a slight forward tilt of the mast will make unloading easier. Fork Extensions - Used to handle loads especially big size and small mass. The weight and center of gravity must match the truck's lift chart.
Actions prohibited when working with a loader. Do not drive a truck if you have a medical condition or lack of authority Do not drive under the influence of alcohol, intoxicants or other misconduct. It is forbidden to use the trolley for purposes other than those intended. Do not overload the loader. It is forbidden to accelerate and stop the wheelchair, accelerate, stop and stop on railway crossings, pedestrian crossings, etc. never slide down a slope with the engine off or idling.
Task number 2. Two cars left the same point in opposite directions at speeds of 60 km/h and 80 km/h. Determine the rate at which machines are removed.
υ 1 = 60 km/h
υ 2 = 80 km/h
Find υ beats
Solution.
υ beats = υ 1 + υ 2- removal rate (the “+” sign, since it is clear from the condition that the cars are moving in different directions)
υ beats = 80 + 60 = 140 (km/h)
Answer: the removal speed is 140 km/h.
Do not use slippers with your hands or shoes. It is forbidden to manipulate the mast during sharp turns. Do not carry people on the forks Do not allow the truck to be operated by unauthorized persons Do not leave the truck with the engine running or place it in an unsafe position. When driving, do not smoke or use fire under open sky. Do not allow to stay or walk under raised forks Do not open doors or gates by hitting them with your cart.
Don't punch the plug with the help of others Vehicle to set them in motion. Do not leave loads on raised forks. Do not remove the protective cover. Do not make any changes to the cart itself. Do not use the cart on unsuitable surfaces. Do not ride your cart higher than the specifications allow; When descending a slope, the load must be directed up the slope; Turning prohibited.
Task number 3. From one point in one direction, first a car left at a speed of 60 km/h, and then a motorcycle at a speed of 80 km/h. Determine the speed at which the cars are approaching.
(We see that here is the case of movement in pursuit, so we find the speed of approach)
υ av = 60 km/h
υ mot = 80 km/h
Find υ sat
Solution.
υ sat \u003d υ 1 - υ 2- closing speed (the “–” sign, since it is clear from the condition that the cars are moving in one direction)
υ sat \u003d 80 - 60 \u003d 20 (km / h)
Answer: speed of approach is 20 km/h.
That is, the name of the speed - approach or removal - does not affect the sign between the speeds. Only direction matters.
Let's consider other tasks.
Task number 4. Two pedestrians left the same point in opposite directions. The speed of one of them is 5 km / h, the other - 4 km / h. How far apart will they be after 3 hours?
υ 1 = 5 km/h
υ 2 = 4 km/h
t = 3 h
Find S
Solution.
in different directions)
υ beats = 5 + 4 = 9 (km/h)
S = υ beat t
S = 9 3 = 27 (km)
Answer: after 3 hours the distance will be 27 km.
Task number 5. Two cyclists simultaneously started towards each other from two points, the distance between which is 36 km. The speed of the first is 10 km/h, the second is 8 km/h. In how many hours will they meet?
S = 36 km
υ 1 = 10 km/h
υ 2 = 8 km/h
Find t
Solution.
υ sat \u003d υ 1 + υ 2 - speed of approach (the “+” sign, since it is clear from the condition that the cars are moving in different directions)
υ sat = 10 + 8 = 18 (km/h)
(meeting time can be calculated using the formula)
t = S: υ Sat
t = 36: 18 = 2 (h)
Answer: See you in 2 hours.
Task number 6. Two trains left the same station in opposite directions. Their speeds are 60 km/h and 70 km/h. In how many hours will the distance between them be 260 km?
υ 1 = 60 km/h
υ 2 = 70 km/h
S = 260 km
Find t
Solution .
1 way
υ beats \u003d υ 1 + υ 2 - removal rate (sign “+” since it is clear from the condition that pedestrians are moving in different directions)
υ beats = 60 + 70 = 130 (km/h)
(The distance traveled is found by the formula)
S = υ beat t ⇒ t= S: υ beats
t = 260: 130 = 2 (h)
Answer: after 2 hours the distance between them will be 260 km.
