Topic: THERMAL PHENOMENA. CHANGES IN AGGREGATE STATES OF SUBSTANCE»
OPTION #1
Formulate a definition internal energy substances.
Formulate a definition specific heat fuel combustion. Write a formula for calculating the amount of heat released during the complete combustion of fuel, indicating the quantities included in the formula and their units.
Formulate the definitions of melting and solidification of crystalline bodies. Write a formula for calculating the amount of heat required to melt a substance taken at the melting point, indicating the quantities included in the formula and their units.
Formulate definitions of humidity and relative humidity of air. Write a formula for calculating the relative humidity of the air, indicating the quantities included in the formula and their units.
Formulate a definition heat engine. List the types of heat engines.
What is called the boiling of a liquid? On what and how does the boiling point of a liquid depend?
OPTION #2
Name the ways of changing the internal energy of the body.
Formulate the definition of the amount of heat. Write a formula for calculating the amount of heat required to heat a substance in the same state of aggregation, indicating the quantities included in the formula, and their units of measurement.
Formulate the definitions of evaporation, vaporization and condensation of matter. Write a formula for calculating the amount of heat required to evaporate a liquid taken at the boiling point, indicating the quantities included in the formula and their units.
Formulate definition of efficiency thermal engine. Write a formula for calculating the efficiency of a heat engine, indicating the quantities included in the formula and their units.
List the methods for determining humidity and relative humidity of air. Formulate the definition of dew point.
Name the types of heat transfer, formulate the definitions of each of them.
Topic "ELECTRIC PHENOMENA"
OPTION #1
What is electric current?
What are the conditions for the existence of a current in a substance?
The direction of movement of which particles in the conductor is taken as the direction of the current?
Write a formula to determine electrical voltage, name the quantities included in this formula, and their units of measurement.
What is the name of a device for measuring current? How is this device connected to the circuit? What current strength is considered safe for the human body?
Formulate Ohm's law for a section of the circuit and write it down in mathematical form.
List the main patterns serial connection conductors.
Formulate the definition of power electric current. Write a formula for calculating the current power, indicating the quantities included in the formula and their units.
9* Current in the circuit electric lamp equal to 0.3 A. What electric charge goes through transverse section her spirals in 10 minutes?
10* Draw a diagram electrical circuit, consisting of a battery, a lamp, a key, an ammeter and a voltmeter, for the case when the voltage at the poles of a current source is measured with a voltmeter.
OPTION #2
What is a source of electric current?
What energy transformations take place inside the current source?
Name the actions of electric current.
Write a formula for determining the current strength, name the quantities included in this formula, and their units of measurement.
What is a device for measuring electrical voltage called? How is this device connected to the circuit? What voltage is considered safe for the human body?
Formulate the Joule-Lenz law and write it down in mathematical form.
List the main patterns parallel connection conductors.
Formulate the definition of the work of electric current. Write a formula for calculating the current work, indicating the quantities included in the formula and their units.
9* Determine the work of the electric current in the spiral of the iron, included in the lighting network with a voltage of 220 V, if the charge passing through the cross section of the spiral is 10 kC.
10 * Draw a diagram of an electrical circuit consisting of a battery of galvanic cells, a resistor, a key, an ammeter and a voltmeter, for the case when the voltage across the resistor is measured with a voltmeter.
Topic "ELECTROMAGNETIC PHENOMENA"
OPTION #1
Define magnetic field.
What is an electromagnet?
Where are magnetic poles Earth?
Describe the device of a technical electric motor.
OPTION #2
What is called magnetic lines magnetic field?
What methods of amplifying the magnetic field of a coil with current do you know?
What bodies are called permanent magnets?
Where are electric motors used, and what are their advantages over heat engines?
Theme "LIGHT PHENOMENA"
OPTION #1
What is a beam of light? List the types of light sources and give examples for each.
Formulate the laws of light reflection.
What is a lens? What is called focal length lenses, how is it indicated and in what units is this value measured?
Construct and describe an image of an object between the focus and the double focus of a converging lens.
OPTION #2
State the law rectilinear propagation Sveta. What kind natural phenomena can be explained using this law?
Formulate the laws of refraction of light.
What types of lenses do you know? What quantity is called the optical power of the lens, how is it denoted and in what units is it measured?
