June 21, 1941, 13:00. German troops receive the code signal "Dortmund", confirming that the invasion will begin the next day.
Commander of the 2nd Panzer Group, Army Group Center Heinz Guderian writes in his diary: “Careful observation of the Russians convinced me that they did not suspect anything about our intentions. In the courtyard of the fortress of Brest, which was visible from our observation posts, to the sounds of an orchestra, they were holding guards. Coastal fortifications along the Western Bug were not occupied by Russian troops.21:00. Soldiers of the 90th border detachment of the Sokal commandant's office detained a German soldier who had crossed the border river Bug by swimming. The defector was sent to the headquarters of the detachment in the city of Vladimir-Volynsky.
23:00. German minelayers, who were in Finnish ports, began to mine the way out of the Gulf of Finland. At the same time, Finnish submarines began laying mines off the coast of Estonia.
June 22, 1941, 0:30. The defector was taken to Vladimir-Volynsky. During interrogation, the soldier named himself Alfred Liskov, servicemen of the 221st regiment of the 15th infantry division of the Wehrmacht. He reported that at dawn on June 22 the German army would go on the offensive along the entire length of the Soviet-German border. The information has been passed on to the higher command.
At the same time, the transfer of directive No. 1 of the People's Commissariat of Defense for parts of the western military districts begins from Moscow. “During June 22-23, 1941, a sudden attack by the Germans on the fronts of the LVO, PribOVO, ZAPOVO, KOVO, OdVO is possible. The attack may begin with provocative actions,” the directive said. “The task of our troops is not to succumb to any provocative actions that could cause major complications.”
The units were ordered to be put on alert, covertly occupy the firing points of fortified areas on the state border, and aviation was dispersed over field airfields.
It is not possible to bring the directive to the military units before the start of hostilities, as a result of which the measures indicated in it are not carried out.
Mobilization. Columns of fighters are moving to the front. Photo: RIA Novosti
“I realized that it was the Germans who opened fire on our territory”
1:00. The commandants of the sections of the 90th border detachment report to the head of the detachment, Major Bychkovsky: "nothing suspicious was noticed on the adjacent side, everything is calm."
3:05 . A group of 14 German Ju-88 bombers drops 28 magnetic mines near the Kronstadt raid.
3:07. The commander of the Black Sea Fleet, Vice Admiral Oktyabrsky, reports to the Chief of the General Staff, General Zhukov: “The VNOS [airborne surveillance, warning and communications] system of the fleet reports on the approach from the sea of a large number of unknown aircraft; The fleet is on full alert.
3:10. The UNKGB in the Lvov region transmits by telephone to the NKGB of the Ukrainian SSR the information obtained during the interrogation of the defector Alfred Liskov.
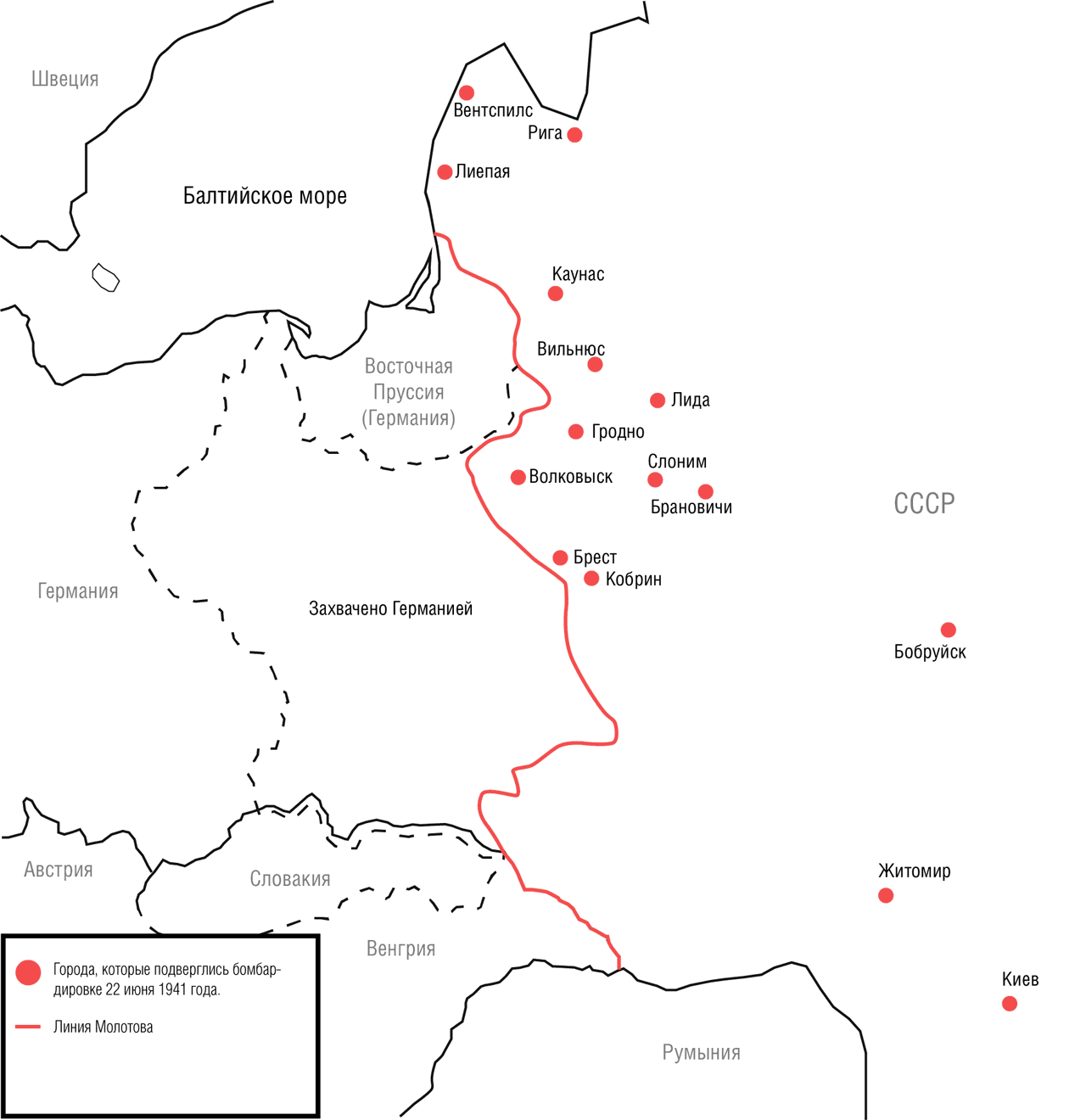
From the memoirs of the head of the 90th border detachment, Major Bychkovsky: “Not having finished interrogating the soldier, I heard strong artillery fire in the direction of Ustilug (the first commandant's office). I realized that it was the Germans who opened fire on our territory, which was immediately confirmed by the interrogated soldier. I immediately began to call the commandant by phone, but the connection was broken ... "3:30. Chief of Staff of the Western District General Klimovsky reports on enemy air raids on the cities of Belarus: Brest, Grodno, Lida, Kobrin, Slonim, Baranovichi and others.
3:33. The chief of staff of the Kyiv district, General Purkaev, reports on air raids on the cities of Ukraine, including Kyiv.
3:40. Commander of the Baltic Military District General Kuznetsov reports on enemy air raids on Riga, Siauliai, Vilnius, Kaunas and other cities.
"Enemy raid repulsed. An attempt to strike our ships has been thwarted."
3:42. Chief of the General Staff Zhukov calls Stalin and announces the start of hostilities by Germany. Stalin orders Tymoshenko and Zhukov to arrive at the Kremlin, where an emergency meeting of the Politburo is being convened.
3:45. The 1st frontier post of the 86th Augustow border detachment was attacked by an enemy reconnaissance and sabotage group. Outpost personnel under command Alexandra Sivacheva, having joined the battle, destroys the attackers.
4:00. The commander of the Black Sea Fleet, Vice Admiral Oktyabrsky, reports to Zhukov: “The enemy raid has been repulsed. An attempt to strike our ships has been thwarted. But there is destruction in Sevastopol.”4:05. The outposts of the 86th August Frontier Detachment, including the 1st Frontier Post of Senior Lieutenant Sivachev, are subjected to heavy artillery fire, after which the German offensive begins. The border guards, deprived of communication with the command, engage in battle with superior enemy forces.
4:10. The Western and Baltic Special Military Districts report the start of hostilities by German troops on land.
4:15. The Nazis open massive artillery fire on the Brest Fortress. As a result, warehouses were destroyed, communications were disrupted, and there were a large number of dead and wounded.
4:25. The 45th Infantry Division of the Wehrmacht begins an attack on the Brest Fortress.

The Great Patriotic War of 1941-1945. Residents of the capital on June 22, 1941 during the announcement on the radio of a government message about the perfidious attack of Nazi Germany on the Soviet Union. Photo: RIA Novosti
"Defending not individual countries, but ensuring the security of Europe"
4:30. A meeting of members of the Politburo begins in the Kremlin. Stalin expresses doubt that what happened is the beginning of the war and does not exclude the version of a German provocation. People's Commissar of Defense Timoshenko and Zhukov insist: this is war.
4:55. In the Brest Fortress, the Nazis manage to capture almost half of the territory. Further progress was stopped by a sudden counterattack by the Red Army.
5:00. German Ambassador to the USSR Count von Schulenburg presents the People's Commissar for Foreign Affairs of the USSR Molotov“Note from the German Foreign Ministry to the Soviet Government”, which states: “The German government cannot be indifferent to a serious threat on the eastern border, therefore the Führer ordered the German armed forces to ward off this threat by all means.” An hour after the actual start of hostilities, Germany de jure declares war on the Soviet Union.
5:30. On German radio, the Reich Minister of Propaganda Goebbels read out an appeal Adolf Hitler to the German people in connection with the outbreak of war against the Soviet Union: “Now the hour has come when it is necessary to oppose this conspiracy of the Jewish-Anglo-Saxon warmongers and also the Jewish rulers of the Bolshevik center in Moscow ... what the world has only seen ... The task of this front is no longer the protection of individual countries, but the security of Europe and thereby the salvation of all.7:00. Reich Minister for Foreign Ribbentrop begins a press conference at which he announces the start of hostilities against the USSR: "The German army invaded the territory of Bolshevik Russia!"
“The city is on fire, why aren’t you broadcasting anything on the radio?”
7:15. Stalin approves the directive on repelling the attack of Nazi Germany: "The troops will attack the enemy forces with all their strength and means and destroy them in areas where they have violated the Soviet border." The transfer of "Directive No. 2" due to the violation by saboteurs of the communication lines in the western districts. Moscow does not have a clear picture of what is happening in the war zone.
9:30. It was decided that at noon Molotov, People's Commissar for Foreign Affairs, would address the Soviet people in connection with the outbreak of war.
10:00. From the memories of the announcer Yuri Levitan: “They call from Minsk: “Enemy planes are over the city”, they call from Kaunas: “The city is on fire, why are you not transmitting anything on the radio?”, “Enemy planes are over Kyiv.” Women's crying, excitement: “Is it really a war? ..” However, no official messages are transmitted until 12:00 Moscow time on June 22.
10:30. From the report of the headquarters of the 45th German division on the battles on the territory of the Brest Fortress: “The Russians are fiercely resisting, especially behind our attacking companies. In the citadel, the enemy organized defense by infantry units supported by 35-40 tanks and armored vehicles. The fire of enemy snipers led to heavy losses among officers and non-commissioned officers.11:00. The Baltic, Western and Kyiv special military districts were transformed into the Northwestern, Western and Southwestern fronts.
“The enemy will be defeated. Victory will be ours"
12:00. People's Commissar for Foreign Affairs Vyacheslav Molotov read out an appeal to the citizens of the Soviet Union: "Today at 4 o'clock in the morning, without presenting any claims against the Soviet Union, without declaring war, German troops attacked our country, attacked our borders in many places and bombed from our cities - Zhytomyr, Kyiv, Sevastopol, Kaunas and some others - more than two hundred people were killed and wounded. Enemy aircraft raids and artillery shelling were also carried out from Romanian and Finnish territory ... Now that the attack on the Soviet Union has already taken place, the Soviet government has given an order to our troops to repel the piratical attack and drive the German troops from the territory of our homeland ... The government calls on you, citizens and citizens of the Soviet Union, to rally their ranks still more closely around our glorious Bolshevik Party, around our Soviet government, around our great leader Comrade Stalin.
Our cause is right. The enemy will be defeated. Victory will be ours" .
12:30. Advanced German units break into the Belarusian city of Grodno.
13:00.
The Presidium of the Supreme Soviet of the USSR issues a decree "On the mobilization of those liable for military service ..."
“On the basis of Article 49 of paragraph “o” of the Constitution of the USSR, the Presidium of the Supreme Soviet of the USSR announces mobilization on the territory of the military districts - Leningrad, Special Baltic, Western Special, Kyiv Special, Odessa, Kharkov, Oryol, Moscow, Arkhangelsk, Ural, Siberian, Volga, North - Caucasian and Transcaucasian.
13:30. The Chief of the General Staff, General Zhukov, flies to Kyiv as a representative of the newly created Headquarters of the High Command on the Southwestern Front.

