slide presentation
Slide text: Geographical pattern of settlement and economy of foreign Europe Presentation on geography Completed by: 11th grade student of MBOU secondary school No. 51 Emelyanova Yulia Khabarovsk 2012

Slide text: Contents Introduction: territorial structure of the population and economy Highly developed areas Old industrial areas Backward agrarian areas Areas of new development The impact of international economic integration on the territorial structure of the economy

Slide text: 1. Introduction: territorial structure of the population and economy Description: Basically, it was formed in the 19th century. The main placement factor: natural resource. The emergence of coal-metallurgical regions; After World War 2: the main factors are labor resources and the benefits of the EGP; Recently, science-intensive and environmental factors have played a huge role; There are about 400 urban agglomerations and about 100 industrial areas; The “central axis” of development is the territory of 8 countries: the Rhine-Rhone line. 120 million people live here and 2/3 of the entire economic potential of the region is concentrated here.
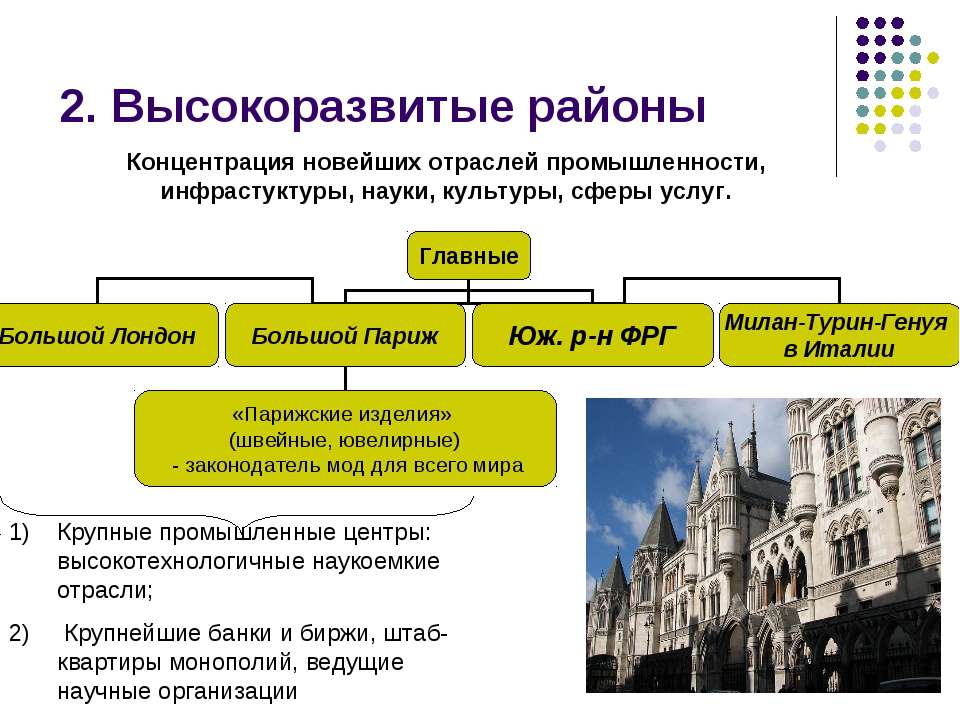
Slide text: 2. Highly developed areas Large industrial centers: high-tech science-intensive industries; Major banks and stock exchanges, headquarters of monopolies, leading scientific organizations Concentration of the latest industries, infrastructure, science, culture, services.
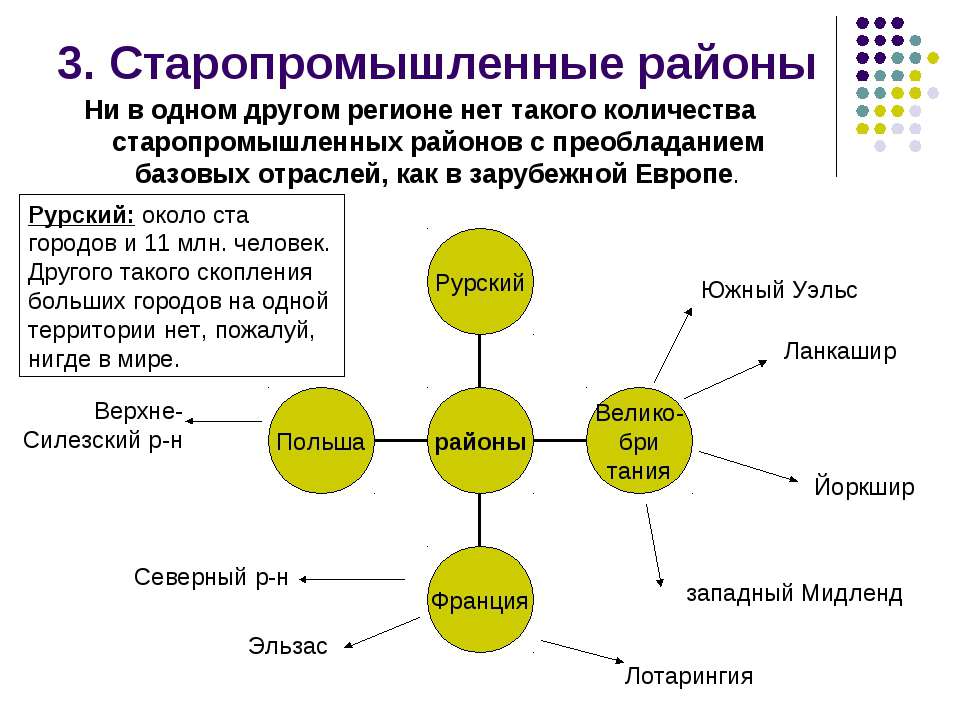
Slide text: 3. Old industrial districts No other region has such a number of old industrial districts with a predominance of basic industries as in foreign Europe. Lancashire Yorkshire West Midland South Wales North Alsace Lorraine Upper Silesian Ruhr: about a hundred cities and 11 million people. There is probably no other such cluster of large cities in one territory anywhere in the world.

Slide text: 4. Backward agrarian areas In foreign Europe there are still quite a few rather backward, predominantly agrarian areas: South of Italy (40% of the country's territory, > 35% of the population and only 18% of those employed in industry); western part of France; central and southwestern parts of Spain; some areas of Portugal and Greece All of them are located outside the "central axis". The problem of the rise of backward regions is even more urgent for many countries of Eastern Europe.

Slide text: 5. Areas of new development 1) In the early 60s. there was a discovery of a large oil and gas basin in the North Sea; 2) by the mid-90s. more than 450 oil and natural gas fields have been discovered there - the largest are Statfjord, Ekofisk and Troll; 3) In the Netherlands - one of the world's largest gas fields - Slochteren; The North Sea region satisfies 1/3 of the needs of foreign Europe in oil and 2/5 in natural gas. But in this regard, there is a considerable environmental threat, not to mention fisheries, which have suffered irreparable damage.

Slide text: 6. The impact of international economic integration on the territorial structure of the economy Favorable preconditions for the development of integration: territorial proximity; high development of the territory; high level of socio-economic development; good transport service. During the existence of the EU, all this has already led to further merging of the territorial structures of the economy of individual countries. In addition, border integration regions are being formed: Germany and France, France and Belgium, France and Italy, and so on.