Construct and describe an image of an object between the focus and the double focus of a diverging lens.
Didactic task cards in physics. 7th grade. To the textbook Peryshkin A.V. - Chebotareva A.V.

M.: 2010. - 1 12 p.
The manual contains task cards for organizing independent work of seventh graders in physics. Their content covers all the basic physical issues considered in the 7th grade. The use of these cards helps to individualize the learning process of students and makes it easier to check their understanding and assimilation educational material. The variety of tasks and questions included in the cards allows, taking into account the characteristics and interests of students, to offer them personally oriented tasks.
Format: pdf
The size: 2.1 MB
Watch, download: drive.google
CONTENT
Preface 4
Introduction 5
Physical body and substance. Observations and experiments 5
Physical quantities. Their dimension 7
I. Initial information about the structure of matter 9
The structure of matter. Molecules. nine
The movement of molecules. Diffusion 13
Mutual attraction and repulsion of molecules 13
Three states of matter. Molecular structure solids, liquids and gases. fifteen
II. Interaction of bodies 19
Mechanical movement 19
Speed. Speed units 21
Distance and time calculation 23
Inertia. Interaction of bodies 27
Body weight 31
Calculation of the mass and volume of a body by the density of its substance
Elastic force. Hooke's Law
Units of power. Dynamometer
Addition of two forces in the same straight line
III. Pressure of solids, liquids and gases 57
Pressure. Pressure units 57
Gas pressure 59
Transmission of pressure by liquids and gases. Pascal's Law 63
Pressure in liquid and gas. 65
Fluid Pressure Calculation 67
Communicating vessels 69
Air weight. Atmosphere pressure 71
Measurement of atmospheric pressure. Experience Torricelli 73
Barometers. Atmospheric pressure at different heights 77
Pressure gauges 79
piston pump. Hydraulic press 81
The action of liquid and gas on a body immersed in them 83
Archimedean strength 85
Swimming bodies 87
Sailing ships. Aeronautics 91
IV. work and power. Energy 93
Mechanical work. Units of work 93
Power. Power units 95
simple mechanisms. Lever 99
Moment of power. Application of levers 101
Equality of work when using simple mechanisms. The golden rule of mechanics 105
Mechanism efficiency 105
Energy. Potential energy 107
Kinetic energy. Transformation of one kind mechanical energy in. other 109
Skill analyze and build graphs changes thermodynamic state ideal gas is an indicator of good assimilation of the material of the topic " Gas laws". If the student formally memorized the equation of state of an ideal gas and mathematical expressions Boyle-Mariotte, Gay-Lussac and Charles laws, then for him the construction and analysis of graphs of isoprocesses will be difficult mathematical problem. But if the student really understands the material, if he has a good idea of the processes of changing the state of the gas (for example, without analyzing the equation “sensually knows” that when the gas in a closed vessel is heated, its pressure rises, and when it cools down), then he will read and build graphs easily.
The set contains 32 options for tasks.
At the first physics lesson in the 8th grade, which in the 7th grade was not mine, i.e. the children are not familiar to me, I spend a short test on the material of the 7th grade. I do this in order to reveal their level of knowledge (estimated, taking into account what was forgotten over the summer), to see “who is who” in the class.
12 options. Each option has 4 tasks.
I announce to the students that only fives will be put in the magazine, deuces will not be put in the magazine, and the rest of the grades are optional.
Option 1
- A cyclist traveled a distance of 12 km in 40 minutes. Find its speed.
- The newspaper sheet is 80 cm wide and 0.9 m long. Find its area.
- What is a barometer used for?
- What is the formula for the density of a substance? In what units is the density of a substance measured?
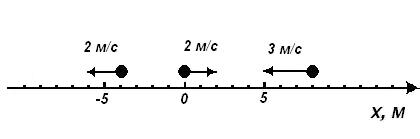
According to the figure, it is required to write the equations of motion of each of three bodies, calculate the place and time of the meeting of two bodies, find the distance between the two bodies in a certain moment time and plot x(t) for one of the bodies.
The completion of these tasks by students precedes the completion of the previously posted tasks. individual assignments on the topic "Schedule of uniform rectilinear motion».