Photo: RIA Novosti
14:00. The Brest Fortress is completely surrounded by German troops. Soviet units blockaded in the citadel continue to offer fierce resistance.
14:05. Foreign Minister of Italy Galeazzo Ciano declares: “In view of the current situation, due to the fact that Germany has declared war on the USSR, Italy, as an ally of Germany and as a member of the Tripartite Pact, also declares war on the Soviet Union from the moment the German troops enter Soviet territory.”
14:10. The 1st frontier post of Alexander Sivachev has been fighting for more than 10 hours. The border guards, who had only small arms and grenades, destroyed up to 60 Nazis and burned three tanks. The wounded head of the outpost continued to command the battle.
15:00. From the notes of Field Marshal Commander of Army Group Center bokeh background: “The question of whether the Russians are carrying out a planned withdrawal is still open. There is now ample evidence both for and against this.
It is surprising that nowhere is any significant work of their artillery visible. Strong artillery fire is conducted only in the north-west of Grodno, where the VIII Army Corps is advancing. Apparently, our air force has an overwhelming superiority over Russian aviation.Of the 485 frontier posts attacked, none retreated without an order.
16:00. After a 12-hour battle, the Nazis occupy the positions of the 1st frontier post. This became possible only after all the border guards who defended it died. The head of the outpost, Alexander Sivachev, was posthumously awarded the Order of the Patriotic War, 1st class.
The feat of the outpost of Senior Lieutenant Sivachev became one of the hundreds accomplished by the border guards in the first hours and days of the war. The state border of the USSR from the Barents to the Black Sea on June 22, 1941 was guarded by 666 border outposts, 485 of them were attacked on the very first day of the war. None of the 485 outposts attacked on June 22 withdrew without orders.
The Nazi command took 20 minutes to break the resistance of the border guards. 257 Soviet frontier posts held the defense from several hours to one day. More than one day - 20, more than two days - 16, more than three days - 20, more than four and five days - 43, from seven to nine days - 4, more than eleven days - 51, more than twelve days - 55, more than 15 days - 51 outposts. Up to two months, 45 outposts fought.

The Great Patriotic War of 1941-1945. The working people of Leningrad listen to the message about the attack of fascist Germany on the Soviet Union. Photo: RIA Novosti
Of the 19,600 border guards who met the Nazis on June 22 in the direction of the main attack of Army Group Center, more than 16,000 died in the first days of the war.
17:00. Hitler's units manage to occupy the southwestern part of the Brest Fortress, the northeast remained under the control of Soviet troops. Stubborn battles for the fortress will continue for another week.
"The Church of Christ blesses all Orthodox for the defense of the sacred borders of our Motherland"
18:00. The Patriarchal Locum Tenens, Metropolitan Sergius of Moscow and Kolomna, addresses the faithful with a message: “Fascist robbers have attacked our homeland. Trampling all sorts of treaties and promises, they suddenly fell upon us, and now the blood of peaceful citizens is already irrigating our native land ... Our Orthodox Church has always shared the fate of the people. Together with him, she carried trials, and consoled herself with his successes. She will not leave her people even now… The Church of Christ blesses all Orthodox to defend the sacred borders of our Motherland.”
19:00. From the notes of the Chief of the General Staff of the Wehrmacht Ground Forces, Colonel General Franz Halder: “All the armies, except for the 11th Army of the Army Group South in Romania, went on the offensive according to the plan. The offensive of our troops, apparently, was a complete tactical surprise for the enemy on the entire front. The border bridges across the Bug and other rivers have been everywhere captured by our troops without a fight and in complete safety. The complete surprise of our offensive for the enemy is evidenced by the fact that the units were taken by surprise in the barracks, the planes stood at the airfields, covered with tarpaulins, and the advanced units, suddenly attacked by our troops, asked the command what to do ... The Air Force command reported, that today 850 enemy aircraft have been destroyed, including entire squadrons of bombers, which, having taken to the air without fighter cover, were attacked by our fighters and destroyed.20:00. Directive No. 3 of the People's Commissariat of Defense was approved, ordering the Soviet troops to go on the counteroffensive with the task of defeating the Nazi troops on the territory of the USSR with further advance into the territory of the enemy. The directive prescribed by the end of June 24 to capture the Polish city of Lublin.

Great Patriotic War 1941-1945. June 22, 1941 Nurses assist the first wounded after the Nazi air raid near Chisinau. Photo: RIA Novosti
"We must give Russia and the Russian people all the help we can"
21:00. Summary of the High Command of the Red Army for June 22: “At dawn on June 22, 1941, the regular troops of the German army attacked our border units on the front from the Baltic to the Black Sea and were held back by them during the first half of the day. In the afternoon, the German troops met with the advanced units of the field troops of the Red Army. After fierce fighting, the enemy was repulsed with heavy losses. Only in the Grodno and Krystynopol directions did the enemy manage to achieve minor tactical successes and occupy the towns of Kalvaria, Stoyanuv and Tsekhanovets (the first two at 15 km and the last at 10 km from the border).
Enemy aviation attacked a number of our airfields and settlements, but everywhere they met with a decisive rebuff from our fighters and anti-aircraft artillery, which inflicted heavy losses on the enemy. We shot down 65 enemy planes."
23:00. Message from the British Prime Minister Winston Churchill to the British people in connection with the German attack on the USSR: “At 4 o’clock this morning, Hitler attacked Russia. All his usual formalities of treachery were observed with scrupulous precision ... suddenly, without a declaration of war, even without an ultimatum, German bombs fell from the sky on Russian cities, German troops violated Russian borders, and an hour later the German ambassador, who just the day before generously lavished his assurances to the Russians in friendship and almost an alliance, paid a visit to the Russian Minister of Foreign Affairs and declared that Russia and Germany were in a state of war ...
No one has been a more staunch opponent of communism over the past 25 years than I have been. I will not take back a single word said about him. But all this pales before the spectacle unfolding now.The past, with its crimes, follies and tragedies, recedes. I see Russian soldiers standing on the border of their native land and guarding the fields that their fathers have plowed since time immemorial. I see how they guard their homes; their mothers and wives pray—oh, yes, because at such a time everyone prays for the preservation of their loved ones, for the return of the breadwinner, patron, their protectors ...
We must give Russia and the Russian people all the help we can. We must call on all our friends and allies in all parts of the world to follow a similar course and pursue it as steadfastly and steadily as we will, to the very end.
June 22 has come to an end. Ahead were another 1417 days of the most terrible war in the history of mankind.
June, 22. Ordinary Sunday. More than 200 million citizens are planning how to spend their day off: go on a visit, take their children to the zoo, someone is in a hurry to play football, someone is on a date. Soon they will become heroes and victims of the war, killed and wounded, soldiers and refugees, blockade runners and prisoners of concentration camps, partisans, prisoners of war, orphans, and invalids. Winners and veterans of the Great Patriotic War. But none of them know about it yet.
In 1941 The Soviet Union stood quite firmly on its feet - industrialization and collectivization bore fruit, industry developed - out of ten tractors produced in the world, four were Soviet-made. Dneproges and Magnitogorsk have been built, the army is being re-equipped - the famous T-34 tank, Yak-1, MIG-3 fighters, Il-2 attack aircraft, Pe-2 bomber have already entered service with the Red Army. The situation in the world is turbulent, but the Soviet people are sure that "the armor is strong and our tanks are fast." In addition, two years ago, after three-hour talks in Moscow, USSR People's Commissar for Foreign Affairs Molotov and German Foreign Minister Ribbentrop signed a 10-year non-aggression pact.
After the abnormally cold winter of 1940-1941. A rather warm summer has come to Moscow. Amusements operate in the Gorky Park, football matches are held at the Dynamo stadium. The Mosfilm film studio is preparing the main premiere of the summer of 1941 - the editing of the lyrical comedy Hearts of Four, which will be released only in 1945, has just been completed here. Starring the favorite of Joseph Stalin and all Soviet moviegoers, actress Valentina Serova.


June, 1941 Astrakhan. Near the village of Liney

1941 Astrakhan. On the Caspian Sea

July 1, 1940 A scene from the film "My Love" directed by Vladimir Korsh-Sablin. In the center, actress Lidia Smirnova as Shurochka


April, 1941 Peasant greets the first Soviet tractor

July 12, 1940 Residents of Uzbekistan work on the construction of a section of the Great Fergana Canal

August 9, 1940 Byelorussian SSR. Collective farmers of the village of Tonezh, Turovsky district, Polesye region, for a walk after a hard day's work



May 05, 1941 Kliment Voroshilov, Mikhail Kalinin, Anastas Mikoyan, Andrey Andreev, Alexander Shcherbakov, Georgy Malenkov, Semyon Timoshenko, Georgy Zhukov, Andrey Eremenko, Semyon Budyonny, Nikolai Bulganin, Lazar Kaganovich and others in the presidium of the ceremonial meeting dedicated to graduation commanders who graduated from military academies. Joseph Stalin speaking



June 1, 1940. Classes in civil defense in the village of Dikanka. Ukraine, Poltava region

In the spring and summer of 1941, exercises of the Soviet military began to be carried out more and more often on the western borders of the USSR. War is already in full swing in Europe. Rumors reach the Soviet leadership that Germany could attack at any moment. But such messages are often ignored, since a non-aggression pact was signed just recently.
August 20, 1940 Villagers talking to tankmen during military exercises



"Higher, higher and higher
We strive for the flight of our birds,
And breathes in every propeller
The tranquility of our borders."
Soviet song, better known as "March of the Aviators"
June 1, 1941. An I-16 fighter is suspended under the wing of a TB-3 aircraft, under the wing of which a high-explosive bomb weighing 250 kg

September 28, 1939 People's Commissar for Foreign Affairs of the USSR Vyacheslav Mikhailovich Molotov and German Foreign Minister Joachim von Ribbentrop shake hands after the signing of the joint Soviet-German treaty "On Friendship and Borders"

Field Marshal V. Keitel, Colonel General V. von Brauchitsch, A. Hitler, Colonel General F. Halder (left to right in the foreground) near the table with a map during a meeting of the General Staff. In 1940, Adolf Hitler signed the main directive number 21, codenamed "Barbarossa"

On June 17, 1941, V.N. Merkulov sent an intelligence message received by the NKGB of the USSR from Berlin to I.V. Stalin and V.M. Molotov:
“A source working at the headquarters of the German aviation reports:
1. All German military measures to prepare for an armed uprising against the USSR have been completely completed, and a strike can be expected at any time.
2. In the circles of the aviation headquarters, the TASS message of June 6 was perceived very ironically. They emphasize that this statement cannot have any meaning ... "
There is a resolution (regarding 2 points): “To Comrade Merkulov. You can send your "source" from the headquarters of the German aviation to the fucking mother. This is not a "source", but a disinformer. I. Stalin»
July 1, 1940. Marshal Semyon Timoshenko (right), General of the Army Georgy Zhukov (left) and General of the Army Kirill Meretskov (2nd from left) during an exercise in the 99th Rifle Division of the Kyiv Special Military District
June 21, 21:00
At the site of the Sokal commandant's office, a German soldier, Corporal Alfred Liskof, was detained after swimming across the Bug River.