2 way
Let's make an explanatory drawing:
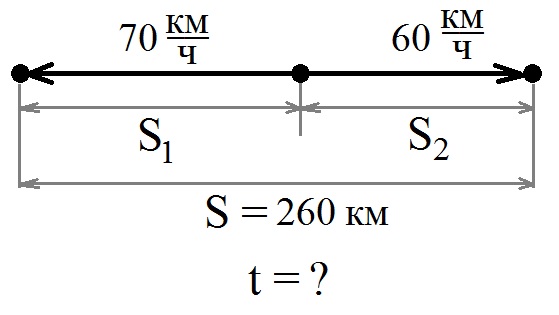
It can be seen from the figure that
1) after a given time, the distance between the trains will be equal to the sum of the distances traveled by each of the trains:
S = S 1 + S 2;
2) each of the trains traveled the same time (from the condition of the problem), which means that
S 1 \u003d υ 1 t-distance traveled by 1 train
S 2 \u003d υ 2 t- distance traveled by train 2
Then,
S= S1 + S2= υ 1 t + υ 2 t = t (υ 1 + υ 2)= t υ beats
t = S: (υ 1 + υ 2)- the time for which both trains will travel 260 km
t \u003d 260: (70 + 60) \u003d 2 (h)
Answer: The distance between trains will be 260 km in 2 hours.
1. Two pedestrians simultaneously came out towards each other from two points, the distance between which is 18 km. The speed of one of them is 5 km / h, the other - 4 km / h. In how many hours will they meet? (2 h)
2. Two trains left the same station in opposite directions. Their speeds are 10 km/h and 20 km/h. In how many hours will the distance between them be 60 km? (2 h)
3. From two villages, the distance between which is 28 km, two pedestrians came out towards each other at the same time. The speed of the first is 4 km/h, the speed of the second is 5 km/h. How many kilometers per hour do pedestrians approach each other? How far apart will they be after 3 hours? (9 km, 27 km)
4. The distance between the two cities is 900 km. Two trains left these cities towards each other with speeds of 60 km/h and 80 km/h. How far apart were the trains 1 hour before the meeting? Is there an extra condition in the task? (140 km, yes)
5. A cyclist and a motorcyclist left the same point in the same direction at the same time. The speed of a motorcyclist is 40 km/h and that of a cyclist is 12 km/h. What is the speed of their removal from each other? In how many hours will the distance between them be 56 km? (28 km/h, 2 h)
6. From two points 30 km apart, two motorcyclists left at the same time in the same direction. The speed of the first is 40 km/h, the second is 50 km/h. In how many hours will the second overtake the first?
7. The distance between cities A and B is 720 km. A fast train leaves A for B at a speed of 80 km/h. After 2 hours, a passenger train left B to A towards him at a speed of 60 km/h. In how many hours will they meet?
8. A pedestrian left the village at a speed of 4 km/h. After 3 hours, a cyclist followed him at a speed of 10 km / h. How many hours does it take the cyclist to overtake the pedestrian?
9. The distance from the city to the village is 45 km. A pedestrian left the village for the city at a speed of 5 km/h. An hour later, a cyclist rode towards him from the city to the village at a speed of 15 km/h. Which of them will be closer to the village at the time of the meeting?
10. Old task. A young man went from Moscow to Vologda. He walked 40 miles a day. A day later, another young man was sent after him, passing 45 versts a day. In how many days will the second overtake the first?
11. Old problem. The dog saw a hare in 150 fathoms, which runs 500 fathoms in 2 minutes, and the dog in 5 minutes - 1300 fathoms. The question is, at what time will the dog overtake the hare?
12. Old problem. Two trains left Moscow for Tver at the same time. The first passed at an hour of 39 versts and arrived in Tver two hours earlier than the second, which passed at an hour of 26 versts. How many miles from Moscow to Tver?