Tasks are given in 12 options. They test (and practice) many skills and abilities, starting with correct definition scale along the axis and ending with an assessment of the correctness of the result (for example, the coordinate of the first body in the above figure cannot be positive), i.e. ability to represent a physical situation.
Students should note that the bodies in the figure are numbered from left to right: 1st, 2nd, 3rd.
 Individual task cards allow you to most actively carry out independent work students in the lesson. Using them is also convenient because they make it easy to compile and replenish an extensive catalog of tasks on any topic, classifying tasks according to the level of complexity. In ordinary collections of problems there is not a sufficient set of training problems of the same type, and cards allow you to create such sets. In addition, the use a large number options for tasks on the cards allows you to deal with cheating.
Individual task cards allow you to most actively carry out independent work students in the lesson. Using them is also convenient because they make it easy to compile and replenish an extensive catalog of tasks on any topic, classifying tasks according to the level of complexity. In ordinary collections of problems there is not a sufficient set of training problems of the same type, and cards allow you to create such sets. In addition, the use a large number options for tasks on the cards allows you to deal with cheating.
The presented set of cards on the topic "Schedule of uniform rectilinear motion" contains 20 options for tasks. In accordance with the role of the task in learning, these task cards can be used in self-study. training work students and for tests.
Graph Reading - important skill to which little attention has been paid. In the problem book, “one or two” tasks are solved per schedule, and these cards allow you to practice this skill many times.
Cards are presented in sections: What physics studies. Measurement of physical quantities, physical body, structure of matter, inertia. Phone interaction. Body mass. Speed. Calculation of the path and time of movement. Calculation of the mass and volume of a body by its density. Pressure of solids, liquids and gases. Forces. Graphic image forces. Addition of forces. Archimedean strength. Swimming tel. Work, power, efficiency, energy. The resource is useful for any practicing teacher to organize the testing or development of knowledge.
Download:
Preview:
Option 1
a B C) and the volume of water in the beakers.
Option 2
a B C)
Option 3
Chalk, lightning, dawn, water drop, Moon, shot, compass, mercury, honey, flood, milk, fountain pen, plastic, melting ice, blizzard, water.
Option 4
2. Write which of the following words denote the physical body.
Option 5
Option 1
1. Determine the division value of each of the beakers (see fig. a B C) and the volume of water in the beakers.
2. Write which of the following words denote the physical body.
Chalk, lightning, dawn, water drop, Moon, shot, compass, mercury, honey, flood, milk, fountain pen, plastic, melting ice, blizzard, water.
Option 2
1. Determine the division value of each of the thermometers (see fig. a B C) and the temperature shown by thermometers.
2. Write which of the following words denote a substance.
Water, ice melt, milk, dawn, drop of water, fountain pen, compasses, mercury, honey, flood, shot, Moon, plastic, lightning, blizzard, chalk
Option 3
1. The figure shows two voltmeters. What is the price of division of devices? What is the voltmeter reading?
2. Write which of the following words denote a phenomenon.
Chalk, lightning, dawn, water drop, Moon, shot, compass, mercury, honey, flood, milk, fountain pen, plastic, melting ice, blizzard, water.
Option 4
1. The figure shows two ammeters. What is the price of division of devices? What is the ammeter reading?
2. Write which of the following words denote the physical body.
Textbook, volume, detail, water, mass, cylinder, thermometer, piece of ice, mercury, beaker, tape measure, height, ice, water vapor, lead
Option 5
1. Determine the division value of the measuring tape (see thumbnail) and the size of the arrows.
2. Write which of the following words denote physical devices.
Lead, height, volume, water, mass, beaker, cylinder, thermometer, piece of ice, mercury, tape measure, detail, ice, water vapor, textbook
Option 1
1. Determine the division value of each of the beakers (see fig. a B C) and the volume of water in the beakers.
2. Write which of the following words denote the physical body.
Chalk, lightning, dawn, water drop, Moon, shot, compass, mercury, honey, flood, milk, fountain pen, plastic, melting ice, blizzard, water.
Option 2
1. Determine the division value of each of the thermometers (see fig. a B C) and the temperature shown by thermometers.
2. Write which of the following words denote a substance.
Water, ice melt, milk, dawn, drop of water, fountain pen, compasses, mercury, honey, flood, shot, Moon, plastic, lightning, blizzard, chalk