From the testimony of the head of the 90th border detachment, Major Bychkovsky:“Due to the fact that the translators in the detachment are weak, I called a German teacher from the city ... and Liskof repeated the same thing again, that is, that the Germans were preparing to attack the USSR at dawn on June 22, 1941 ... Without finishing the interrogation of the soldier, he heard in the direction Ustilug (first commandant's office) strong artillery fire. I realized that it was the Germans who opened fire on our territory, which was immediately confirmed by the interrogated soldier. I immediately began to call the commandant by phone, but the connection was broken.
21:30
In Moscow, a conversation took place between People's Commissar for Foreign Affairs Molotov and German Ambassador Schulenburg. Molotov protested in connection with the numerous violations of the borders of the USSR by German aircraft. Schulenburg evaded answering.
From the memoirs of Corporal Hans Teuchler:“At 22 o’clock we were lined up and the order of the Fuhrer was read out. Finally, they told us directly why we are here. Not at all for a rush to Persia to punish the British with the permission of the Russians. And not in order to lull the vigilance of the British, and then quickly transfer troops to the English Channel and land in England. No. We - soldiers of the Great Reich - are waiting for a war with the Soviet Union itself. But there is no such force that could hold back the movement of our armies. For the Russians it will be a real war, for us it will be just a victory. We will pray for her."
June 22, 00:30
Directive No. 1 was sent to the districts, containing an order to covertly occupy firing points on the border, not to succumb to provocations and put the troops on alert.

From the memoirs of the German General Heinz Guderian:“On the fateful day of June 22 at 2:10 in the morning, I went to the command post of the group ...
At 03:15 our artillery preparation began.
At 0340 hours - the first raid of our dive bombers.
At 4:15 a.m., the crossing over the Bug began.
03:07
The commander of the Black Sea Fleet, Admiral Oktyabrsky, called the Chief of the General Staff of the Red Army Georgy Zhukov and said that a large number of unknown aircraft were approaching from the sea; The fleet is in full combat readiness. The admiral offered to meet them with fleet air defense fire. He was instructed: "Act and report to your people's commissar."
03:30
Chief of Staff of the Western District, Major General Vladimir Klimovskikh, reported on a German air raid on the cities of Belarus. Three minutes later, the chief of staff of the Kyiv district, General Purkaev, reported on an air raid on the cities of Ukraine. At 03:40, the commander of the Baltic District, General Kuznetsov, reported a raid on Kaunas and other cities.

From the memoirs of I. I. Geibo, deputy regiment commander of the 46th IAP, ZapVO:“... My chest went cold. In front of me are four twin-engine bombers with black crosses on their wings. I even bit my lip. Why, these are Junkers! German Ju-88 bombers! What to do? .. Another thought arose: "Today is Sunday, and on Sundays the Germans do not have training flights." So it's a war? Yes, war!
03:40
People's Commissar of Defense Timoshenko asks Zhukov to report to Stalin about the start of hostilities. Stalin responded by ordering all members of the Politburo to gather in the Kremlin. At that moment, Brest, Grodno, Lida, Kobrin, Slonim, Baranovich, Bobruisk, Volkovysk, Kyiv, Zhytomyr, Sevastopol, Riga, Vindava, Libava, Siauliai, Kaunas, Vilnius and many other cities were bombed.
From the memoirs of Alevtina Kotik, born in 1925 (Lithuania):“I woke up from the fact that I hit my head on the bed - the ground shook from falling bombs. I ran to my parents. Dad said: “The war has begun. We have to get out of here!” We did not know with whom the war started, we did not think about it, it was just very scary. Dad was a military man, and therefore he was able to call a car for us, which took us to the railway station. They took only clothes with them. All furniture and household utensils remained. At first we rode on a freight train. I remember how my mother covered me and my brother with her body, then they transferred to a passenger train. The fact that the war with Germany, they learned somewhere around 12 noon from people they met. Near the city of Siauliai, we saw a large number of wounded, stretchers, doctors.
At the same time, the Belostok-Minsk battle began, as a result of which the main forces of the Soviet Western Front were surrounded and defeated. German troops captured a significant part of Belarus and advanced to a depth of over 300 km. On the part of the Soviet Union in the Bialystok and Minsk “boilers”, 11 rifle, 2 cavalry, 6 tank and 4 motorized divisions were destroyed, 3 commanders and 2 commanders were killed, 2 commanders and 6 division commanders were captured, another 1 corps commander and 2 commanders divisions were missing.
04:10
The Western and Baltic Special Districts reported on the start of hostilities by German troops on land.
04:12
German bombers appeared over Sevastopol. The enemy raid was repulsed, and an attempt to strike at the ships was thwarted, but residential buildings and warehouses were damaged in the city.
From the memoirs of Sevastopol Anatoly Marsanov:“I was then only five years old ... The only thing that remains in my memory: on the night of June 22, parachutes appeared in the sky. It became light, I remember, the whole city was illuminated, everyone was running, so joyful ... They shouted: “Paratroopers! Paratroopers!”… They don't know that these are mines. And they both gasped - one in the bay, the other - down the street below us, they killed so many people!
04:15
The defense of the Brest Fortress began. By the first attack, by 04:55, the Germans occupied almost half of the fortress.
From the memoirs of the defender of the Brest Fortress Pyotr Kotelnikov, born in 1929:“In the morning we were awakened by a strong blow. Broke the roof. I was stunned. I saw the wounded and the dead, I realized: this is no longer an exercise, but a war. Most of the soldiers of our barracks died in the first seconds. Following the adults, I rushed to the weapon, but they did not give me rifles. Then I, with one of the Red Army soldiers, rushed to extinguish the clothing warehouse. Then he moved with the soldiers to the cellars of the barracks of the neighboring 333rd Infantry Regiment ... We helped the wounded, brought them ammunition, food, water. Through the western wing at night they made their way to the river to draw water, and returned back.
05:00
Moscow time, Reich Minister of Foreign Affairs Joachim von Ribbentrop summoned Soviet diplomats to his office. When they arrived, he informed them of the start of the war. The last thing he said to the ambassadors was: "Tell Moscow that I was against the attack." After that, telephones did not work in the embassy, and the building itself was surrounded by SS detachments.
5:30
Schulenburg officially informed Molotov about the beginning of the war between Germany and the USSR, reading out a note: “Bolshevik Moscow is ready to stab in the back of National Socialist Germany, which is fighting for existence. The German government cannot be indifferent to the serious threat on the eastern border. Therefore, the Fuhrer gave the order to the German armed forces to ward off this threat with all their might and means ... "

From the memoirs of Molotov:"The adviser to the German ambassador Hilger, when he handed the note, shed a tear."

From Hilger's memoirs:“He gave vent to his indignation by declaring that Germany had attacked a country with which it had a non-aggression pact. This has no precedent in history. The reason given by the German side is an empty pretext ... Molotov concluded his angry speech with the words: “We did not give any grounds for this.”
07:15
Directive No. 2 was issued, ordering the troops of the USSR to destroy enemy forces in areas of violation of the border, destroy enemy aircraft, and also “bomb Koenigsberg and Memel” (modern Kaliningrad and Klaipeda). The USSR Air Force was allowed to go "to the depth of German territory up to 100-150 km." At the same time, the first counterattack of the Soviet troops took place near the Lithuanian town of Alytus.
09:00

At 7:00 Berlin time, Reich Minister of Public Education and Propaganda Joseph Goebbels read out on the radio Adolf Hitler's appeal to the German people in connection with the outbreak of war against the Soviet Union: “... Today I decided to once again put the fate and future of the German Reich and our people into the hands of our soldier. May the Lord help us in this struggle!
09:30
Chairman of the Presidium of the Supreme Soviet of the USSR Mikhail Kalinin signed a number of decrees, including the decree on the introduction of martial law, on the formation of the Headquarters of the High Command, on military tribunals and on general mobilization, to which all those liable for military service from 1905 to 1918 were born.

10:00
German bombers raided Kyiv and its suburbs. The railway station, the Bolshevik plant, an aircraft plant, power plants, military airfields, and residential buildings were bombed. According to official data, 25 people died as a result of the bombing, according to unofficial data, there were many more victims. However, peaceful life continued in the capital of Ukraine for several more days. Only the opening of the stadium, scheduled for June 22, was canceled; on this day, the football match Dynamo (Kyiv) - CSKA was supposed to take place here.
12:15
Molotov made a speech on the radio about the beginning of the war, where he first called it patriotic. Also in this speech, for the first time, the phrase that became the main slogan of the war is heard: “Our cause is just. The enemy will be defeated. Victory will be ours".

From Molotov's address:“This unprecedented attack on our country is an unparalleled perfidy in the history of civilized peoples... This war was imposed on us not by the German people, not by the German workers, peasants and intelligentsia, whose suffering we understand well, but by a clique of bloodthirsty fascist rulers of Germany who enslaved the French, Czechs , Poles, Serbs, Norway, Belgium, Denmark, Holland, Greece and other peoples ... This is not the first time our people have to deal with an attacking arrogant enemy. At one time, our people responded to Napoleon's campaign in Russia with a Patriotic War, and Napoleon was defeated and came to his own collapse. The same will happen to the arrogant Hitler, who has announced a new campaign against our country. The Red Army and all our people will again wage a victorious patriotic war for the Motherland, for honor, for freedom.

The working people of Leningrad listen to the message about the attack of fascist Germany on the Soviet Union

From the memoirs of Dmitry Savelyev, Novokuznetsk: “We gathered at the poles with loudspeakers. We listened carefully to Molotov's speech. For many, there was a feeling of some kind of wariness. After that, the streets began to empty, after a while food disappeared from the shops. They weren’t bought up – just the supply was reduced… People weren’t scared, but rather focused, doing everything the government told them to do.”

After some time, the text of Molotov's speech was repeated by the famous announcer Yuri Levitan. Thanks to his soulful voice and the fact that Levitan read the front-line reports of the Soviet Information Bureau throughout the war, it is believed that he was the first to read the message about the beginning of the war on the radio. Even marshals Zhukov and Rokossovsky thought so, as they wrote about in their memoirs.
Moscow. Announcer Yuri Levitan during filming in the studio

From the memoirs of announcer Yuri Levitan:“When we, the announcers, were called to the radio early in the morning, the calls had already begun to ring out. They call from Minsk: “Enemy planes over the city”, they call from Kaunas: “The city is on fire, why are you not transmitting anything on the radio?”, “Enemy planes are over Kyiv.” Women's crying, excitement - "is it really a war"? .. And now I remember - I turned on the microphone. In all cases, I remember myself that I only worried internally, only experienced internally. But here, when I uttered the word “Moscow is speaking”, I feel that I can’t continue to speak - a lump stuck in my throat. They are already knocking from the control room - “Why are you silent? Go on! He clenched his fists and continued: "Citizens and citizens of the Soviet Union ..."

Stalin delivered a speech to the Soviet people only on July 3, 12 days after the start of the war. Historians are still arguing why he was silent for so long. Here is how Vyacheslav Molotov explained this fact:“Why me and not Stalin? He didn't want to go first. It is necessary that there be a clearer picture, what tone and what approach ... He said that he would wait a few days and speak when the situation on the fronts cleared up.

And here is what Marshal Zhukov wrote about this:"AND. V. Stalin was a strong-willed man and, as they say, "not from a cowardly dozen." Confused, I saw him only once. It was at dawn on June 22, 1941, when Nazi Germany attacked our country. During the first day, he could not really pull himself together and firmly direct events. The shock produced on I. V. Stalin by the attack of the enemy was so strong that his voice even dropped, and his orders for organizing armed struggle did not always correspond to the situation.

From a speech by Stalin on the radio on July 3, 1941:“The war with fascist Germany cannot be considered an ordinary war... Our war for the freedom of our Fatherland will merge with the struggle of the peoples of Europe and America for their independence, for democratic freedoms.”
12:30
At the same time, German troops entered Grodno. A few minutes later, the bombardment of Minsk, Kyiv, Sevastopol and other cities began again.
From the memoirs of Ninel Karpova, born in 1931 (Kharovsk, Vologda region):“We listened to the message about the beginning of the war from the loudspeaker at the House of Defense. There were a lot of people there. I was not upset, on the contrary, I became proud: my father will defend the Motherland ... In general, people were not afraid. Yes, women, of course, were upset, crying. But there was no panic. Everyone was sure that we would quickly defeat the Germans. The men said: "Yes, the Germans will drape from us!"
Recruiting stations were opened in the military registration and enlistment offices. Queues lined up in Moscow, Leningrad and other cities.
From the memoirs of Dina Belykh, born in 1936 (Kushva, Sverdlovsk region):“All men immediately began to call, including my dad. Dad hugged mom, they both cried, kissed ... I remember how I grabbed him by the tarpaulin boots and shouted: “Daddy, don’t go! They'll kill you there, they'll kill you!" When he got on the train, my mother took me in her arms, we both sobbed, she whispered through her tears: “Wave to dad ...” What is there, I sobbed so much, I could not move my hand. We never saw him again, our breadwinner."


Calculations and experience of the mobilization carried out showed that in order to transfer the army and navy to wartime, 4.9 million people were required to be called up. However, when mobilization was announced, 14 ages of conscripts were called up, the total number of which was about 10 million people, that is, almost 5.1 million people more than what was required.

The first day of mobilization in the Red Army. Volunteers in the Oktyabrsky military registration and enlistment office

The conscription of such a mass of people was not caused by military necessity and introduced disorganization into the national economy and anxiety among the masses. Without realizing this, Marshal of the Soviet Union G. I. Kulik suggested that the government additionally call on older ages (1895-1904), the total number of which was 6.8 million people.

13:15
To capture the Brest Fortress, the Germans brought into action new forces of the 133rd Infantry Regiment on the Southern and Western Islands, but this "did not bring changes in the situation." The Brest Fortress continued to hold the line. Fritz Schlieper's 45th Infantry Division was thrown into this sector of the front. It was decided that only infantry would take the Brest Fortress - without tanks. No more than eight hours were allotted for the capture of the fortress.

From a report to the headquarters of the 45th Infantry Division Fritz Schlieper:“The Russians are fiercely resisting, especially behind our attacking companies. In the Citadel, the enemy organized defense with infantry units supported by 35-40 tanks and armored vehicles. The fire of Russian snipers led to heavy losses among officers and non-commissioned officers.
14:30
Italian Foreign Minister Galeazzo Ciano told the Soviet ambassador in Rome, Gorelkin, that Italy had declared war on the USSR "from the moment German troops entered Soviet territory."

From Ciano's diaries:“He perceives my message with rather great indifference, but this is in his nature. The message is very short, without unnecessary words. The conversation lasted two minutes.
15:00
The pilots of the German bombers reported that they had nothing more to bomb, all airfields, barracks and concentrations of armored vehicles were destroyed.

From the memoirs of Air Marshal, Hero of the Soviet Union G.V. Zimina:“On June 22, 1941, large groups of fascist bombers attacked 66 of our airfields, on which the main aviation forces of the western border districts were based. First of all, airfields were subjected to air strikes, on which aviation regiments were based, armed with aircraft of new designs ... As a result of attacks on airfields and in fierce air battles, the enemy managed to destroy up to 1,200 aircraft, including 800 at airfields.
16:30
Stalin left the Kremlin for the Near Dacha. Until the end of the day, even members of the Politburo are not allowed to see the leader.

From the memoirs of Politburo member Nikita Khrushchev:
“Beria told the following: when the war began, members of the Politburo gathered at Stalin's. I don’t know, all or only a certain group, which most often met with Stalin. Stalin was morally completely depressed and made the following statement: “The war has begun, it is developing catastrophically. Lenin left us the proletarian Soviet state, and we pissed it off.” Literally said so.
“I,” he says, “refuse leadership,” and left. He left, got into the car and drove to a nearby dacha.
Some historians, referring to the memories of other participants in the events, argue that this conversation took place a day later. But the fact that in the first days of the war Stalin was confused and did not know how to act is confirmed by many witnesses.

18:30
The commander of the 4th Army, Ludwig Kubler, gives the order to "pull his own forces" at the Brest Fortress. This is one of the first orders for the retreat of German troops.
19:00
The commander of Army Group Center, General Fedor von Bock, gives the order to stop the execution of Soviet prisoners of war. After that, they were kept in hastily fenced fields with barbed wire. This is how the first camps for prisoners of war appeared.

From the notes of SS Brigadeführer G. Keppler, commander of the "Der Fuhrer" regiment from the SS division "Das Reich":“In the hands of our regiment were rich trophies and a large number of prisoners, among whom were many civilians, even women and girls, the Russians forced them to defend themselves with weapons in their hands, and they bravely fought along with the Red Army.”
23:00
British Prime Minister Winston Churchill delivers a radio address in which he stated that England "will give Russia and the Russian people all the help it can."

Winston Churchill's speech on the air of the BBC radio station:“Over the past 25 years, no one has been a more consistent opponent of communism than me. I won't take back a single word I said about him. But all this pales before the spectacle now unfolding. The past with its crimes, follies and tragedies is disappearing... I see Russian soldiers standing on the threshold of their native land, guarding the fields that their fathers have cultivated since time immemorial... I see how the vile Nazi war machine is approaching all this.
23:50
The Main Military Council of the Red Army sent out Directive No. 3, ordering June 23 to launch counterattacks against enemy groups.
Text: Information Center of the Kommersant Publishing House, Tatiana Mishanina, Artem Galustyan
Video: Dmitry Shelkovnikov, Alexey Koshel
A photo: TASS, RIA Novosti, Ogonyok, Dmitry Kuchev
Design, programming and layout: Anton Zhukov, Alexey Shabrov
Kim Voronin
Commissioning Editor: Artem Galustyan
USSR in 1941-1953
Persons: O. V. Kuusinen, V. Leeb, F. Bock, G. Rundstedt, E. Manstein. G. K. Zhukov, A. M. Vasilevsky, K. K. Rokosovsky, F. Paulus, W. Churchill, F. D. Roosevelt. S. Mikhoels, A. A. Kuznetsov, N. A. Voznesensky, M. I. Rodionov, G. Truman, Mao Zedong, J. Broz Tito
Dates: August 23, 1939 - the signing of the Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact, September 1 - the beginning of World War II, September 17 - the invasion of Soviet troops in Poland, September 28, 1941 - the signing of an agreement with Germany "On Friendship and Border", November 30, 1939 - the beginning of the war with Finland, December 14, 1939 - the exclusion of the USSR from the League of Nations, March 12, 1940 - the conclusion of a peace treaty with Finland, April 13, 1941 - the signing of a non-aggression pact with Japan, June 22, 1941 - invasion of Germany and its allies into the Soviet Union, June 23, 1941 - the Headquarters of the High Command was formed, June 28, 1941 - the capture of Minsk by German troops, June 30, 1941 - the establishment of the State Defense Committee (GKO), August 5 - October 16, 1941 - the defense of Odessa, September 8, 1941 - the beginning of the blockade of Leningrad, September 29 - October 1, 1941 - the Moscow Conference, September 30, 1941 - the beginning of the Typhoon plan, October 30, 1941 - July 4 1942 - defense of Sevastopol, December 5-6, 1941 - the beginning of the counteroffensive of the Soviet troops in the battle of Moscow, January 1, 1942, the accession of the USSR to the United Nations Declaration, May 1942 - the defeat of the Soviet army during the Kharkov operation. July 17, 1942 - the beginning of the Battle of Stalingrad, November 19-20, 1942 - the beginning of the implementation of Operation Uranus, January 10, 1943 - the beginning of Operation Ring, January 18, 1943 - the end of the blockade of Leningrad, July 5, 1943 - the beginning of the battle on the Kursk Bulge, July 12 - the beginning of the counteroffensive of the Soviet troops in the Battle of the Kursk Bulge, November 6, 1943 - the liberation of Kiev, November 28 - December 1, 1943 - Tehran Conference, June 23-24, 1944 - the beginning of the operation "Bagration", August 20, 1944 - the beginning of the Iasi-Kishinev operation, January 12-14, 1945 - the beginning of the Vistula-Oder operation, February 4-11, 1945 -Yalta conference, April 16-18, 1945 - the beginning of the Berlin operation, May 2, 1945 - the surrender of the Berlin garrison, May 8, 1945 - the signing of the act of unconditional surrender of Germany, July 17 - August 2, 1945 - the Potsdam Conference., August 8, 1945 - declaration of war on the USSR Japan, September 2, 1945 - Japanese surrender. 1946 - W. Churchill's Fulton speech, 1947 - "Truman Doctrine", 1948 - case of the Jewish Anti-Fascist Committee, 1949 - "Leningrad case", 1949 - testing of Soviet nuclear weapons, 1949 - the collapse of a united Germany, the formation of the FRG and the GDR, 1949 - the formation of the Council for Mutual Economic Assistance (CMEA), 1950-1953. — Korean War, 1952 - XIX Party Congress, 1952-1953. - "the case of doctors."
Material study plan:
Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact. Soviet-Finnish war. Soviet occupation of the Baltic states and Bessarabia. Preparing for war with Germany. Distribution of forces. First stage of the war. Battle for Moscow. Formation of the anti-Hitler coalition. partisan movement. Military operations in May - August 1942 Battle of Stalingrad. Battle of Kursk. Tehran conference. Military operations in 1944 Military operations in January - February 1945 Yalta Conference. Defeat of Germany. Potsdam conference. War of the USSR with Japan. Repression Post-war economy. 19th Party Congress. Foreign policy in 1945-1953 Beginning of the Cold War.
On the eve of the Great Patriotic War and its first stage. The beginning of the Second World War was preceded by the conclusion of a secret Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact August 23, 1939, actually establishing the delimitation of spheres of influence in Europe. September 1 Germany invaded Poland, thereby unleashing a world war. On September 3, England and France declared war on Germany. On September 17, Soviet troops crossed the Polish border and occupied Western Belarus and Ukraine. September 28, 1939 The Treaty "On Friendship and Border" was signed between the USSR and Germany. In accordance with the Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact, the USSR undertook aggression against Finland. The Soviet government put forward an unacceptable demand for the Finns to exchange the Finnish territory adjoining Leningrad for some regions of Karelia. On the pretext of an imaginary shelling of Soviet troops by Finnish artillery November 30, 1939 The USSR began hostilities. On December 1, 1939, by order of I.V. Stalin, a puppet government of the Democratic Republic of Finland was formed. It was headed by a representative of the Comintern O. V. Kuusinen. He was to become the head of the Finnish state after the end of the war. However, the fighting developed unsuccessfully for the USSR. Mannerheim line(the system of defensive structures) for a long time remained impregnable for the Red Army. She suffered serious losses. In addition, the war complicated the foreign policy situation of the USSR. December 14, 1939 The USSR was expelled from the League of Nations for aggression against Finland. Only in February 1940 did the Red Army break through the Mannerheim Line. Finland was forced to negotiate. March 12, 1940 in Moscow, a peace treaty was signed, according to which the USSR received the area around Vyborg, and a Soviet military base was created on the Hanko peninsula, at the entrance to the Gulf of Finland. As a result of the war, the Soviet Union managed to move the border away from Leningrad. However, the consequences of the clash with Finland were generally negative. The USSR suffered heavy human and material losses. Serious damage was done to the foreign policy authority of the USSR. The whole world (including Germany) was convinced of the relatively low combat capability of the Red Army. This greatly contributed to the optimism of the German command regarding the upcoming war with the USSR. That it was inevitable became more and more clear, judging by the course of the war on the western front. In April - May 1940, Denmark and Norway were occupied. On June 22, 1940, the Compiègne armistice was signed, signifying the defeat of France and its occupation. September 27 was formed Triple Alliance, which included Germany, Italy, Japan. On December 18, the plan was approved "Barbarossa" assuming a lightning victory over the USSR as a result of a blitzkrieg (a short war of several months).
At this time, the Stalinist government, in accordance with the Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact, continued the policy of forcible annexation of adjacent territories. In June 1940, the Baltic states were occupied (Lithuania, Latvia, Estonia). At the end of June, Bessarabia and Northern Bukovina, which were under the control of Romania, were occupied. In August 1940, the Supreme Soviet of the USSR decided to form new socialist republics within the Soviet Union - Moldavian, Latvian, Lithuanian, Estonian SSR. Together with the newly formed Karelo-Finnish SSR The Soviet Union now consisted of 16 republics.
For the Soviet government, the likelihood of an imminent war with Germany was obvious. It was in connection with this that, from September 1939, universal military service was introduced in the USSR, a seven-day work week (i.e., there was no fixed day of general rest), punishments for violations of labor discipline became tougher, and investments in the military-industrial complex increased. For the same reason, negotiations with Japan are speeding up, and on April 13, 1941, a non-aggression pact is signed with it. This was supposed to secure the eastern borders of the country. However, by 1941 the USSR was not ready for a full-scale war. Stalin was extremely afraid of provoking a possible attack from Germany, therefore, in response to the incoming information about the impending German invasion, no measures were taken. This greatly complicated the position of the state in the first months of the war.
First stage of the war. On June 22, 1941, the troops of Germany and its allies crossed the border of the Soviet Union. It was 3.3 million people, 3.7 thousand tanks and assault guns, more than 4 thousand aircraft, about 200 ships. The offensive was to go in three directions: for this, three armies were formed "North"(headed by Field Marshal V. Leeb), Center (Field Marshal F. Side),"South" (Field Marshal G. Rundstedt). The operation was supposed to be completed in 3-5 months. In many respects, the Red Army was heavily outnumbered. German troops met resistance from 186 divisions numbering 3 million people. The Red Army had at its disposal 13,000 tanks, about 40,000 mortars, more than 9,000 aircraft (not counting Navy aircraft), and 182 warships. Despite this, the German troops advanced inland at a tremendous pace. In this case, both the country's unpreparedness for the start of the war, and the lack of professionalism and inexperience of the Red Army command staff, who were seriously injured during the mass repressions, affected. In addition, the tactical training of the Red Army did not correspond to the latest achievements of military science.
June 22, 1941 the German army advanced 60 km., destroyed a significant part of the Soviet aviation. Germany completely dominated the air. On June 23, Vilnius was taken, June 28 - Minsk, July 1 - Riga. On July 10-30, the Battle of Smolensk took place, which delayed the advance of German troops to the east. On August 5, the Germans approached Odessa. 8 September The blockade of Leningrad began. Meanwhile, 5 armies of the Southwestern Front were surrounded by German troops. On 27 September they ceased resistance.
The Soviet government was forced to adapt the system of government in the country to the needs of wartime. On June 23, 1941, the Headquarters of the High Command was formed. From June 30 all power in the country was concentrated in State Defense Committee (GKO), headed by I. V. Stalin. A general mobilization was announced. The evacuation of the civilian population and industrial production began. From September 12, 1941, barrage detachments were introduced into the army, which were supposed to shoot the retreating. In August
1941 a decision was made to resettle Germans Volga region to Siberia and Kazakhstan. (In 1944, the resettlement policy affected Kalmyks, Chechens, Ingush, Karachays, Balkars.)
To solve the fundamental problem of the war, the capture of Moscow, the Nazi command developed a plan "Typhoon". Its implementation began September 30, 1941 Initially, events at the front developed in accordance with this plan. By the end of October, German troops captured Mozhaisk, Kaluga, Kalinin, and at the cost of huge losses of the Soviet army, they managed to stop the offensive along the Mozhaisk line of defense. Unexpectedly, early frosts noticeably hampered the advance of the Germans to the east. As a result of a new November offensive against Moscow, the army of F. Beck failed to encircle the capital, but from the north-west it approached it at a distance of 27 km. 5-6 December Soviet counteroffensive began. German troops were driven back from Moscow by 100-250 km. By the end of December, the front line was stabilized: severe frosts, as well as the lack of a clear plan from the Soviet command, prevented success. Nevertheless, the defeat of Germany near Moscow actually marked a turning point in the course of hostilities.
At this time, hostilities developed on other fronts. On October 16, 1941, Odessa fell. On October 30, the defense of Sevastopol began (which lasted until July 4, 1942). On November 28, 1941, Soviet troops liberated Rostov-on-Don.
Since 1941, the anti-Hitler coalition began to take shape. The first step towards this is the signing of the Soviet-British agreement on July 12, 1941 on joint military operations. On September 24, 1941, the Soviet Union acceded to the Atlantic Charter, signed earlier by Great Britain and the United States. This document outlined the intention to form an anti-fascist coalition. September 29 - October 1 During the Moscow Conference, representatives of the Soviet Union, Great Britain and the United States of America agreed on the amount of military supplies to the USSR. January 1, 1942 The USSR joined the Declaration of the United Nations, in which the countries of the anti-Hitler coalition (26 states in total) undertook the obligation not to enter into a separate agreement with the enemy. Legally, the anti-Hitler coalition took shape thanks to the Soviet-British agreement on May 26, 1942 and the Soviet-American agreement on June 11, 1942. Significant assistance from the allies came under the program "lend-lease"("loan or lease"). Food, transport, means of communication were delivered to the USSR in a significant amount. A painful issue in the Soviet Union's relations with its allies is the problem of opening a second front in Europe. The military forces of England and the USA were diverted by the fighting in North Africa and the Pacific region, so they did not dare to confront the Nazi army in Europe.
In the occupied territory, the German authorities implemented the Ost plan, aimed at the partial extermination (or resettlement) of the local population in the name of further colonization of Eastern Europe. Many Soviet citizens (about 6 million) were deported to forced labor in Germany. A policy was pursued for the complete extermination of the Jewish population. All this provoked a partisan movement in the occupied territories. Detachments of S. A. Kovpak, A. N. Saburov, A. F. Fedorov and others were formed.
In May 1942, the Soviet army attempted an offensive by the forces of the Southern and Southwestern fronts. The purpose of this operation is the liberation of Kharkov. The offensive was not sufficiently prepared, so that the Soviet troops were surrounded and suffered serious losses. At the same time, the Soviet army of the Crimean Front was defeated. On June 28, 1942, German troops went on the offensive in a southerly direction. Eastern Donbass was captured. On July 24, Rostov-on-Don was captured. In August 1942, Stavropol, Maykop, and Krasnodar were occupied. German troops were now threatening Stalingrad and Transcaucasia.
A radical change and the end of the war. July 17, 1942 German offensive against Stalingrad was initiated. This was the beginning of the Battle of Stalingrad. On August 23, the Germans reached the Volga. From September 13, fighting continued in the city itself. The German troops failed to completely suppress the pockets of resistance in Stalingrad. At this time, the Soviet command (first of all, the Deputy Supreme Commander G. K. Zhukov and Chief of the General Staff A. M. Vasilevsky) developed a counterattack plan "Uranus". Its implementation began on November 19-20, 1942. On November 23, the German army was surrounded. Since January 10, 1943, Soviet troops under the command K. K. Rokosovsky launched Operation Ring to destroy enemy forces. January 31 - February 2, 1943 field marshal's army F. Paulus capitulated. The Soviet army is developing success. On February 12, Krasnodar was liberated; on February 14, Rostov-on-Don. Voronezh, Belgorod, Kursk, Kharkov were liberated. January 18, 1943 The blockade of Leningrad was broken. However, in March 1943, E. Manstein's army group managed to return Kharkov and Belgorod. As a result, a wedge-shaped ledge of the territory occupied by German troops formed near Kursk. This is what got the name Kursk Bulge.
The Nazi command planned decisive battles in this region. A plan was developed "Citadel" for the destruction of the Soviet group. New tanks T-V ("Panther"), T-VI ("Tiger") were involved in the battles. The Soviet commanders knew about the plans of the enemy and decided to prevent the attack. July 5, 1943 artillery fired on the German grouping of troops. A few hours later, the German army nevertheless went on the offensive. The Soviet troops at the cost of extremely heavy losses managed to stop the advance of the Germans. Particularly heavy fighting unfolded in the area of the village Prokhorovka. July, 12 Soviet troops launched a counteroffensive. August 5 managed to return Orel and Belgorod, August 23 - Kharkov. By the end of August, the entire Left-Bank Ukraine and Donbass were under the control of Soviet forces. Since September 1943, the battles for the Dnieper began. In October, Dnepropetrovsk was liberated, and November 6- Kyiv.
November 28 - December 1, 1943 took place Tehran Conference with the participation of the leaders of the USSR, Great Britain and the USA (JV Stalin, W. Churchill, F. D. Roosevelt). At this conference, the Allies managed to agree on the opening of a second front in Europe. Stalin also promised the participation of the Soviet Union in the war with Japan after the final defeat of Germany. In addition, the anti-Hitler coalition discussed the fate of Europe.
The Soviet army continued to advance in all directions. On January 20, 1944, Novgorod was liberated, on April 10 - Odessa, on May 9 - Sevastopol. At the same time, June 6, 1944 a second front was opened in Normandy, so that the Nazi command was forced to transfer part of the troops from the eastern front to the western. June 23-24 operation started "Bagration" for the liberation of Belarus. On July 3, Minsk was taken. Soviet troops entered the territory of Poland. But further active actions in this direction were suspended. This is all the more strange because on August 1 an anti-German uprising broke out in Warsaw, initiated by Polish emigrants in England. The uprising continued until October 2, but the Soviet troops did not help him, despite the fact that a relatively limited contingent of the German army was located in Warsaw. There is an assumption in historiography that I.V. Stalin was counting on the defeat of the Polish rebels, led by the pro-British government. As a result of the Yas-sko-Chisinau operation, which began on August 20, Moldavia (as well as Romania) was liberated. September 8, Soviet troops entered Bulgaria, September 28 - Yugoslavia. Belgrade was liberated on October 20. *
January 12-14, 1945 started Vistula-Oder operation, as a result of which it was possible to take Warsaw, Lodz, Krakow. Soviet troops entered German territory. At the same time, the East Prussian operation was unfolding to capture Koenigsberg. On April 13, Koenigsberg fell. In January-February 1945, Budapest was liberated.
February 4-11, 1945 took place Yalta Conference with the participation of Stalin, Churchill and Roosevelt, dedicated to the post-war structure of Europe. It was decided to divide Germany into zones of occupation. East Prussia and Silesia were supposed to move away from Germany. The USSR confirmed its readiness to participate in the war with Japan. For this, he was to receive South Sakhalin and the Kuril Islands.
On April 13, Vienna was taken by Soviet troops. April 16-18 The Berlin operation began. On April 30, Hitler committed suicide. 2 May capitulated Berlin. 8 May 1945 on the outskirts of Berlin Karlhorst K. Doenitz, on behalf of the German government, signed the Act of Germany's unconditional surrender. 9 May 1945 Prague was liberated by Soviet troops.
July 17 - August 2, 1945 took place near Berlin Potsdam Conference victorious powers. The zones of occupation of Germany and the size of reparations were determined there. It was decided to carry out the denazification and demilitarization of Germany. Germany was losing the lands of East Prussia and Silesia, which were given to Poland and the Soviet Union. The Allies recognized the territorial acquisitions of 1939-1940 for the USSR.
August 8, 1945 The USSR declared war on Japan. On August 9, the Manchurian operation began. On August 19, the Japanese army began to surrender to the Soviet troops. August 22 was taken Port Arthur, August 24 - Pyongyang. September 2, 1945 On board the USS Missouri, Japan signed the Instrument of Surrender. This marked the end of World War II.
The war took a heavy toll on the USSR. His military losses ranged from 27 to 31 million people. More than 1700 cities and towns, more than 70 thousand villages and villages were destroyed.
USSR after the war, 1945-1953 The post-war years in the history of the USSR were marked by the tightening of repressions and the strengthening of the totalitarian state. All this happened against the backdrop of an unfavorable economic situation: the famine of 1946-1947, economic ruin. The terror affected former prisoners of war and internees, Baltic and Ukrainian nationalists. AT 1948 a case was initiated Jewish Anti-Fascist Committee, whose members were accused of espionage and sabotage. His head, an actor, was killed S. Mikhoels. S. A. Lozovsky, P. D. Markish, D. R. Bergelson were shot. AT 1949 d. terror touched a wide range of party leaders in connection with "Leningrad case". The secretary of the Central Committee of the All-Union Communist Party of Bolsheviks A. A. Kuznetsov, the chairman of the State Planning Committee of the USSR N. A. Voznesensky, and the chairman of the Council of Ministers of the RSFSR M. I. Rodionov were sentenced to death. AT 1952 The so-called "doctors' case" was opened, directed mainly against the Jews. Only thanks to the death of I. V. Stalin, it did not find its logical conclusion.
Economy. In the economic sphere, the task was set to restore the previous level of production. For this, a four-year plan for the restoration of the national economy (1946-1950) was developed. In industrial policy, the bet on metallurgy remained. The military-industrial complex grew rapidly. The agricultural sector remained in a reduced position: it gave away what it produced at low prices and at the same time paid higher taxes. Largely due to this, the government pursued a policy of lowering prices, and in 1947 abolished cards.
19th Party Congress. In 1952 was held XIX Congress parties. He changed its name to CPSU. In addition, the Politburo of the Central Committee was drastically expanded, which received the new name of the Presidium. In the inner circle, Stalin was perceived as a sign of new repressions against the former party leadership and the leader's stake in new cadres.
Foreign policy. In 1946 Former British Prime Minister W. Churchill delivered a speech in the USA in Fulton about the "Iron Curtain" that separated the entire free world from the countries of the socialist camp (the countries of Eastern Europe that were under the control of the USSR). From that moment on, it is customary to count the Cold War of two opposing camps that offered competing models of development, capitalist and socialist. AT 1947 US President G. Truman, sensing the menacing strengthening of the USSR, proposed the doctrine ("Truman Doctrine") according to which it was necessary to restrain the growth of the foreign political power of the Soviet Union. It would be preferable to return the USSR to the state in which it was before the start of the war. For this purpose, it was implemented Marshall plan in 1947. He assumed economic assistance to European countries from the United States in exchange for the removal of communists from their governments. 1949 became extremely alarming for the countries of Western Europe. First, the communists came to power in China, led by Mao Zedong. Second, the Soviet Union conducted a successful nuclear test. Thus, the US monopoly on this means of defeating the enemy was destroyed. In large measure, in response to this, the United States and its allies formed a military organization - North Atlantic Alliance (NATO). AT volume same 1949 The victorious powers provoked the disintegration of a united Germany. As a result, on the territory of the zones of occupation of Great Britain, the USA, France, a Federal Republic of Germany (FRG), in the zone of occupation of the USSR - German Democratic Republic (GDR). In response to the consolidation of Western countries, the USSR initiated the formation Council for Mutual Economic Assistance (CMEA), united the countries of Eastern Europe. In this region, the Soviet Union suffered only one serious defeat. Socialist Yugoslavia led by I. Broz Tito refused to recognize the hegemony of the USSR and pursued an independent policy. Korea became the place of an open clash between the USSR and the USA. The Communists of the north of Korea, with the support of the USSR and China, decided to take control of the south of the war, which the United States began to help. The war started at 1950 d. Thanks to Soviet military instructors and numerous Chinese "volunteers", the Korean communists managed for some time to control the southern provinces of Korea. However, an open clash with the United States, which such military successes were fraught with, frightened the Soviet leadership. As a result, after the death of Stalin, in the spring 1953 , managed to reach an agreement according to which the border between socialist and non-socialist Korea began to run along the 38th parallel.
Chronology
- 1941, June 22 - 1945, May 9 The Great Patriotic War
- 1941 October - December Battle of Moscow
- November 1942 - February 1943 Battle of Stalingrad
- 1943, July - August Battle of Kursk
- January 1944 Liquidation of the blockade of Leningrad
- 1944 Liberation of the territory of the USSR from fascist invaders
- 1945 April - May Battle of Berlin
- May 9, 1945 Victory Day of the Soviet Union over Germany
- 1945, August - September Defeat of Japan
Great Patriotic War (1941 - 1945)
The Great Patriotic War of the Soviet Union 1941-1945 as an integral and decisive part of the Second World War of 1939-1945. has three periods:
June 22, 1941 - November 18, 1942. It is characterized by measures to turn the country into a single military camp, the collapse of Hitler's strategy of "blitzkrieg" and the creation of conditions for a radical change in the war.
Early 1944 - May 9, 1945. Complete expulsion of the fascist invaders from Soviet soil; the liberation by the Soviet Army of the peoples of Eastern and South-Eastern Europe; final defeat of Nazi Germany.
By 1941, Nazi Germany and its allies captured virtually all of Europe: Poland was defeated, Denmark, Norway, Belgium, Holland and Luxembourg were occupied. The French army resisted for only 40 days. The English expeditionary army suffered a major defeat, and its formations were evacuated to the British Isles. Fascist troops entered the territory of the Balkan countries. In Europe, in essence, there was no force that could stop the aggressor. The Soviet Union became such a force. The great feat was accomplished by the Soviet people, who saved world civilization from fascism.
In 1940, the fascist leadership developed a plan “ Barbarossa”, the purpose of which was the lightning defeat of the Soviet Armed Forces and the occupation of the European part of the Soviet Union. Further plans included the complete destruction of the USSR. The ultimate goal of the Nazi troops was to reach the Volga-Arkhangelsk line, and it was planned to paralyze the Urals with the help of aircraft. For this, 153 German divisions and 37 divisions of its allies (Finland, Romania and Hungary) were concentrated in the eastern direction. They had to strike in three directions: central(Minsk - Smolensk - Moscow), northwestern(Baltic - Leningrad) and southern(Ukraine with access to the Black Sea coast). A lightning campaign was planned to capture the European part of the USSR until the autumn of 1941.
The first period of the Great Patriotic War (1941-1942)
The beginning of the war

Implementation of the plan Barbarossa”began at dawn June 22, 1941. extensive air bombardments of the largest industrial and strategic centers, as well as the offensive of the ground forces of Germany and its allies along the entire European border of the USSR (over 4.5 thousand km).
Nazi planes are dropping bombs on peaceful Soviet cities. June 22, 1941
In the first few days, German troops advanced tens and hundreds of kilometers. On the central direction in early July 1941, all of Belarus was captured, and German troops reached the approaches to Smolensk. On the northwestern- the Baltic states are occupied, Leningrad is blocked on September 9. On the south Nazi troops occupied Moldova and the Right-Bank Ukraine. Thus, by the autumn of 1941, Hitler's plan to capture the vast territory of the European part of the USSR was carried out.
153 Nazi divisions (3,300,000 men) and 37 divisions (300,000 men) of Nazi Germany's satellite states were thrown against the Soviet state. They were armed with 3,700 tanks, 4,950 aircraft, and 48,000 guns and mortars.
By the beginning of the war against the USSR, as a result of the occupation of Western European countries, weapons, ammunition and equipment of 180 Czechoslovak, French, British, Belgian, Dutch and Norwegian divisions were at the disposal of fascist Germany. This not only made it possible to equip the fascist troops in sufficient quantities with military equipment and equipment, but also ensured an advantage in military potential over the Soviet troops.
In our western districts, there were 2.9 million people, armed with 1,540 new types of aircraft, 1,475 modern T-34 and KV tanks, and 34,695 guns and mortars. The fascist German army had a great superiority in forces.
Describing the reasons for the failures of the Soviet Armed Forces in the first months of the war, many historians today see them in serious mistakes made by the Soviet leadership in the prewar years. In 1939, large mechanized corps, so necessary in modern warfare, were disbanded, production of 45 and 76 mm anti-tank guns was stopped, fortifications on the old Western border were dismantled, and much more.
The weakening of the command staff caused by pre-war repressions also played a negative role. All this led to an almost complete change in the command and political composition of the Red Army. By the beginning of the war, about 75% of commanders and 70% of political workers had been in their positions for less than one year. Even the chief of the general staff of the ground forces of fascist Germany, General F. Halder, noted in his diary in May 1941: “The Russian officer corps is exceptionally bad. It makes a worse impression than in 1933. It will take Russia 20 years to reach its former height.” It was necessary to recreate the officer corps of our country already in the conditions of the outbreak of war.
Among the serious mistakes of the Soviet leadership, one should also include a miscalculation in determining the time of a possible attack by fascist Germany on the USSR.
Stalin and his entourage believed that the Nazi leadership would not dare to violate the non-aggression pact concluded with the USSR in the near future. All information received through various channels, including military and political intelligence, about the upcoming German attack was considered by Stalin as provocative, aimed at exacerbating relations with Germany. This may also explain the government's assessment, transmitted in a TASS statement on June 14, 1941, in which rumors of an impending German attack were declared provocative. This also explained the fact that the directive on bringing the troops of the western military districts to combat readiness and occupying combat lines by them was given too late. In essence, the directive was received by the troops when the war had already begun. Therefore, the consequences of this were extremely severe.
At the end of June - the first half of July 1941, large defensive border battles unfolded (the defense of the Brest Fortress, etc.).
Defenders of the Brest Fortress. Hood. P. Krivonogov. 1951
From July 16 to August 15, the defense of Smolensk continued in the central direction. In the northwestern direction, the German plan to capture Leningrad failed. In the south, until September 1941, the defense of Kyiv was carried out, until October - Odessa. The stubborn resistance of the Red Army in the summer and autumn of 1941 frustrated Hitler's plan for a blitzkrieg. At the same time, by the fall of 1941, the capture by the fascist command of the vast territory of the USSR with its most important industrial centers and grain regions was a serious loss for the Soviet government. (Reader T11 No. 3)
Restructuring the life of the country on a war footing
Immediately after the German attack, the Soviet government carried out major military-political and economic measures to repel the aggression. On June 23, the Headquarters of the High Command was formed. July 10 it was converted to Headquarters of the Supreme High Command. It included I.V. Stalin (appointed commander-in-chief and soon became People's Commissar of Defense), V.M. Molotov, S.K. Timoshenko, S.M. Budyonny, K.E. Voroshilov, B.M. Shaposhnikov and G.K. Zhukov. By a directive of June 29, the Council of People's Commissars of the USSR and the Central Committee of the All-Union Communist Party of Bolsheviks set the task for the entire country to mobilize all forces and means to fight the enemy. On June 30, the State Defense Committee was created(GKO), concentrating all power in the country. The military doctrine was radically revised, the task was put forward to organize a strategic defense, wear down and stop the offensive of the fascist troops. Large-scale measures were taken to transfer industry to a military footing, to mobilize the population into the army and to build defensive lines.
Page of the newspaper "Moskovsky Bolshevik" dated July 3, 1941 with the text of I.V. Stalin's speech. Fragment
One of the main tasks, which had to be solved from the first days of the war, was the fastest restructuring of the national economy, the entire economy of the country on military rails. The main line of this restructuring was defined in the Directive of June 29, 1941. Specific measures for the restructuring of the national economy began to be carried out from the very beginning of the war. On the second day of the war, a mobilization plan for the production of ammunition and cartridges was introduced. And on June 30, the Central Committee of the All-Union Communist Party of Bolsheviks and the Council of People's Commissars of the USSR approved a mobilization national economic plan for the third quarter of 1941. However, events at the front developed so unfavorably for us that this plan turned out to be unfulfilled. Given the current situation, on July 4, 1941, a decision was made to urgently develop a new plan for the development of military production. The GKO decree on July 4, 1941 noted: develop a military-economic plan for ensuring the defense of the country, referring to the use of resources and enterprises located on the Volga, in Western Siberia and the Urals”. Within two weeks this commission developed a new plan for the fourth quarter of 1941 and for 1942 for the regions of the Volga region, the Urals, Western Siberia, Kazakhstan and Central Asia.
For the speedy deployment of a production base in the regions of the Volga region, the Urals, Western Siberia, Kazakhstan and Central Asia, it was decided to bring industrial enterprises of the People's Commissariat of Ammunition, the People's Commissariat for Armaments, the People's Commissariat of Aviation Industry, etc.
Members of the Politburo, who were at the same time members of the State Defense Committee, carried out general management of the main branches of the military economy. The issues of the production of weapons and ammunition were handled by N.A. Voznesensky, aircraft and aircraft engines - G.M. Malenkov, tanks - V.M. Molotov, food, fuel and clothing - A.I. Mikoyan and others. Industrial People's Commissariats were headed by: A.L. Shakhurin - aviation industry, V.L. Vannikov - ammunition, I.F. Tevosyan - ferrous metallurgy, A.I. Efremov - machine tool industry, V.V. Vakhrushev - coal, I.I. Sedin - oil.
The main link in the restructuring of the national economy on a war footing has become industrial restructuring. Almost all mechanical engineering was transferred to military production.
In November 1941, the People's Commissariat for General Engineering was transformed into the People's Commissariat for the Mortar Industry. In addition to the People's Commissariats of the aviation industry, shipbuilding, armaments and ammunition, created before the war, two People's Commissariats were formed at the beginning of the war - for the tank and mortar industries. Thanks to this, all the main branches of the military industry received specialized centralized management. The production of jet mortars, which existed before the war only in prototypes, was started. Their production is organized at the Moscow plant "Compressor". The front-line soldiers gave the name "Katyusha" to the first missile combat installation.
At the same time, the process workforce training through the labor reserve system. In just two years, about 1,100,000 people were trained through this sphere for work in industry.
For the same purposes, in February 1942, the Decree of the Presidium of the Supreme Soviet of the USSR “On the mobilization of the able-bodied urban population for work in production and construction” was adopted in February 1942.
In the course of the restructuring of the national economy, the main center of the war economy of the USSR became eastern industrial base, which was significantly expanded and strengthened with the outbreak of war. As early as 1942, the proportion of the eastern regions in all-Union production increased.
As a result, the main burden of supplying the army with weapons and equipment fell on the eastern industrial base. In 1942, the production of military products in the Urals increased by more than 6 times in comparison with 1940, in Western Siberia - 27 times, and in the Volga region - 9 times. On the whole, industrial production in these regions more than tripled during the war. It was a great military and economic victory achieved by the Soviet people during these years. It laid a solid foundation for the final victory over fascist Germany.
The course of hostilities in 1942
The Nazi leadership in the summer of 1942 staked on the capture of the oil regions of the Caucasus, the fertile regions of southern Russia and the industrial Donbass. Kerch and Sevastopol were lost.
At the end of June 1942, a general German offensive was launched in two directions: on Caucasus and east to Volga.
Great Patriotic War of the Soviet Union (July 22, 1941 - May 9, 1945)
On the Caucasian direction at the end of July 1942, a strong Nazi group crossed the Don. As a result, Rostov, Stavropol and Novorossiysk were captured. Stubborn battles were fought in the central part of the Main Caucasian Range, where specially trained enemy Alpine riflemen operated in the mountains. Despite the successes achieved in the Caucasian direction, the fascist command failed to solve its main task - to break through into the Transcaucasus to master the oil reserves of Baku. By the end of September, the offensive of the fascist troops in the Caucasus was stopped.
An equally difficult situation for the Soviet command developed on eastbound. Created to cover it Stalingrad Front under the command of Marshal S.K. Timoshenko. In connection with the current critical situation, an order of the Supreme Commander-in-Chief No. 227 was issued, which stated: “To retreat further means to ruin ourselves and at the same time our Motherland.” At the end July 1942. enemy in command General von Paulus dealt a powerful blow to Stalingrad front. However, despite the significant superiority in forces, during the month the fascist troops managed to advance only 60-80 km.
From the first days of September began heroic defense of Stalingrad, which actually lasted until the end of 1942. Its significance during the Great Patriotic War is enormous. Thousands of Soviet patriots heroically proved themselves in the battles for the city.
Street fighting in Stalingrad. 1942
As a result, in the battles for Stalingrad, the enemy troops suffered colossal losses. Every month of the battle, about 250 thousand new soldiers and officers of the Wehrmacht, the bulk of military equipment, were sent here. By mid-November 1942, the Nazi troops, having lost more than 180 thousand people killed, 500 thousand wounded, were forced to stop the offensive.
During the summer-autumn campaign of 1942, the Nazis managed to occupy a huge part of the European part of the USSR, but the enemy was stopped.
Second period of the Great Patriotic War (1942-1943)
The final stage of the war (1944 - 1945)
Great Patriotic War of the Soviet Union (July 22, 1941 - May 9, 1945)
In the winter of 1944, the offensive of the Soviet troops near Leningrad and Novgorod began.
900 day blockade heroic Leningrad, broken through in 1943, was completely removed.
Connected! Breaking the blockade of Leningrad. January 1943
Summer 1944. The Red Army carried out one of the largest operations of the Great Patriotic War (“ Bagration”). Belarus was completely released. This victory opened the way for advances into Poland, the Baltic states and East Prussia. In the middle of August 1944. Soviet troops in the western direction reached border with Germany.
At the end of August, Moldova was liberated.
These largest operations of 1944 were accompanied by the liberation of other territories of the Soviet Union - Transcarpathian Ukraine, the Baltic states, the Karelian Isthmus and the Arctic.
The victories of the Russian troops in 1944 helped the peoples of Bulgaria, Hungary, Yugoslavia, and Czechoslovakia in their struggle against fascism. In these countries, pro-German regimes were overthrown, and patriotic forces came to power. Created back in 1943 on the territory of the USSR, the Polish Army took the side of the anti-Hitler coalition.
Main results offensive operations carried out in 1944, consisted in the fact that the liberation of the Soviet land was completely completed, the state border of the USSR was completely restored, military operations were transferred outside our Motherland.
Front commanders at the final stage of the war
A further offensive of the Red Army against the Nazi troops was launched on the territory of Romania, Poland, Bulgaria, Hungary, and Czechoslovakia. The Soviet command, developing the offensive, conducted a number of operations outside the USSR (Budapest, Belgrade, etc.). They were caused by the need to destroy large enemy groupings in these territories in order to prevent the possibility of their transfer to the defense of Germany. At the same time, the introduction of Soviet troops into the countries of Eastern and Southeastern Europe strengthened the leftist and communist parties in them and, in general, the influence of the Soviet Union in this region.
T-34-85 in the mountains of Transylvania
AT January 1945. Soviet troops began broad offensive operations in order to complete the defeat of fascist Germany. The offensive was on a huge 1,200 km front from the Baltic to the Carpathians. Polish, Czechoslovak, Romanian and Bulgarian troops acted together with the Red Army. The French aviation regiment "Normandy - Neman" also fought as part of the 3rd Belorussian Front.
By the end of the winter of 1945, the Soviet Army had completely liberated Poland and Hungary, a significant part of Czechoslovakia and Austria. In the spring of 1945, the Red Army reached the approaches to Berlin.
Berlin offensive operation (16.IV - 8.V 1945)

It was a difficult battle in a burning, dilapidated city. On May 8, representatives of the Wehrmacht signed an act of unconditional surrender.
The signing of the act of unconditional surrender of Nazi Germany
On May 9, Soviet troops completed their last operation - they defeated the grouping of the Nazi army that surrounded the capital of Czechoslovakia - Prague, and entered the city.
The long-awaited Victory Day has come, which has become a great holiday. The decisive role in achieving this victory, in carrying out the defeat of fascist Germany and ending the Second World War, belongs to the Soviet Union.
Defeated fascist standards22 JUNE 1941 OF THE YEAR - THE BEGINNING OF THE GREAT PATRIOTIC WAR
On June 22, 1941, at 4 am, without declaring war, Nazi Germany and its allies attacked the Soviet Union. The beginning of the Great Patriotic War fell not just on Sunday. It was a church holiday of All Saints who shone in the Russian land.
Parts of the Red Army were attacked by German troops along the entire length of the border. Riga, Vindava, Libava, Siauliai, Kaunas, Vilnius, Grodno, Lida, Volkovysk, Brest, Kobrin, Slonim, Baranovichi, Bobruisk, Zhytomyr, Kyiv, Sevastopol and many other cities, railway junctions, airfields, naval bases of the USSR were bombed , artillery shelling of border fortifications and areas of deployment of Soviet troops near the border from the Baltic Sea to the Carpathians was carried out. The Great Patriotic War began.
Then no one knew that it would go down in the history of mankind as the most bloody. No one guessed that the Soviet people would have to go through inhuman trials, go through and win. Rid the world of fascism, showing everyone that the spirit of a Red Army soldier cannot be broken by the invaders. No one could have imagined that the names of the hero cities would become known to the whole world, that Stalingrad would become a symbol of the resilience of our people, Leningrad a symbol of courage, Brest a symbol of courage. That, on a par with male warriors, old men, women and children will heroically defend the earth from the fascist plague.
1418 days and nights of war.
Over 26 million human lives...
These photographs have one thing in common: they were taken in the first hours and days of the beginning of the Great Patriotic War.

On the eve of the war

Soviet border guards on patrol. The photograph is interesting because it was taken for a newspaper at one of the outposts on the western border of the USSR on June 20, 1941, that is, two days before the war.



German air raid





The first to take the blow were the border guards and the fighters of the cover units. They not only defended, but also went on the counterattack. For a whole month, the garrison of the Brest Fortress fought in the rear of the Germans. Even after the enemy managed to capture the fortress, some of its defenders continued to resist. The last of them was captured by the Germans in the summer of 1942.




The picture was taken on June 24, 1941.
During the first 8 hours of the war, Soviet aviation lost 1,200 aircraft, of which about 900 were lost on the ground (66 airfields were bombed). The Western Special Military District suffered the greatest losses - 738 aircraft (528 on the ground). Having learned about such losses, the head of the Air Force of the district, Major General Kopets I.I. shot himself.


On the morning of June 22, Moscow radio broadcast the usual Sunday programs and peaceful music. Soviet citizens learned about the beginning of the war only at noon, when Vyacheslav Molotov spoke on the radio. He reported: "Today, at 4 o'clock in the morning, without presenting any claims against the Soviet Union, without declaring war, German troops attacked our country."




.jpg)
1941 poster
On the same day, a decree was published by the Presidium of the Supreme Soviet of the USSR on the mobilization of those liable for military service born in 1905-1918 on the territory of all military districts. Hundreds of thousands of men and women received summons, appeared at the military registration and enlistment offices, and then went to the front in trains.
The mobilization capabilities of the Soviet system, multiplied during the Great Patriotic War by the patriotism and sacrifice of the people, played an important role in organizing a rebuff to the enemy, especially at the initial stage of the war. The call "Everything for the front, everything for victory!" was accepted by all the people. Hundreds of thousands of Soviet citizens voluntarily went into the army. In just a week since the beginning of the war, more than 5 million people were mobilized.
The line between peace and war was invisible, and people did not immediately perceive the change of reality. It seemed to many that this was just some kind of masquerade, a misunderstanding, and soon everything would be resolved.





The fascist troops met stubborn resistance in the battles near Minsk, Smolensk, Vladimir-Volynsky, Przemysl, Lutsk, Dubno, Rovno, Mogilev and others.And yet, in the first three weeks of the war, the troops of the Red Army left Latvia, Lithuania, Belarus, a significant part of Ukraine and Moldova. Minsk fell six days after the start of the war. The German army advanced in various directions from 350 to 600 km. The Red Army lost almost 800 thousand people.





The turning point in the perception of the war by the inhabitants of the Soviet Union, of course, was August 14. It was then that the whole country suddenly learned that The Germans occupied Smolensk . It really was a bolt from the blue. While the fighting was going on "somewhere out there, in the west," and cities flashed in the reports, the location of which many could imagine with great difficulty, it seemed that the war was still far away anyway. Smolensk is not just the name of the city, this word meant a lot. Firstly, it is already more than 400 km from the border, and secondly, only 360 km from Moscow. And thirdly, unlike Vilna, Grodno and Molodechno, Smolensk is an ancient purely Russian city.



The stubborn resistance of the Red Army in the summer of 1941 frustrated Hitler's plans. The Nazis failed to quickly take either Moscow or Leningrad, and in September the long defense of Leningrad began. In the Arctic, Soviet troops, in cooperation with the Northern Fleet, defended Murmansk and the main base of the fleet - Polyarny. Although in Ukraine in October-November the enemy captured the Donbass, captured Rostov, and broke into the Crimea, nevertheless, here, too, his troops were fettered by the defense of Sevastopol. The formations of the Army Group "South" could not reach the rear of the Soviet troops remaining in the lower reaches of the Don through the Kerch Strait.







Minsk 1941. Execution of Soviet prisoners of war


September 30th within Operation Typhoon the Germans started general attack on Moscow . Its beginning was unfavorable for the Soviet troops. Pali Bryansk and Vyazma. On October 10, G.K. was appointed commander of the Western Front. Zhukov. On October 19, Moscow was declared under a state of siege. In bloody battles, the Red Army still managed to stop the enemy. Having strengthened the Army Group Center, the German command resumed the attack on Moscow in mid-November. Overcoming the resistance of the Western, Kalinin and right flanks of the Southwestern fronts, the enemy strike groups bypassed the city from the north and south and by the end of the month reached the Moscow-Volga canal (25-30 km from the capital), approached Kashira. On this, the German offensive bogged down. The bloodless Army Group Center was forced to go on the defensive, which was also facilitated by the successful offensive operations of the Soviet troops near Tikhvin (November 10 - December 30) and Rostov (November 17 - December 2). On December 6, the counteroffensive of the Red Army began. , as a result of which the enemy was driven back from Moscow by 100 - 250 km. Kaluga, Kalinin (Tver), Maloyaroslavets and others were liberated.

On guard of the Moscow sky. Autumn 1941

The victory near Moscow was of great strategic and moral-political significance, since it was the first since the beginning of the war. The immediate threat to Moscow was eliminated.
Although, as a result of the summer-autumn campaign, our army retreated 850-1200 km inland, and the most important economic regions fell into the hands of the aggressor, the plans for the "blitzkrieg" were nevertheless frustrated. The Nazi leadership faced the inevitable prospect of a protracted war. The victory near Moscow also changed the balance of power in the international arena. They began to look at the Soviet Union as the decisive factor in the Second World War. Japan was forced to refrain from attacking the USSR.
In winter, units of the Red Army carried out an offensive on other fronts. However, it was not possible to consolidate the success, primarily because of the dispersal of forces and means along a front of enormous length.







During the offensive of the German troops in May 1942, the Crimean Front was defeated on the Kerch Peninsula in 10 days. May 15 had to leave Kerch, and July 4, 1942 after a hard defense fell Sevastopol. The enemy completely took possession of the Crimea. In July - August, Rostov, Stavropol and Novorossiysk were captured. Stubborn battles were fought in the central part of the Caucasus Range.
Hundreds of thousands of our compatriots found themselves in more than 14 thousand concentration camps, prisons, ghettos scattered throughout Europe. Dispassionate figures testify to the scale of the tragedy: only on the territory of Russia, the fascist invaders shot, choked in gas chambers, burned, and hanged 1.7 million. people (including 600 thousand children). In total, about 5 million Soviet citizens died in concentration camps.
..jpg)



..jpg)



But, despite the stubborn battles, the Nazis failed to solve their main task - to break through into the Transcaucasus to master the oil reserves of Baku. At the end of September, the offensive of the fascist troops in the Caucasus was stopped.
To contain the enemy onslaught in the east, the Stalingrad Front was created under the command of Marshal S.K. Timoshenko. On July 17, 1942, the enemy under the command of General von Paulus delivered a powerful blow on the Stalingrad front. In August, the Nazis broke through to the Volga in stubborn battles. From the beginning of September 1942, the heroic defense of Stalingrad began. The battles went on literally for every inch of land, for every house. Both sides suffered huge losses. By mid-November, the Nazis were forced to stop the offensive. The heroic resistance of the Soviet troops made it possible to create favorable conditions for them to launch a counteroffensive near Stalingrad and thereby initiate a radical change in the course of the war.



.jpg)
By November 1942, almost 40% of the population was under German occupation. The regions captured by the Germans were subject to military and civil administration. In Germany, even a special ministry for the affairs of the occupied regions was created, headed by A. Rosenberg. Political supervision was in charge of the SS and police services. On the ground, the occupiers formed the so-called self-government - city and district councils, in the villages the posts of elders were introduced. Persons dissatisfied with the Soviet government were involved in cooperation. All residents of the occupied territories, regardless of age, were required to work. In addition to participating in the construction of roads and defensive structures, they were forced to clear minefields. The civilian population, mostly young people, was also sent to forced labor in Germany, where they were called "Ostarbeiter" and used as cheap labor. In total, 6 million people were hijacked during the war years. From hunger and epidemics in the occupied territory, more than 6.5 million people were killed, more than 11 million Soviet citizens were shot in camps and at their places of residence.
November 19, 1942 Soviet troops moved into counteroffensive at Stalingrad (Operation Uranus). The forces of the Red Army surrounded 22 divisions and 160 separate units of the Wehrmacht (about 330 thousand people). The Nazi command formed the Don Army Group, consisting of 30 divisions, and tried to break through the encirclement. However, this attempt was not successful. In December, our troops, having defeated this grouping, launched an offensive against Rostov (Operation Saturn). By the beginning of February 1943, our troops liquidated the grouping of fascist troops caught in the ring. 91 thousand people were taken prisoner, led by the commander of the 6th German Army, Field Marshal von Paulus. Behind 6.5 months of the Battle of Stalingrad (July 17, 1942 - February 2, 1943) Germany and its allies lost up to 1.5 million people, as well as a huge amount of equipment. The military power of fascist Germany was significantly undermined.
The defeat at Stalingrad caused a deep political crisis in Germany. It was declared three days of mourning. The morale of the German soldiers fell, defeatist sentiments swept over the general population, which less and less believed the Fuhrer.
The victory of the Soviet troops near Stalingrad marked the beginning of a radical turning point in the course of World War II. The strategic initiative finally passed into the hands of the Soviet Armed Forces.
In January-February 1943, the Red Army was conducting an offensive on all fronts. In the Caucasian direction, Soviet troops advanced by the summer of 1943 by 500-600 km. In January 1943, the blockade of Leningrad was broken.
The command of the Wehrmacht planned summer 1943 conduct a major strategic offensive operation in the area of the Kursk salient (Operation Citadel) , defeat the Soviet troops here, and then strike at the rear of the Southwestern Front (Operation Panther) and subsequently, building on success, again create a threat to Moscow. To this end, up to 50 divisions were concentrated in the area of the Kursk Bulge, including 19 tank and motorized divisions, and other units - a total of over 900 thousand people. This grouping was opposed by the troops of the Central and Voronezh fronts, which had 1.3 million people. During the Battle of Kursk, the largest tank battle of the Second World War took place.




On July 5, 1943, a massive offensive of the Soviet troops began. Within 5 - 7 days, our troops, stubbornly defending themselves, stopped the enemy, who had penetrated 10 - 35 km beyond the front line, and launched a counteroffensive. It started July 12 near Prokhorovka , where the largest oncoming tank battle in the history of wars (with the participation of up to 1,200 tanks on both sides) took place. In August 1943, our troops captured Orel and Belgorod. In honor of this victory in Moscow, a salute was fired for the first time with 12 artillery volleys. Continuing the offensive, our troops inflicted a crushing defeat on the Nazis.
In September, Left-bank Ukraine and Donbass were liberated. On November 6, formations of the 1st Ukrainian Front entered Kyiv.

Having thrown the enemy back 200-300 km from Moscow, the Soviet troops set about liberating Belarus. From that moment on, our command held the strategic initiative until the end of the war. From November 1942 to December 1943, the Soviet Army advanced 500-1300 km to the west, freeing about 50% of the territory occupied by the enemy. 218 enemy divisions were destroyed. During this period, partisan formations inflicted great damage on the enemy, in the ranks of which up to 250 thousand people fought.
Significant successes of the Soviet troops in 1943 intensified diplomatic and military-political cooperation between the USSR, the USA and Great Britain. On November 28 - December 1, 1943, the Tehran Conference of the "Big Three" was held with the participation of I. Stalin (USSR), W. Churchill (Great Britain) and F. Roosevelt (USA). The leaders of the leading powers of the anti-Hitler coalition determined the timing of the opening of a second front in Europe (the landing operation "Overlord" was scheduled for May 1944).

Tehran Conference of the "Big Three" with the participation of I. Stalin (USSR), W. Churchill (Great Britain) and F. Roosevelt (USA).
In the spring of 1944 Crimea was cleared of the enemy.
Under these favorable conditions, the Western Allies, after two years of preparation, opened a second front in Europe in northern France. June 6, 1944 the combined Anglo-American forces (General D. Eisenhower), numbering over 2.8 million people, up to 11 thousand combat aircraft, over 12 thousand combat and 41 thousand transport ships, having crossed the English Channel and the Pas de Calais, started the biggest war in years landing Norman operation ("Overlord") and entered Paris in August.
Continuing to develop the strategic initiative, in the summer of 1944, Soviet troops launched a powerful offensive in Karelia (June 10 - August 9), Belarus (June 23 - August 29), in Western Ukraine (July 13 - August 29) and in Moldova (June 20 - 29 August).
During Belarusian operation (code name "Bagration") Army Group Center was defeated, Soviet troops liberated Belarus, Latvia, part of Lithuania, eastern Poland and reached the border with East Prussia.
The victories of the Soviet troops in the southern direction in the autumn of 1944 helped the Bulgarian, Hungarian, Yugoslav and Czechoslovak peoples in their liberation from fascism.
As a result of the hostilities of 1944, the state border of the USSR, treacherously violated by Germany in June 1941, was restored along its entire length from the Barents to the Black Sea. The Nazis were expelled from Romania, Bulgaria, from most regions of Poland and Hungary. In these countries, pro-German regimes were overthrown, and patriotic forces came to power. The Soviet Army entered the territory of Czechoslovakia.
While the block of fascist states was falling apart, the anti-Hitler coalition was growing stronger, as evidenced by the success of the Crimean (Yalta) conference of the leaders of the USSR, the United States and Great Britain (from February 4 to 11, 1945).
But still the decisive role in defeating the enemy at the final stage was played by the Soviet Union. Thanks to the titanic efforts of all the people, the technical equipment and armament of the army and navy of the USSR reached the highest level by the beginning of 1945. In January - early April 1945, as a result of a powerful strategic offensive on the entire Soviet-German front, the Soviet Army decisively defeated the main enemy forces with the forces of ten fronts. During the East Prussian, Vistula-Oder, West Carpathian and the completion of the Budapest operations, Soviet troops created the conditions for further strikes in Pomerania and Silesia, and then for an attack on Berlin. Almost all of Poland and Czechoslovakia, the entire territory of Hungary were liberated.
.jpg)
The capture of the capital of the Third Reich and the final defeat of fascism was carried out during Berlin operation (April 16 - May 8, 1945).
April 30 in the bunker of the Reich Chancellery Hitler committed suicide .
.jpg)
On the morning of May 1, over the Reichstag, sergeants M.A. Egorov and M.V. Kantaria was hoisted the Red Banner as a symbol of the Victory of the Soviet people. On May 2, Soviet troops completely captured the city. The attempts of the new German government, which on May 1, 1945, after the suicide of A. Hitler, was headed by Grand Admiral K. Doenitz, to achieve a separate peace with the USA and Great Britain failed.

May 9, 1945 at 0043 In the Berlin suburb of Karlshorst, the Act of Unconditional Surrender of the Armed Forces of Nazi Germany was signed. On behalf of the Soviet side, this historical document was signed by the hero of the war, Marshal G.K. Zhukov, from Germany - Field Marshal Keitel. On the same day, the remnants of the last large enemy grouping on the territory of Czechoslovakia in the Prague region were defeated. City Liberation Day - May 9 - became the Day of Victory of the Soviet people in the Great Patriotic War. The news of the Victory spread like lightning all over the world. The Soviet people, who suffered the greatest losses, greeted her with popular rejoicing. Truly, it was a great holiday "with tears in the eyes."
.jpg)
In Moscow, on Victory Day, a festive salute was fired from a thousand guns.
Great Patriotic War 1941-1945
Material prepared by Sergey SHULYAK


